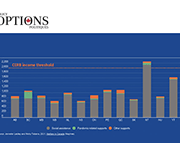
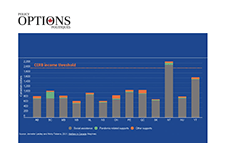
Welfare in Canada, 2021
Using data provided by provincial and territorial government sources, Welfare in Canada, 2021 describes the components of welfare incomes, how they have changed from previous years, and how they compared to low-income thresholds. Access the report here. During the launch event, the report’s authors, Jennefer Laidley and Mohy Tabbara, broke down the latest welfare income data from all 13 provinces and territories and presented the key takeaways. Recorded on November 24, the Welfare in Canada, 2021 launch event started with a brief presentation of the report’s key findings, followed by a panel discussion. Presenters: Moderator:
Social assistance summaries
The Social Assistance Summaries series tracks the number of recipients of social assistance (welfare payments) in each province and territory. It was established by the Caledon Institute of Social Policy to maintain data previously published by the federal government as the Social Assistance Statistical Report. The data is provided by provincial and territorial government officials.
Singles in deep poverty neglected by pandemic supports
In 2020, the federal government spent over $160 billion on COVID-19 pandemic response measures. These expenses were critical in supporting recently unemployed workers and affected businesses in a time of uncertainty. However, supports through programs like the Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB) and the Canada Recovery Benefit (CRB) were not extended to those who had less attachment to the labour market, such as a large proportion of social assistance recipients. This pattern of exclusion has continued with the more recent Canada Worker Lockdown Benefit, which was created to support workers affected by new pandemic-related shutdowns, and not people who were already living in deep poverty before the pandemic. The pandemic benefits are intended to support people during a specific time of crisis — but what about those who have been living with low and insecure incomes for decades? This report analyzes the welfare incomes of 53 example households, divided into four types, focusing here on unattached singles considered employable, as they are the most likely to be living in poverty.
Canada’s Forgotten Poor? Putting Singles Living in Deep Poverty on the Policy Radar
This report presents the findings of extensive research about employable singles on social assistance undertaken by Toronto Employment and Social Services, in partnership with the Ontario Centre for Workforce Innovation. Drawing on data from 69,000 singles who were receiving social assistance in Toronto in 2016, and 51 interviews with randomly selected participants, the report highlights these individuals’ characteristics, their complex needs, and the barriers they face in moving off social assistance and into employment. Complementing the quantitative analysis, the interviews provide important insights into the daily realities of participants’ lives and their journeys on and off assistance.
Social Assistance Summaries
The Social Assistance Summaries series tracks the number of recipients of social assistance (welfare payments) in each province and territory. It was established by the Caledon Institute of Social Policy to maintain data previously published by the federal government as the Social Assistance Statistical Report. The data is provided by provincial and territorial government officials.
Welfare in Canada, 2018
These reports look at the total incomes available to those relying on social assistance (often called “welfare”), taking into account tax credits and other benefits along with social assistance itself. The reports look at four different household types for each province and territory. Established by the Caledon Institute of Social Policy, Welfare in Canada is a continuation of the Welfare Incomes series originally published by the National Council of Welfare, based on the same approach.