National Indigenous Economic Strategy 2022
This National Indigenous Economic Strategy for Canada is the blueprint to achieve the meaningful engagement and inclusion of Indigenous Peoples in the Canadian economy. It has been initiated and developed by a coalition of national Indigenous organizations and experts in the field of economic development. The Strategy is supported by four Strategic Pathways: People, Lands, Infrastructure, and Finance. Each pathway is further defined by a Vision that describes the desired outcomes for the actions and results of individual Strategic Statements. The Calls to Economic Prosperity recommend specific actions to achieve the outcomes described in the Strategic Statements. This document is not intended as a strategic plan specifically, but rather a strategy that others can incorporate into their own strategic plans.
Empower U Evaluation Report
For a family living in poverty, every day is about making tough choices – to pay rent or buy groceries? Having the means to attain the basic necessities, is one thing. Having the skills, confidence and access to resources to manage finances in ways that build pathways out of poverty is something far different. Thanks to the generosity of partners, supporters and donors of Empower U, families can move beyond just managing the day-to-day challenges of poverty. Participants in the program learn valuable money management skills and are given the means to build savings and assets to create financial stability. A future where they and their families can thrive.
Building Understanding: The First Report of the National Advisory Council on Poverty
In August 2018, the Government of Canada announced Opportunity for All – Canada's First Poverty Reduction Strategy. The Strategy included a commitment to the UN Sustainable Development Goal's target of reducing poverty by 20% by 2020 and 50% by 2030. Opportunity for All included the adoption of the Market Basket Measure (MBM) as Canada's Official Poverty Line and the creation of the National Advisory Council on Poverty (Council) to report on progress made toward the poverty reduction targets. This is the first report of the National Advisory Council on Poverty. It continues Canada's discussion on poverty by bringing forward the voices of individuals with lived expertise of poverty. It details progress toward our poverty targets and recommends improvements to our poverty reduction efforts.
Opportunity for All – Canada’s First Poverty Reduction Strategy
Canada is a prosperous country, yet in 2015 roughly 1 in 8 Canadians lived in poverty. The vision of Opportunity for All – Canada's First Poverty Reduction Strategy is a Canada without poverty, because we all suffer when our fellow citizens are left behind. We are all in this together, from governments, to community organizations, to the private sector, to all Canadians who are working hard each and every day to provide for themselves and their families. For the first time in Canada's history, the Strategy sets an official measure of poverty: Canada's Official Poverty Line, based on the cost of a basket of goods and services that individuals and families require to meet their basic needs and achieve a modest standard of living in communities across the country. Opportunity for All sets, for the first time, ambitious and concrete poverty reduction targets: a 20% reduction in poverty by 2020 and a 50% reduction in poverty by 2030, which, relative to 2015 levels, will lead to the lowest poverty rate in Canada's history. Through Opportunity for All, we are putting in place a National Advisory Council on Poverty to advise the Minister of Families, Children and Social Development on poverty reduction and to publicly report, in each year, on the progress that has been made toward poverty reduction. The Government also proposes to introduce the first Poverty Reduction Act in Parliament in Canada’s history. This Act would entrench the targets, Canada's Official Poverty Line, and the Advisory Council into legislation.
Yukon Poverty Report Card 2020
This report was released as part of public education movement Campaign 2000's annual assessment of child and family poverty in Canada, providing an overview of the following key issues relating to poverty in Yukon:
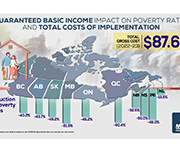
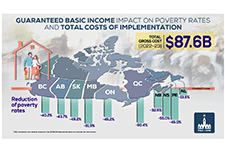
Distributional and Fiscal Analysis of a National Guaranteed Basic Income
Several parliamentarians requested that the PBO prepare a distributional analysis of Guaranteed Basic Income using parameters set out in Ontario’s basic income pilot project, examine the impact across income quintiles, family types and gender, and identify the net federal revenue increase required to offset the net cost of the new program. This analysis also accounts for the behavioural response.
Together BC: British Columbia’s Poverty Reduction Strategy
British Columbia’s Poverty Reduction Strategy, sets a path to reduce overall poverty in B.C. by 25% and child poverty by 50% by 2024. With investments from across Government, TogetherBC reflects government’s commitment to reduce poverty and make life more affordable for British Columbians. It includes policy initiatives and investments designed to lift people up, break the cycle of poverty and build a better B.C. for everyone. Built on the principles of Affordability, Opportunity, Reconciliation, and Social Inclusion, TogetherBC focuses on six priority action areas:
Overcoming Poverty Together 3: The New Brunswick Economic and Social Inclusion Plan 2020-2025
The new Economic and Social Inclusion plan for New Brunswick builds upon progress accomplished over the past 10 years. It includes nine priority actions divided into three pillars: The objective of the plan is to reduce income poverty by at least 50 per cent by 2030, in line with the objectives of Opportunity for All, Canada’s first poverty reduction strategy, and those of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainability of the United Nations.
Cities Reducing Poverty: 2020 Impact Report
The Vibrant Communities – Cities Reducing Poverty 2020 Impact Report is the Tamarack Institute's first attempt at capturing and communicating national trends in poverty reduction and the important ways in which member Cities Reducing Poverty collaboratives are contributing to those changes. This impact report is meant for poverty reduction organizers and advocates, and public decision-makers to get a sense for how collaborative, multi-sectoral local roundtables with comprehensive plans contribute to poverty reduction in their communities and beyond; and spotlights high-impact initiatives that are demonstrating promising results.
Voice of Experience: Engaging people with lived experience of poverty in consultations
Defining Disposable income in the Market Basket Measure
This paper discusses the concept of disposable income used in the MBM. Disposable income is a measure of the means available to a Canadian family to meet its basic needs and achieve a modest standard of living. The disposable income of families surveyed in the Canadian Income Survey (CIS) is compared to the cost of the MBM basket for the size of the family and the region, and families with disposable incomes below that cost are deemed to be living in poverty.
State of Cities Reducing Poverty
How has the Vibrant Communities – Cities Reducing Poverty (VC – CRP) network contributed to poverty reduction in Canada? In seeking to answer this central question, the State of Cities Reducing Poverty paper highlights the network’s numerous and varied impacts.
Asset Building: An Effective Poverty-Reduction Strategy
This brief explains the asset-building approach to poverty reduction. While many families who live on low incomes struggle to meet basic needs, they miss out on opportunities to save and invest - opportunities that are critical in overcoming poverty. Without income, people are unable to get by and without assets, people are unable to get ahead. At Momentum, we call opportunities to save or invest, Asset Building.
With financial assets, individuals can pay down debt, save more, earn a good credit rating, save for a down payment on a home, and build a sustainable livelihood.