Guidance on digital delivery of financial education
Innovative uses of digital technologies in the delivery of financial education can serve multiple complementary objectives and effectively support the building blocks of financial education. This Guidance was developed to assist policy makers in deciding when to adopt digital delivery, and how to effectively design and implement digital financial education initiatives, by offering non-binding actionable directions. It builds on the work undertaken by the OECD and its International Network on Financial Education, including the G20/OECD-INFE Policy Guidance Note on Digitalisation and Financial Literacy and international comparative analyses on how public authorities design, deliver and evaluate digital financial education initiatives, notably in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. The report on digital delivery of financial education design and practice builds on over 70 case studies from members of the OECD International Network on Financial Education, contributes to a better understanding of how public authorities worldwide are designing, delivering and evaluating digital financial education initiatives, and prepares forthcoming work on the development of high-level international guidance on the digital delivery of financial education.
Government response to the Countervailing Power: Review of the coordination and funding for financial counselling services across Australia
In 2019, a comprehensive review (The Countervailing Power: Review of the coordination and funding for financial counselling services across Australia) of financial counselling services in Australia was undertaken and recommendations to ensure the long-term viability of the financial counselling sector, including the establishment of a nationally coordinated approach, and industry funding to strengthen the predictability and stability of funding for financial counselling were made. This document is the Australian Government's response to the review, outlining their response to each of the recommendations, and sets out their commitment to the following:
Countervailing Power: Review of the coordination and funding for financial counselling services across Australia
In 2019, the Australian Government committed to additional actions to improve the financial outcomes of Australians, including undertaking an immediate review of the coordination and funding of financial counselling services that disadvantaged Australians rely on. The review noted the benefits of financial counselling to the community, including early intervention and prevention of further financial hardship, advocacy support, and referral to other services for complex issues. The review also highlighted the challenges faced by the financial counselling sector, including increasing demand, fragmented delivery, and the array of complex situations and financial products that can lead to financial hardship. The review:
Financial Consumer Protection responses to COVID-19
This policy brief provides recommendations that can assist policy makers in their consideration of appropriate measures to help financial consumers, depending on the contexts and circumstances of individual jurisdictions, during the COVID-19 crisis. These options are consistent with the G20/OECD High Level Principles on Financial Consumer Protection that set out the foundations for a comprehensive financial consumer protection framework.
Supporting the financial resilience of citizens throughout the COVID-19 crisis
This policy brief outlines initial the measures that policy makers can make to increase citizen awareness about effective means of mitigation for the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and its potential consequences on their financial resilience and well-being.
National Strategies for Financial Education: OECD/INFE Policy Handbook
Financial education has become an important complement to market conduct and prudential regulation and improving individual financial behaviours a long-term policy priority in many countries. The OECD and its International Network on Financial Education (INFE) conducts research and develops tools to support policy makers and public authorities to design and implement national strategies for financial education. This handbook provides an overview of the status of national strategies worldwide, an analysis of relevant practices and case studies and identifies key lessons learnt. The policy handbook also includes a checklist for action, intended as a self-assessment tool for governments and public authorities.
G20/OECD INFE Core Competencies Framework on financial literacy for Adults (aged 18+)
This document describes the types of knowledge that adults aged 18 or over could benefit from, what they should be capable of doing and the behaviours that may help them to achieve financial well-being, as well as the attitudes and confidence that will support this process. It can be used to inform the development of a national strategy on financial education, improve programme design, identify gaps in provision, and create assessment, measurement and evaluation tools.
How to really build financial capability
Recent years have seen an explosion in interventions designed to improve financial outcomes of participants. Yet on-the-ground evidence suggests that not all financial education programs are equally successful at achieving this aim. This paper examines the difference between interventions that work, and those than do not. It attempts to answer the question: “How do you actually build financial capability?” In doing so, we aim to help interested parties enhance the effectiveness of their programs and policies by providing them with evidence-based recommendations to drive positive outcomes in participants.
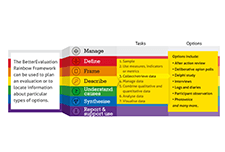
Rainbow Framework
The Rainbow Framework organizes different methods and processes that can be used in monitoring and evaluation. The range of tasks are organised into seven colour-coded clusters: Manage, Define, Frame, Describe, Understand Causes, Synthesise, and Report & Support Use. Users can use the framework to plan an evaluation that covers all necessary tasks or choose from an approach which contains a pre-packaged combination of task options.
Money stories: Financial resilience among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians
This report builds on previous work on financial resilience in Australia and represents the beginning of an exploration of the financial resilience of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Overall, we found significant economic disparity between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. This is not surprising, given the histories of land dispossession, stolen wages and the late entry of Indigenous Australians into free participation in the economy (it is only 50 years since the referendum to include Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples as members of the Australian population). Specifically, we found: Severe financial stress is present for half the Indigenous population, compared with one in ten in the broader Australian population. Read the report to find out more about the financial barriers faced by Indigenous people in Australia, and the sharing economy in which money as a commodity can both help and hurt financial resilience.