San’yas Indigenous Cultural Safety Training
Cultural safety is about fostering a climate where the unique history of Indigenous peoples is recognized and respected in order to provide appropriate care and services in an equitable and safe way, without discrimination. This website includes information about the San’yas: Indigenous Cultural Safety Training Program delivered by the Provincial Health Services Authority of British Columbia.
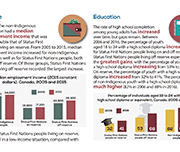
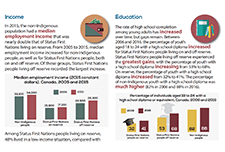
A snapshot: Status First Nations people in Canada
This is a custom report produced in collaboration between the Assembly of First Nations and Statistics Canada. It includes a variety of social and economic statistics for Status First Nations people living on and off reserve and includes comparisons with the non-Indigenous population.
Children’s Savings Account: Survey of Private and Public Funding 2019
Children’s Savings Account (CSA) programs offer a promising strategy to build a college-bound identity and make post-secondary education an achievable goal for more low- and moderate-income children. CSAs provide children (starting in elementary school or younger) with savings accounts and financial incentives for the purpose of education after high school. Beyond their financial value, CSAs are associated with beneficial effects for children and parents, including improved early child development. child health, maternal mental health, educational expectations, and academic performance. Many of these benefits are strongest for children from low-income families. This report shares a snapshot of the scale and makeup of the funding for the CSA field in 2019. It follows similar AFN reports on CSA funding in 2014-2015 and 2017 and captures the following data on CSA programs’ financial support in calendar year 2019:
Yukon Poverty Report Card 2020
This report was released as part of public education movement Campaign 2000's annual assessment of child and family poverty in Canada, providing an overview of the following key issues relating to poverty in Yukon:
The Cost of Poverty in the Atlantic Provinces
This report costs poverty based on three broad measurable components: opportunity costs, remedial costs and intergenerational costs. The authors state that these costs could potentially be reallocated, and benefits could potentially be realized if all poverty were eliminated. The total cost of poverty in the Atlantic region ranges from $2 billion per year in Nova Scotia to $273 million in Prince Edward Island. It is close to a billion in Newfoundland and Labrador, $959 million, and $1.4 billion in New Brunswick. These costs represent a significant loss of economic growth of 4.76% of Nova Scotia’s GDP to 2.9% in Newfoundland and Labrador. The impact on Prince Edward Island’s GDP is 4.10%, and 3.71% in New Brunswick.
The purpose of this costing exercise is to illustrate the shared economic burden of poverty, and the urgency that exists for Atlantic Canadian governments to act to eradicate it.
2021 Reports of the Auditor General of Canada to the Parliament of Canada – Report 4 – Canada Child Benefit
A report from Auditor General Karen Hogan concludes that the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) managed the Canada Child Benefit (CCB) program so that millions of eligible families received accurate and timely payments. The audit also reviewed the one-time additional payment of up to $300 per child issued in May 2020 to help eligible families during the COVID‑19 pandemic. The audit noted areas where the agency could improve the administration of the program by changing how it manages information it uses to assess eligibility to the CCB. For example, better use of information received from other federal organizations would help ensure that the agency is informed when a beneficiary has left the country. This would avoid cases where payments are issued on the basis of outdated information. To enhance the integrity of the program, the agency should request that all applicants provide a valid proof of birth when they apply for the benefit. The audit also raised the concept of female presumption and noted that given the diversity of families in Canada today, this presumption has had an impact on the administration of the Canada Child Benefit program.
CPA Canada 2020 Canadian Finance Study
Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada (CPA Canada) has released its comprehensive Canadian Finance Study 2020, which examines people's attitudes and feelings towards their personal finances. The results highlight the new financial realities that Canadians are experiencing during these unprecedented times. Nielsen conducted the CPA Canada 2020 Canadian Finance Study via an online questionnaire, from September 4 to 16, 2020 with 2,008 randomly selected Canadian adults, aged 18 years and over, who are members of their online panel. Among the key pandemic-related findings:
COVID-19: Exclusive resources for service provider heroes
Families Canada is the national association of Family Support Centres. With a network of 500+ member agencies and thousands of frontline family service workers across Canada, they committed to providing leadership and support in the campaign for Canada’s children. Families Canada has compiled resources for service providers to support families during COVID-19.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Women living with Disabilities in Canada
DisAbled Women’s Network (DAWNRAFH) Canada is a national, feminist, cross-disability organization whose mission is to end the poverty, isolation, discrimination and violence experienced People with disabilities, specifically women with disabilities face unique barriers related to Covid-19. This includes both the increased risk oftransmission and death from COVID-19, as well as the unique ways policies targeting COVID-19 impact this group. Prior to COVID-19 more than 50% of human rights complaints at the Federal, Provincial and Territorial levels in Canada for the last four years have been disability related, which speaks to systemic failures that have been exacerbated under COVID-19. In this brief, DAWN Canada highlights these unique considerations, as well as significant and existing policy gaps facing this group.
by Canadian women with disabilities and Deaf women.
Women and Wealth: Insights for Grantmakers
The women’s wealth gap has been largely overlooked in discussions of women’s economic security, yet wealth is the most comprehensive indicator of financial health. Without wealth, families are one paycheck away from financial disaster. The brief Women and Wealth: Insights for Grantmakers examines the causes and dimensions of the women’s wealth gap and provides recommendations and best practices for grantmakers to reduce the women’s wealth gap and improve women’s access to the wealth escalator. Improving women’s ability to build wealth is not only good for women, but is essential for the economic well-being of children, families, and our nation. The webinar, included Mariko Chang, PhD, K. Sujata, President and CEO, Chicago Foundation for Women, and Dena L. Jackson, PhD, Vice President – Grants & Research, Texas Women’s Foundation.