Benefits & credits: factsheets from the CRA
The CRA has compiled benefits and credits factsheets for: These are available in English and French.
Dimensions of poverty hub
Statistics Canada has created an "Opportunity for All"; a dashboard of 12 indicators to track progress on deep income poverty as well as the aspects of poverty other than income, including indicators of material deprivation, lack of opportunity and resilience. These indicators are broadly grouped into three categories: dignity, opportunity and inclusion and resilience and security.
Urban, Rural, and Northern Indigenous Housing
This report examines Indigenous housing in urban, rural, and northern areas, an expression which is taken to refer to Indigenous housing in all areas of Canada other than on reserves. This report is intended to provide an analysis of unmet Indigenous housing need and homelessness in these areas, and of government spending to address those issues. The report ends with a range
of estimated costs for addressing housing need to various extents under various programs.
This report was prepared at the request of the House of Commons Standing Committee on Human Resources, Skills and Social Development and the Status of Persons with Disabilities (HUMA).
Housing insecurity and the COVID-19 pandemic
CFPB released their first analysis of the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on housing in the United States. Actions taken by both the public and private sector have, so far, prevented many families from losing their homes during the height of the public health crisis. However, as legal protections expire in the months ahead, over 11 million families — nearly 10 percent of U.S. households — are at risk of eviction and foreclosure.
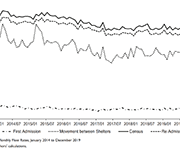
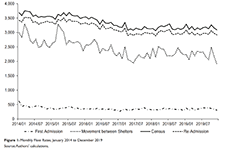
Homeless Shelter Flows in Calgary and the Potential Impact of COVID-19
Social distancing and self-isolation are two of the key responses asked of citizens during a pandemic. For people without a home, this advice is rather more difficult to follow. This article uses daily data describing the movements of 36,855 unique individuals who used emergency homeless shelters in Calgary over the period 1 January 2014–31 December 2019. The use of emergency shelters is characterized by large flows from and into the broader community and smaller flows between individual shelters. Between admissions of new people into the shelter system and multiple re-admissions of current clients, there were an average of 43,613 movements between the community and between shelters each month. The size of these flows provide a measure of the extent to which people reliant on homeless shelters are exposed to the risk of transmission of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
One in five Canadians with mental health-related disabilities lives in core housing need
Canadians with mental health-related disabilities were more than twice as likely as those without disabilities to live in households considered to be in core housing need in 2017. Canadians with mental health-related disabilities were also more likely than those without disabilities to live alone, to rent their homes and to live in subsidized housing, according to the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability (CSD). The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) has identified those living with pre-existing mental health-related disabilities as a particularly vulnerable population because of the impacts of isolation and disruptions to mental health-related services during the COVID-19 pandemic. A recent crowdsourcing survey by Statistics Canada found that almost three-quarters (73%) of participants with mental health-related disabilities stated that their mental health had worsened since the beginning of the pandemic. In addition, PHAC has indicated that those living with inadequate or unsuitable housing are also more vulnerable during the pandemic and are at higher risk of contracting COVID-19. This infographic presents pre-existing living situations and housing conditions among Canadians with mental health-related disabilities that may put them at greater risk of contracting COVID-19, as well as the emotional and psychosocial impacts of living through a pandemic.
The Canadian Housing Survey, 2018: Core housing need of renter households living in social and affordable housing
This article provides a high level overview of those living in social and affordable housing by painting a portrait of them based on the results of the 2018 CHS. Socio-demographic and household characteristics are examined using housing indicators such as core housing need.
Youth Reconnect Program Guide: An Early Intervention Approach to Preventing Youth Homelessness
Since 2017, the Canadian Observatory on Homelessness and A Way Home Canada have been implementing and evaluating three program models that are situated across the continuum of prevention, in 10 communities and 12 sites in Ontario and Alberta. Among these is an early intervention called Youth Reconnect. This document describes the key elements of the YR program model, including program elements and objectives, case examples of YR in practice, and necessary conditions for implementation. It is intended for communities who are interested in pursuing similar early intervention strategies. The key to success, regardless of the approaches taken, lies in building and nurturing community partnerships with service providers, educators, policy professionals, and young people.
Shelters for victims of abuse with ties to Indigenous communities or organizations in Canada, 2017/2018
There were 85 shelters for victims of abuse that had ties to First Nations, Métis or Inuit communities or organizations operating across Canada in 2017/2018. These Indigenous shelters, which are primarily mandated to serve victims of abuse, play an important role for victims leaving abusive situations by providing a safe environment and basic living needs, as well as different kinds of support and outreach services. Over a one-year period, there were more than 10,500 admissions to Indigenous shelters; the vast majority of these admissions were women (63.7%) and their accompanying children (36.1%). This article uses data from the Survey of Residential Facilities for Victims of Abuse (SRFVA). Valuable insight into shelter use in Canada and the challenges that shelters and victims of abuse were facing in 2017/2018 is presented.
A Pandemic Response and Recovery Toolkit for Homeless System Leaders in Canada
The Pandemic Response and Recovery Toolkit is intended to assist System Leaders plan and navigate the next steps in their community’s response and recovery as it pertains to people experiencing homelessness and people supported in housing programs. The Toolkit outlines phases and action steps – many that have yet to be mobilized - to help with planning, implementation and evaluation of pandemic response and recovery activities in communities. Furthermore, it contains a compendium of resources to help System Leaders along the way. This could be a time of doom and gloom. But there is a silver lining. With innovation and the courage to capitalize on emerging opportunities, the homelessness response and housing support system may emerge from this situation stronger and better than before the pandemic hit. It is possible that we can achieve Recovery for All.
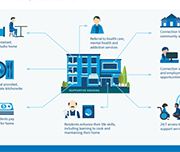
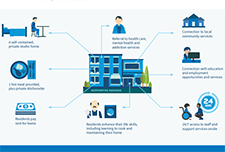
Community Benefits of Supportive Housing
This report highlights mostly B.C.-based research and includes key information, facts, and statistics to answer common questions that neighbours, local government, and other stakeholders may have about supportive housing. The easy-to-read question and answer format also includes infographics to showcase the benefits of supportive housing in neighbourhoods across British Columbia and beyond.
State of homelessness in Canada 2016
Ending homelessness in Canada requires partnerships across public, private, and not-for-profit sectors. Preventative measures, and providing safe, appropriate, and affordable housing with supports for those experiencing homelessness is needed. This paper provides a series of joint recommendations – drafted by the Canadian Observatory on Homelessness and the Canadian Alliance to end Homelessness – for the National Housing Strategy.
State of Cities Reducing Poverty
How has the Vibrant Communities – Cities Reducing Poverty (VC – CRP) network contributed to poverty reduction in Canada? In seeking to answer this central question, the State of Cities Reducing Poverty paper highlights the network’s numerous and varied impacts.
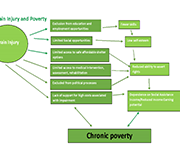
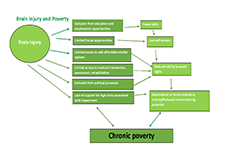
Child Welfare and Youth Homelessness in Canada: A Proposal for Action