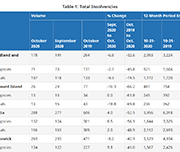
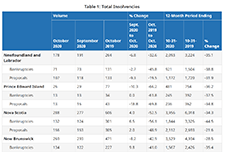
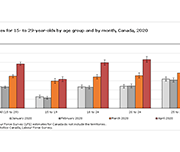
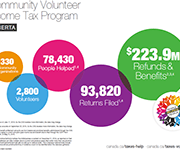
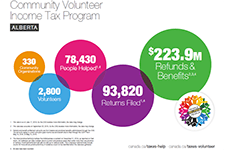
Insights into the risks and benefits of digital financial services for consumers
One of the consequences of social distancing and other restrictions, during the pandemic, such as those on business operating hours, is that consumers spent more of their time searching for information, shopping, and streaming entertainment on-line. With more free time on their hands and money in the bank, a larger percentage of the population took up an interest in investing, often through on-line brokerage platforms or in the cryptoasset markets. Because consumers have been spending more time on-line since the start of the pandemic, they have been more exposed to on-line fraud. In addition to phishing and malware, consumers are dealing with known scams but in digital form, often on social media. For some consumers, the evergrowing number of reliable and accessible information sources could lead to information overload, also known as “infobesity, where there is so much information that the consumer cannot process it all. Infobesity can lead to decision paralysis. In this paper the AMF make the most of their 360-degree view on the financial industry’s digital transformation to review the main changes that occurred in each of their areas of focus, describe the risk of digitalization for the consumers of financial products and services and present the potential opportunities that have been identified to mitigate these risks.