While automation has changed the nature of work in Canada over the past few decades, this change was very gradual, and did not accelerate with the very recent developments in artificial intelligence.
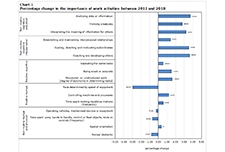
The results of this study reveal that the share of Canadians working in managerial, professional and technical occupations increased from 23.8% in 1987 to 31.2% in 2018, while the share employed in service occupations increased more moderately from 19.2% to 21.8% over the same timeframe. Jobs in both of these occupational groups are generally difficult to automate.
Meanwhile, the share of workers employed in production, craft, repair and operative occupations (more automatable tasks) went from 29.7% in 1987 to 22.2% in 2018, while the share employed in sales, clerical and administrative support occupations also fell over the period (from 27.3% in 1987 to 24.9% in 2018). These jobs are generally more amenable to automation.