Beware: Crypto scams on the rise
Fraudsters often use emotions to lure people in, making a person feel afraid of missing out on an opportunity that others are profiting from. With all the cryptocurrency hype in the media and online, it’s no surprise that scammers are taking note and trying to cash in on investors’ interest in digital currencies. Read this article for more information on the top crypto-related scams you should know.
Eyeing the ID: Bio-metric Banking for Saint John
NB Social Pediatrics and the Saint John Community Loan Fund recently surveyed 157 New Brunswick and Nova Scotia residents about their experiences with finances, banking, and ID to better understand if biometrics or ID banks could be effective solutions for people living without ID. Eyeing the ID: Bio-metric Banking for Saint John identifies access to identification, as well as stringent identification requirements as the most prevalent barriers to receiving services in the community and were also inherently linked to other barriers, such as housing and finances. For example, lack of address was identified as a barrier to accessing an ID because government agencies require a mailing address to send ID documents to customers, but lack of ID is also directly linked to precarious housing because you often need ID to be placed on local subsidized housing lists, and to set up power and utilities. Cyclical barriers to services could be improved by addressing ID requirements and making ID more accessible. The top three solutions identified to mitigate ID barriers were biometrics, ID banks, and an ID acquisition service. Also available in French: Un regard sur l’identification : Services bancaires à identification biométrique à Saint John
Welfare in Canada, 2020
Maytree released the 2020 edition of the Welfare in Canada report. For each province and territory, this report provides data and analysis on the total welfare income that households receiving social assistance would have qualified for in 2020, including COVID-19 pandemic-related supports. Welfare in Canada is a series that presents the total incomes of four example households who qualify for social assistance benefits in each of Canada’s provinces and territories in a given year. Welfare in Canada, 2020 looks at the maximum total amount that a household would have received over the course of the 2020 calendar year, assuming they had no other source of income and no assets. Some households may have received less if they had income from other sources, while some households may have received more if they had special health- or disability-related needs. The report looks at: In addition, this year the report includes a new section that looks at the adequacy of welfare incomes in each province over time, an analysis that hearkens back to past reports prepared by the National Council of Welfare. Also, please note that this report measures the adequacy of welfare incomes relative to both the Market Basket Measure (MBM) – Canada’s Official Poverty Line – and the Deep Income Poverty threshold (MBM-DIP), which is equivalent to 75 per cent of the MBM. This analysis will replace the low-income threshold comparisons in future reports. We hope these additions will be helpful for those using the report. In each jurisdiction, the total welfare income for which a household is eligible depends on its specific composition. For illustrative purposes, this resource focuses on the welfare incomes of four example household types:
The Cost of Poverty in the Atlantic Provinces
This report costs poverty based on three broad measurable components: opportunity costs, remedial costs and intergenerational costs. The authors state that these costs could potentially be reallocated, and benefits could potentially be realized if all poverty were eliminated. The total cost of poverty in the Atlantic region ranges from $2 billion per year in Nova Scotia to $273 million in Prince Edward Island. It is close to a billion in Newfoundland and Labrador, $959 million, and $1.4 billion in New Brunswick. These costs represent a significant loss of economic growth of 4.76% of Nova Scotia’s GDP to 2.9% in Newfoundland and Labrador. The impact on Prince Edward Island’s GDP is 4.10%, and 3.71% in New Brunswick.
The purpose of this costing exercise is to illustrate the shared economic burden of poverty, and the urgency that exists for Atlantic Canadian governments to act to eradicate it.
Overcoming Poverty Together 3: The New Brunswick Economic and Social Inclusion Plan 2020-2025
The new Economic and Social Inclusion plan for New Brunswick builds upon progress accomplished over the past 10 years. It includes nine priority actions divided into three pillars: The objective of the plan is to reduce income poverty by at least 50 per cent by 2030, in line with the objectives of Opportunity for All, Canada’s first poverty reduction strategy, and those of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainability of the United Nations.
State of the Child Report 2020: Protecting Child Rights in Times of Pandemic
The 2020 State of the Child Report includes six recommendations and gives a snapshot of some of the challenges New Brunswick children and youth will have to overcome as the province moves forward and juggles the new realities of public health measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 while respecting child rights.
State of the Child Report 2019
This report's release was part of Child Rights Education Week and also in celebration of the 30th anniversary of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC). 2019 was declared the International Year of Indigenous Languages by the United Nations. The report contains an overview of some of the serious challenges facing New Brunswick children and youth, including more than 200 statistics presented in the report’s Child Rights Indicators Framework. A special emphasis was placed on education rights. Some of the concerning findings revealed in the report include:
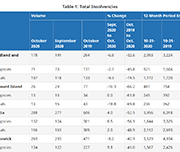
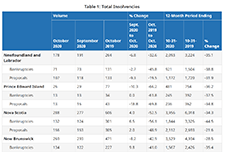
Office of the Superintendent of Bankruptcy Canada: Statistics and Research
The Office of the Superintendent of Bankruptcy Canada releases statistics on insolvency (bankruptcies and proposals) numbers in Canada. The latest statistics released on November 4, 2020 show that the number of insolvencies in Canada increased in the third quarter of 2020 by 7.9% compared to the second quarter.
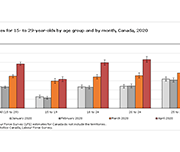
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the NEET (not in employment, education or training) indicator, March and April 2020
A fact sheet released by Statistics Canada shows that, in March and April 2020, the proportion of young Canadians who were not in employment, education or training (NEET) increased to unprecedented levels. The COVID-19 pandemic—and the public health interventions that were put in place to limit its spread—have affected young people in a number of ways, including high unemployment rates, school closures and education moving online.
Social Assistance Summaries
The Social Assistance Summaries series tracks the number of recipients of social assistance (welfare payments) in each province and territory. It was established by the Caledon Institute of Social Policy to maintain data previously published by the federal government as the Social Assistance Statistical Report. The data is provided by provincial and territorial government officials.
Resources
Handouts, slides, and time-stamps
Presentation slides for this webinar
Handouts for this webinar
Introducing the Financial Relief Navigator (FRN)
Access the Financial Relief Navigator here.
Time-stamps for the video recording:
3:22 – Agenda and Introductions
6:00 – Audience poll
9:00 – Why we created the Financial Relief Navigator (Speaker: Janet Flynn)
11:55 – What’s in the Financial Relief Navigator (Speaker: Janet Flynn)
16:35 – FRN Walkthrough using a Persona (Speaker: Galen McLusky)
33:15 – Tips for using the FRN (Speaker: Galen McLusky)
36:00 – The Working Centre experience using the FRN (Speaker: Sue Collison)
41:15 – Q&A
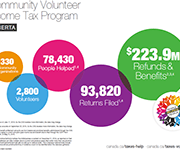
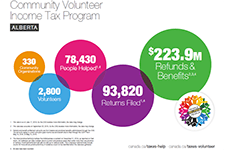
Community Volunteer Income Tax Program (CVITP) provincial snapshots
This infographics from the Community Volunteer Income Tax Program (CVITP) show information about the program by province for the tax filing year 2019, including number of returns filed and amount of refunds and benefits accessed. The information is presented in English and French. Les informations sont présentées en anglais et en français.
Welfare in Canada, 2018
These reports look at the total incomes available to those relying on social assistance (often called “welfare”), taking into account tax credits and other benefits along with social assistance itself. The reports look at four different household types for each province and territory. Established by the Caledon Institute of Social Policy, Welfare in Canada is a continuation of the Welfare Incomes series originally published by the National Council of Welfare, based on the same approach.
Urban Spotlight: Neighbourhood Financial Health Index findings for Canada’s cities
This report examines the financial health and vulnerability of households in Canada’s 35 largest cities, using a new composite index of household financial health at the neighbourhood level, the Neighbourhood Financial Health Index or NFHI. The NFHI is designed to shine a light on the dynamics underlying national trends, taking a closer look at what is happening at the provincial/territorial, community and neighbourhood levels. Update July 22, 2022: Please note that the Neighbourhood Financial Health Index is no longer available
Get Your Piece of the Money Pie
In this presentation, Althea Arsenault, Manager of Resource Development, NB Economic and Social Inclusion Corporation, shares insights from the 'Get Your Piece of the Money Pie' tax clinic program. This program has operated since 2010, and currently files over 23,000 returns each year. This presentation is from the panel discussion 'National and regional strategies to boost tax filing', at the tax research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.