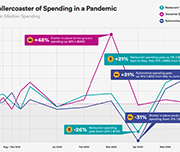
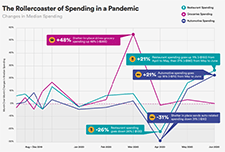
More Canadians are finding it difficult to meet food, shelter and other necessary expenses
In 2022, the Consumer Price Index rose 6.8%, the highest increase since 1982 (+10.9%). Prices for day-to-day goods and services such as transportation (+10.6%), food (+8.9%) and shelter (+6.9%) rose the most. Canadians felt the impact of rising prices. Data from the Canadian Social Survey (CSS) show that the share of persons aged 15 and older living in a household experiencing difficulty meeting its necessary expenses trended upward from just under one-fifth (19%) in the summer of 2021 to just under one-quarter (24%) in the summer of 2022. By the end of 2022, more than one-third (35%) of the population lived in such a household.
Service Matters: Numbers Speak Volumes
The Annual Report by the Office of the taxpayer's ombudsman provides key achievements, identifies Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) service issues and outlines trends in complaints. In addition, the report includes three recommendations to the Minister of National Revenue and the Chair of the Board of Management to improve the CRA’s service to Canadians.
Emergency savings features that work for employees earning low to moderate incomes
Workers earning low to moderate incomes (LMI) continue to face challenges in financial security. The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the financial situation of many workers earning LMI. Along with the current macroeconomic environment, it has become even more challenging to build liquid savings for unexpected expenses. In this brief, we will share insights from our latest research with DCIIA Research Retirement Center on how employers and service providers can build and offer emergency savings solutions that are inclusively designed for workers earning LMI.
Economic impact of COVID-19 among Indigenous people
This article uses data from a recent crowdsourcing data initiative to report on the employment and financial impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on Indigenous participants. It also examines the extent to which Indigenous participants applied for and received federal income support to alleviate these impacts. As Canada gradually enters a recovery phase, the article concludes by reporting on levels of trust among Indigenous participants on decisions to reopen workplaces and public spaces.
The Wealth of Unattached Men and Women Aged 50 and Older, 1999 to 2016
The evolution of the wealth, assets and debts of various groups of Canadians since the late 1990s has been documented in several studies. Yet little is known about the evolution of the wealth holdings of unattached men and women aged 50 and older, who make up a large part of the population. This study assesses how the wealth holdings of unattached men and women aged 50 and older evolved from 1999 to 2016 using data from the Survey of Financial Security of 1999, 2005, 2012 and 2016, and fills this information gap.
Responding to Client’s “Now, Soon, & Later” Needs
This is a three-part webinar series exploring how practitioners, policymakers, and product developers are supporting the diverse savings needs of LMI households during the ongoing crisis. Solutions that help families save flexibly for short, intermediate, and/or long-term goals that address their current and future needs are discussed.
Intersectionality and Economic Justice
Widespread financial precarity for women of color with disabilities existed before the pandemic. Rooted in existing systemic inequities, COVID worsened the situation and created new access barriers. Race, gender, and disability impact financial stability in complex ways. Having a disability may increase living costs and limit economic opportunities. At the same time, women of color face significant disparities in education, income, employment, financial services, and wealth. Faced with institutional barriers that limit earning and wealth building, disabled women of color are more likely to be unbanked, use alternative financial services, have medical debt, lack access to affordable health care, and experience food insecurity. Given these challenges and the dire need to address them, this webinar explored:
Impact of the COVID-19 Crisis on Montreal “Cultural Communities”
This exploratory study aims to better understand the challenges experienced by members of cultural communities in Montreal, particularly the most disadvantaged groups, during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Spring of 2020.
2019 Financial Literacy Annual Report
The 2019 Financial Literacy Annual Report of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau highlights the Bureau’s Start Small, Save Up campaign, the Office of Financial Education’s foundational research, in conjunction with the Office of Older Americans, to understand the pathways to financial well-being, the Office of Servicemembers Affairs’ Misadventures in Money Management online training program, the Office of Older Americans’ Managing Someone Else’s Money guides, and the Office of Community Affairs’ Your Money, Your Goals toolkit, along with other direct to consumer tools, community outreach channels, and areas of research.
Strengthening the Economic Foundation for Youth and Young Adults During COVID & Beyond
The unemployment rate for young workers ages 16–24 jumped from 8.4% to 24.4% from spring 2019 to spring 2020 in the United States, representing four million youth. While unemployment for their counterparts ages 25 and older rose from 2.8% to 11.3% the Spring 2020 unemployment rates were even higher for young Black, Hispanic, and Asian American/Pacific Islander (AAPI) workers (29.6%, 27.5%, and 29.7%, respectively. The following speakers discuss how to build financial security for youth (16-24) in this webinar: Monique Miles, Aspen Institute, Forum for Community Solutions, Margaret Libby, My Path, Amadeos Oyagata, Youth Leader, and Don Baylor, The Annie E. Casey Foundation (moderator).
Roadblock to Recovery: Consumer debt of low- and moderate-income Canadians in the time of COVID-19
Almost half of low-income households and 62 per cent of moderate-income households carry debt, with households on low incomes spending 31 per cent of their income on debt repayments, according to a new report published by national charity, Prosper Canada.
This report analyzes the distribution, amount and composition of non-mortgage debt held by low- and moderate-income Canadian households and explores implications for federal and provincial/territorial policy makers as they develop and implement COVID-19 economic recovery plans and fulfill their respective regulatory roles.
How are Canadians with long-term conditions and disabilities impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?
This infographic focuses on self-reported health, unmet needs for services and therapies, and difficulties meeting certain financial obligations and essential needs since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic among participants aged 15 and older living with long-term conditions and disabilities. Results are based on the recent Statistics Canada crowdsourcing data collection completed by over 13,000 Canadians with long-term conditions or disabilities between June 23 and July 6, 2020.
Making Safety Affordable: Intimate Partner Violence is an Asset-Building Issue
This brief explores three existing unmet needs that contribute to survivors’ inability to build wealth: money, tailored asset-building support, and safe and responsive banking and credit services. Within each identified need, specific issues facing survivors, strategic actions in response to those issues, as well as innovative ideas and existing promising practices to help funders take action to prioritize survivor wealth are discussed.
The Canadian Housing Survey, 2018: Core housing need of renter households living in social and affordable housing
This article provides a high level overview of those living in social and affordable housing by painting a portrait of them based on the results of the 2018 CHS. Socio-demographic and household characteristics are examined using housing indicators such as core housing need.
Wealth and Health Equity: Investing in Structural Change
Building on the Asset Funders Network’s the Health and Wealth Connection: Investment Opportunities Across the Life Course brief, this paper details: On September 29th, AFN hosted a webinar to release the paper with featured speakers: Dr. Annie Harper, Ph.D., Program for Recovery and Community Health, Yale School of Medicine
Joelle-Jude Fontaine, Sr. Program Officer, Human Services, The Kresge Foundation
Dedrick Asante-Muhammad, Chief of Race, Wealth, and Community, National Community Reinvestment Coalition
Lifting the Weight: Consumer Debt Solutions Framework
Aspen Financial Security Program’s the Expanding Prosperity Impact Collaborative (EPIC) has identified seven specific consumer debt problems that result in decreased financial insecurity and well-being. Four of the identified problems are general to consumer debt: households’ lack of savings or financial cushion, restricted access to existing high-quality credit for specific groups of consumers, exposure to harmful loan terms and features, and detrimental delinquency, default, and collections practices. The other three problems relate to structural features of three specific types of debt: student loans, medical debt, and government fines and fees. This report presents a solutions framework to address all seven of these problems. The framework includes setting one or more tangible goals to achieve for each problem, and, for each goal, the solutions different sectors (financial services providers, governments, non-profits, employers, educational or medical institutions) can pursue.
The Economic Toll of COVID-19 on SaverLife Members
SaverLife is an organization that seeks to advance savings programs, analytic insights, and policy initiatives through a network of employers, financial institutions, nonprofits and advocacy groups in the United States. This report provides insight into the financial challenges presented by their savings program members during the COVID-19 pandemic from March to August of 2020.
From the Margins to Center: Responding to COVID-19 with an Equity and Gender Lens
On June 30th, AFN presented an Expert Insights briefing on what it takes to center women of color in the relief, recovery, and rebuild plans for the current health and economic crisis and beyond. The speaker is Dominique Derbigny, deputy director of Closing the Women’s Wealth Gap (CWWG) and author of the report, On the Margins: Economic Security for Women of Color through the Coronavirus Crisis and Beyond. Learn why women of color are suffering severely from the COVID-19 public health and economic crisis, opportunities to advance gender economic equity in near-term recovery efforts, and possible strategies to prevent wealth extraction and foster long-term economic security for women of color.
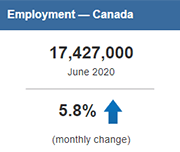
Labour Force Survey, June 2020
Labour Force Survey (LFS) results for June reflect labour market conditions as of the week of June 14 to June 20. A series of survey enhancements continued in June, including additional questions on working from home, difficulty meeting financial needs, and receipt of federal COVID-19 assistance payments. New questions were added to measure the extent to which COVID-19-related health risks are being mitigated through workplace adaptations and protective measures.
Economic impact of COVID-19 among visible minority groups
Since visible minorities often have more precarious employment and higher poverty rates than the White population, their ability to adjust to income losses due to work interruptions is likely more limited. Based on a large crowdsourcing data collection initiative, this study examines the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on visible minority groups. Among the crowdsourcing participants who were employed prior to work stoppages, Whites and most visible minority groups reported similar rates of job loss or reduced work hours. However, visible minority participants were more likely than White participants to report that the COVID-19 pandemic had affected their ability to meet financial obligations or essential needs, such as rent or mortgage payments, utilities, and groceries.
Economic and Fiscal Snapshot 2020
The COVID-19 crisis is a public health crisis and an economic crisis. The Economic and Fiscal Snapshot 2020 lays out the steps Canada is taking to stabilize the economy and protect the health and economic well-being of Canadians and businesses across the country.
Advancing Health and Wealth Integration in the Earliest Years
Despite the well-documented connection between health and wealth, investing in this intersection is still a new approach for many grantmakers. With the goal of inspiring increased philanthropic attention, exploration, and replication, this new spotlight elevates responsive philanthropic strategies that support both health and wealth. This report focuses on the in utero-toddler stage of the life cycle (0-3 years). This age segment has some health-wealth integration activity, primarily through two-generation approaches. The goal is to inspire more philanthropic investment for this cohort by highlighting research and examples and offering recommendations.
Defining disability for social assistance in Ontario: Options for moving forward
Narrowing the definition of disability used by the Ontario Disability Support Program (ODSP) could have serious implications. Improving the program’s assessment process would yield better results for applicants, Ontario's social safety net, and the government. This report explores the role of ODSP, the risks of narrowing the definition of disability, models of disability assessment from other jurisdictions, and alternative ways that the government could reform the program. Most importantly, the paper recommends that the Ministry focus on improving ODSP’s initial application process. A simplified assessment system would save time and money for applicants, medical professionals, legal clinics, adjudicators, and the Social Benefits Tribunal. These savings should be reinvested back into social assistance.
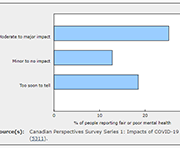
Canadian Perspectives Survey Series 1: Impacts of COVID-19 on job security and personal finances, 2020
Findings from a web panel survey developed by Statistics Canada on how Canadians are coping with COVID-19. More than 4,600 people in the 10 provinces responded to this survey from March 29 to April 3. In addition to content on the concerns of Canadians and the precautions they took to reduce the risk of exposure to COVID-19, the survey includes questions on work location, perceptions of job security, and the impact of COVID-19 on financial security.
A workplace-based economic response to COVID-19
This brief emerged from a conversation, held in late March 2020, among a number of individuals and organizations who work on issues of household financial security. Employers with financial resources and governments have an opportunity to use the workplace as a significant channel to deliver financial relief as part of the economic response to COVID-19, complementing critical supports governments are providing to individuals and businesses.
Economic volatility in childhood and subsequent adolescent mental health problems: a longitudinal population based study of adolescents
This research paper investigates the association between the patterns of duration, timing and sequencing of exposure to low family income during childhood, and symptoms of mental health problems in adolescence.
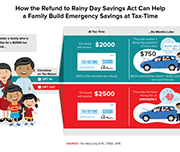
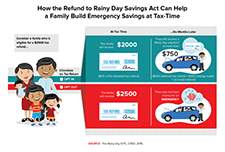
Helping Families Save to Withstand Emergencies
This brief identifies policy solutions to help American families build savings to withstand emergencies that threaten their financial stability.
Removing Savings Penalties for Temporary Assistance for Needy Families
This brief discusses the savings penalties in public assistance programs in the United States, also known as asset limits, and that actions that can be taken to eliminate these limits and the barriers towards building savings for families living on low income.
Running in Place: Why the Racial Wealth Divide Keeps Black and Latino Families From Achieving Economic Security
This report examines data from the Federal Reserve System’s 2016 Survey of Consumer Finances to understand how the wealth of median Black, Latino and White families have changed since the findings of its previous survey were released in 2013.
The Perils of Living Paycheque to Paycheque
This report, 'The Perils of Living Paycheque to Paycheque: The relationship between income volatility and financial insecurity', examines the relationship between income instability and broader measures of financial well-being. This study makes use of a unique dataset that collected self-reported month-to-month volatility in household income, measures of capability, financial knowledge and psychological variables. One in three adult Canadians reported at least some volatility in their monthly incomes, with six per cent reporting that the source and amount were both uncertain. Income volatility is present across a wide swath of the survey respondents, regardless of gender, family status, region of the country, education level and even income sources. Income volatility is correlated with lower financial knowledge, lower financial capability, and stronger beliefs that financial outcomes are up to fate and outside of personal control.
Gig Workers in America: Profiles, Mindset and Financial Wellness
The Gig Worker On-Demand Economy survey was conducted online by Harris Poll on behalf of Prudential from January 5 to February 18, 2017, among a nationally representative (U.S.) sample of 1,491 workers including 514 full-time and 256 part-time traditional employees and 721 gig workers. Gig work was defined as providing a service or labor, and did not include renting out assets. Survey respondents were selected from among adults aged 18+ who had agreed to participate in online surveys from the Harris Poll Online panel and preferred sample partners.
Financial Empowerment: Improving financial outcomes for low-income households
Financial Empowerment is a new approach to poverty reduction that focuses on improving the financial security of low-income people. It is an evidence-driven set of interventions that have proven successful at both eliminating systemic barriers to the full financial inclusion of low-income people and providing enabling supports that help them to acquire and practice the financial skills and behaviours that tangibly improve their financial outcomes and build their financial security. The Financial Empowerment approach focuses on community level strategies that encompass five main types of interventions that have been identified as both necessary for low-income households to improve their financial outcomes, and effective at helping them to do so.