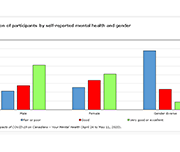
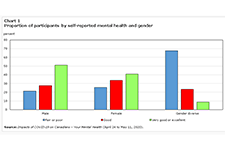
Economic well-being has both a present component and a future component. In the present, economic well-being is characterized by the ability of individuals and small groups, such as families or households, to consistently meet their basic needs, including food, clothing, housing, utilities, health care, transportation, education, and paid taxes. It is also characterized by the ability to make economic choices and feel a sense of security, satisfaction, and personal fulfillment with respect to finances and employment pursuits.
Using Statistics Canada data from a variety of sources, including the Survey of Labour and Income Dynamics, the Canadian Income Survey, the Survey of Financial Security, and the 2016 Census of Population, this chapter of Women in Canada examines women’s economic well-being in comparison with men’s and, where relevant, explores how it has evolved over the past 40 years. In addition to gender, age and family type (i.e., couple families with or without children; lone mothers and fathers; and single women and men without children) are important determinants of economic well-being. Hence, many of the analyses distinguish between women and men in different age groups and/or types of families.