The multiplying movement: the state of the children’s savings field 2022
The Multiplying Movement: The State of the Children’s Savings Field 2022 shares findings from Prosperity Now’s 2022 Children’s Savings Account (CSA) program survey. The report highlights the incredible growth of the field with over 4.9 million children and youth with CSAs across the US. In addition, this report analyzes trends among CSA programs and spotlights new programs across the country. As you will see in the report, the CSA field shows no signs of slowing down.
About the Canada Learning Bond
The Canada Learning Bond (CLB) is money that the Government adds to a Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) for children from low-income families. This money helps to pay the costs of a child’s full- or part-time studies after high school at apprenticeship programs, CEGEPs, trade schools, colleges, or universities. Learn more about eligibility requirements and the application process using this website.
Children’s savings accounts: a core part of the equity agenda
Education after high school, or postsecondary education (PSE), is an important determinant of individuals’ future opportunities, as well as their health and even lifespan. Children’s Savings Accounts (CSAs) are programs that aim to increase access to PSE by building parents’ and children’s educational expectations and a “college-bound identity” starting early in children’s lives. CSAs are a vital part of the equity agenda that remain critically important even as other strategies are put in place to broaden postsecondary access. CSAs programs provide children with savings accounts and financial deposits for the purpose of education after high school or other asset building. CSA program designs, enrollment procedures, and financial incentives vary widely across the U.S. CSAs have been flourishing at the local, city, and state levels over the past two decades. CSAs’ unique value comes down to programs’ financial investment in children coupled with their capacity to bring children and families into frequent contact with information about planning for PSE, savings, and high expectations for the future.
Children’s Savings Account: Survey of Private and Public Funding 2019
Children’s Savings Account (CSA) programs offer a promising strategy to build a college-bound identity and make post-secondary education an achievable goal for more low- and moderate-income children. CSAs provide children (starting in elementary school or younger) with savings accounts and financial incentives for the purpose of education after high school. Beyond their financial value, CSAs are associated with beneficial effects for children and parents, including improved early child development. child health, maternal mental health, educational expectations, and academic performance. Many of these benefits are strongest for children from low-income families. This report shares a snapshot of the scale and makeup of the funding for the CSA field in 2019. It follows similar AFN reports on CSA funding in 2014-2015 and 2017 and captures the following data on CSA programs’ financial support in calendar year 2019:
Expanding Educational Opportunity Through Savings
This brief discusses the benefits that Children's Savings Accounts (CSAs) bring to help more families save for their children's education. Recommendations to federal policies in the United States are made for the purpose of helping families to start saving early to build greater savings and impact.
Why Community Foundations Make Perfect Partners for Children’s Savings Account Programs
In this brief, we articulate why collaboration between community foundations and CSA programs is in their mutual interest. We describe the variety of roles that community foundations can play in promoting the growth and success of CSA programs, and then identify the primary challenges encountered by community foundations in supporting CSAs. The brief concludes with key lessons learned about collaboration between community foundations and CSA programs. This brief was designed primarily to educate CSA practitioners and community foundation staff about the benefits of collaboration. It may also be of interest to a wider audience in the fields of asset building and philanthropy. The ideas and findings in this brief are based primarily on in-depth interviews and in-person meetings with board members, executives and senior staff from three community foundations.
A Growing Movement: The State of the Children’s Savings Field 2016
The Children’s Savings Account (CSA) movement has taken off in the past few years. These programs provide long-term savings or investment accounts and savings incentives to help children build savings for their future. In 2016, CSA initiatives started in a diverse range of locations, such as Durham, NC; Boston, MA; and Worcester, MA. In 2017, we expect several more program launches, including in places like Oakland, CA, and Milwaukee, WI. Based on a recent survey, this document offers a snapshot of this growing field, illustrating the range of program models being customized to meet the needs of the communities and states these programs serve.
Cities and States Developing Creative Approaches to Fund Children’s Savings Accounts
Children’s Savings Accounts (CSA) are proving to be a powerful tool for growing college funds and building children’s aspirations for their future. CSAs are long-term, incentivized savings or investment accounts for post-secondary education that help promote economic mobility for children and youth. Advocates have found that the idea and goals of CSAs can be appealing to policymakers from across the political spectrum. However, while able to generate initial interest from policymakers, advocates often find that their efforts can stall when it comes to the question of how to fund a program. This paper provides advocates and policymakers with several funding options—including examples from the city and state-levels—for establishing publicly-supported CSA programs. For more information about CSAs in general, please visit savingsforkids.org.
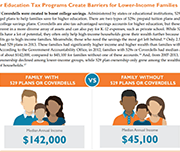
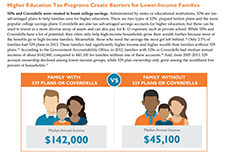
Examining the Canadian Education Savings Program and its Implications for US Child Savings Account (CSA) Policy
This report analyzes the Canadian experience with education savings programs, as the US moves towards more comprehensive Children's Savings Account policy.
“We’re Going to Do This Together”: Examining the Relationship between Parental Educational Expectations and a Community-Based Children’s Savings Account Program
This paper presents quantitative and qualitative evidence of the relationship between exposure to a community-based Children’s Savings Account (CSA) program and parents’ educational expectations for their children. First, we examine survey data collected as part of the rollout and implementation of The Promise Indiana CSA program. Second, we augment these findings with qualitative data gathered from interviews with parents whose children have Promise Indiana accounts. Though results differ by parental income and education, the quantitative results using the full sample suggest that parents are more likely to expect their elementary-school children to attend college if they have a 529 account or were exposed to the additional aspects of The Promise Indiana program (i.e., the marketing campaign, college and career classroom activities, information about engaging champions, trip to a University, and the opportunity to enroll into The Promise).