Household Food Insecurity in Canada, 2017-2018
Food insecurity – inadequate or uncertain access to food because of financial constraints – is a serious public health problem in Canada, and all indications are that the problem is getting worse. Drawing on data for 103,500 households from Statistics Canada’s Canadian Community Health Survey conducted in 2017 and 2018, we found that 12.7% of households experienced some level of food insecurity in the previous 12 months. There were 4.4 million people, including more than 1.2 million children under the age of 18, living in food-insecure households in 2017-18. This is higher than any prior national estimate.
Household food insecurity during the COVID-19 pandemic
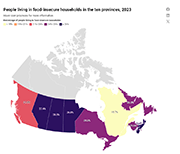
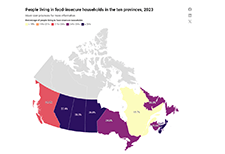
This study presents data on levels of household food insecurity in the 10 provinces from the September to December 2020 cycle of the Canadian Community Health Survey. In this survey, household food security status within the previous 12 months was measured using a scale that has been routinely used to monitor levels of household food insecurity in Canada. This provided the ability to draw comparisons with pre-pandemic levels. Both before and during the pandemic, certain population groups were more vulnerable to food insecurity in their household. They included people with lower levels of education, those who rent their dwelling, those in lone-parent-led households and those in households reliant on social assistance as their primary source of income. Compared with the pre-pandemic period of 2017/2018, levels of household food insecurity were either unchanged or slightly lower in fall 2020 among groups vulnerable to food insecurity.
Food Insecurity amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: Food Charity, Government Assistance, and Employment
To mitigate the effects of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the federal government has implemented several financial assistance programs, including unprecedented funding to food charities. Using the Canadian Perspectives Survey Series 2, the demographic, employment, and behavioural characteristics associated with food insecurity in April–May 2020 was examined. One-quarter of job-insecure individuals experienced food insecurity that was strongly associated with pandemic-related disruptions to employment income, major financial hardship, and use of food charity was found, yet the vast majority of food-insecure households did not report receiving any charitable food assistance. Increased financial support for low-income households would reduce food insecurity and mitigate negative repercussions of the pandemic.
Study: Association between food insecurity and stressful life events among Canadian adults
The COVID-19 pandemic and the related business closures and lockdowns have given rise to a series of unprecedented socioeconomic and health-related challenges, one of which is increasing food insecurity. Throughout the pandemic, Statistics Canada has continued to collect and release data on food insecurity in Canada—including exploring the link between food insecurity and mental health, financial stability and Indigenous people living in urban areas. This study looks at the characteristics of food insecure Canadians, focusing on how losing a job, suffering an injury or illness, or a combination of events can increase the risk of food insecurity. This release compares the food security outcomes of two different subpopulations: those who had experienced a stressful life event and those who had not.
Pandemic to Prosperity – January 21, 2021: One year after the first announcement of Covid on U.S. soil
The National Conference on Citizenship (NCoC) developed the Pandemic to Prosperity series. It builds on NCoC’s data infrastructure and advocacy network developed for its national Civic Health Index, with The New Orleans Index, which informed many public and private decisions and actions post-Katrina. This series is designed to enable a solid understanding of the damage to lives and livelihoods as the pandemic continues to unfold, as the United States enters the era of vaccines, and the nation grapples with new shocks and stressors such as disasters and civil unrest; it will also examine aspirational goals around strong and accountable government, functioning institutions from child care to internet access to local news availability, effective civic participation, and outcomes for people by race regarding employment, health, housing, and more. With each new report in the series, indicators will change as the recovery transitions. This report highlights mostly state-level metrics with breakdowns by race, gender, and age where available, relying on both public and private data sources.
Food insecurity and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic
Canadians living in households that experienced food insecurity (insecure or inadequate access to food because of financial constraints) during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic were significantly more likely to perceive their mental health as fair or poor and to report moderate or severe anxiety symptoms than Canadians in food-secure households. Approximately one in seven Canadians (14.6%) were estimated to live in a food-insecure household in May 2020. This study, released in Health Reports, is the first to examine the association between household food insecurity and self-perceived mental health and anxiety among Canadians during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study also estimated that 9.3% of Canadians living in food-insecure households reported having recently accessed free food or meals from a community organization.
Beyond Hunger: the hidden impacts of food insecurity
This report illustrates the hidden impacts of food insecurity in people’s lives through a survey of 561 people in 22 communities across Canada. The people interviewed shared that food insecurity makes them ill, breaks down relationships, makes it harder to get stable work, and fully participate in society.
Cities Reducing Poverty: 2020 Impact Report
The Vibrant Communities – Cities Reducing Poverty 2020 Impact Report is the Tamarack Institute's first attempt at capturing and communicating national trends in poverty reduction and the important ways in which member Cities Reducing Poverty collaboratives are contributing to those changes. This impact report is meant for poverty reduction organizers and advocates, and public decision-makers to get a sense for how collaborative, multi-sectoral local roundtables with comprehensive plans contribute to poverty reduction in their communities and beyond; and spotlights high-impact initiatives that are demonstrating promising results.
How are Canadians with long-term conditions and disabilities impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?
This infographic focuses on self-reported health, unmet needs for services and therapies, and difficulties meeting certain financial obligations and essential needs since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic among participants aged 15 and older living with long-term conditions and disabilities. Results are based on the recent Statistics Canada crowdsourcing data collection completed by over 13,000 Canadians with long-term conditions or disabilities between June 23 and July 6, 2020.
Wealth and Health Equity: Investing in Structural Change
Building on the Asset Funders Network’s the Health and Wealth Connection: Investment Opportunities Across the Life Course brief, this paper details: On September 29th, AFN hosted a webinar to release the paper with featured speakers: Dr. Annie Harper, Ph.D., Program for Recovery and Community Health, Yale School of Medicine
Joelle-Jude Fontaine, Sr. Program Officer, Human Services, The Kresge Foundation
Dedrick Asante-Muhammad, Chief of Race, Wealth, and Community, National Community Reinvestment Coalition
Canada’s Forgotten Poor? Putting Singles Living in Deep Poverty on the Policy Radar
This report presents the findings of extensive research about employable singles on social assistance undertaken by Toronto Employment and Social Services, in partnership with the Ontario Centre for Workforce Innovation. Drawing on data from 69,000 singles who were receiving social assistance in Toronto in 2016, and 51 interviews with randomly selected participants, the report highlights these individuals’ characteristics, their complex needs, and the barriers they face in moving off social assistance and into employment. Complementing the quantitative analysis, the interviews provide important insights into the daily realities of participants’ lives and their journeys on and off assistance.
Hunger Lives Here: Risks and Challenges Faced by Food Bank Clients During COVID-19
This report provides quantitative and qualitative data about the experience of hunger and poverty in Toronto during COVID-19. Based on phone surveys with over 220 food bank clients in May and June 2020 and an analysis of food bank client intake data, the report demonstrates that COVID-19 has led to increased reliance on food banks. The rate of new clients accessing food banks has tripled since the pandemic began. Among new clients, 76% report that they began accessing food banks as a result of COVID-19 and the associated economic downturn.
Income Volatility: Why it Destabilizes Working Families and How Philanthropy Can Make a Difference
As the work environment has evolved and jobs look more different, it is important to understand the impact of these changes on income—predictability, variability, and frequency—and how this affects the opportunity for mobility. Because of the complexity of income volatility, there is a unique role for philanthropy. This brief helps grantmakers understand the enormous challenges income volatility presents in America and provides an array of strategies for philanthropy to leverage both investments and leadership to empower families to protect themselves from volatility’s worst effects.
Advancing Health and Wealth Integration in the Earliest Years
Despite the well-documented connection between health and wealth, investing in this intersection is still a new approach for many grantmakers. With the goal of inspiring increased philanthropic attention, exploration, and replication, this new spotlight elevates responsive philanthropic strategies that support both health and wealth. This report focuses on the in utero-toddler stage of the life cycle (0-3 years). This age segment has some health-wealth integration activity, primarily through two-generation approaches. The goal is to inspire more philanthropic investment for this cohort by highlighting research and examples and offering recommendations.
The Who’s Hungry Report
The Who’s Hungry Report provides quantitative and qualitative data about the experience of hunger and poverty in Toronto. To create the reports, trained volunteers conduct face-to-face interviews with over 1,400 food bank clients at nearly 40 member agencies, collecting demographic data as well as information about the day-to-day experience of living with hunger.