Sustainable Development Goals: Goal 10, Reduced Inequalities
An infographic from Statistics Canada highlighting the advances made in reaching Goal 10, reducing inequalities, of the sustainable development goals.
8 ways to prepare financially for retirement
This article from OSC provides 8 tips to help you plan for retirement. Transitioning from working life to retirement takes careful financial planning and decision-making – give yourself plenty of time to prepare. Here are some things you can do ahead of time.
Distributional and Fiscal Analysis of a National Guaranteed Basic Income
Several parliamentarians requested that the PBO prepare a distributional analysis of Guaranteed Basic Income using parameters set out in Ontario’s basic income pilot project, examine the impact across income quintiles, family types and gender, and identify the net federal revenue increase required to offset the net cost of the new program. This analysis also accounts for the behavioural response.
Canada’s Forgotten Poor? Putting Singles Living in Deep Poverty on the Policy Radar
This report presents the findings of extensive research about employable singles on social assistance undertaken by Toronto Employment and Social Services, in partnership with the Ontario Centre for Workforce Innovation. Drawing on data from 69,000 singles who were receiving social assistance in Toronto in 2016, and 51 interviews with randomly selected participants, the report highlights these individuals’ characteristics, their complex needs, and the barriers they face in moving off social assistance and into employment. Complementing the quantitative analysis, the interviews provide important insights into the daily realities of participants’ lives and their journeys on and off assistance.
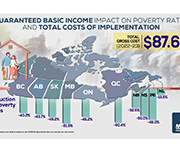
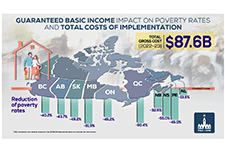
Costing a Guaranteed Basic Income During the COVID Pandemic
The Parliamentary Budget Officer (PBO) supports Parliament by providing economic and financial analysis for the purposes of raising the quality of parliamentary debate and promoting greater budget transparency and accountability. This report responds to a request from Senator Yuen Pau Woo to estimate the post-COVID cost of a guaranteed basic income (GBI) program, using parameters set out in Ontario’s basic income pilot project. In addition, the report provides an estimate of the federal and provincial programs for low-income individuals and families, including many non-refundable and refundable tax credits that could be replaced by the GBI program.
Basic Income: Some Policy Options for Canada
As the need for basic income grows, the Basic Income Canada Network (BICN) is often asked how Canada could best design and pay for it. To answer that in a detailed way, BICN asked a team to model some options that are fair, effective and feasible in Canada. The three options in this report do just that. The three options demonstrate that it is indeed possible for Canada to have a basic income that is progressively structured and progressively funded. BICN wants governments, especially the federal government, to take this seriously—and to act.