The mastering money podcast
Brought to you from CPA Canada, this financial literacy podcast talks about key issues, trends and tips as they relate to financial education. Season 7 of the Mastering Money podcast takes a deep dive into debt and the way it affects Canadians. Season 6 of the Mastering Money podcast will help prepare you for retirement and give you the tools to get there, no matter your age. Season 5 of the Mastering Money podcast unpacks the hard financial conversations you need to be having with your kids, partners, financial planners and more. Season 4 of the Mastering Money podcast explores the role money plays in the lives of women from all walks of life, now and in the future. Season 3 of the Mastering Money podcast looks at the difficult financial decisions Canadians are making during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Season 2 of the podcast takes listeners on a journey across various financial literacy hot topics and trends. These include how to fit financial literacy into existing programs, the financial health of future generations as well what it takes to take the plunge and start your own business. In this introductory season of the podcast, hear from financial educators on topics such as behavioral economics, the emotions of money, financial wellness, and more.
Insights into the risks and benefits of digital financial services for consumers
One of the consequences of social distancing and other restrictions, during the pandemic, such as those on business operating hours, is that consumers spent more of their time searching for information, shopping, and streaming entertainment on-line. With more free time on their hands and money in the bank, a larger percentage of the population took up an interest in investing, often through on-line brokerage platforms or in the cryptoasset markets. Because consumers have been spending more time on-line since the start of the pandemic, they have been more exposed to on-line fraud. In addition to phishing and malware, consumers are dealing with known scams but in digital form, often on social media. For some consumers, the evergrowing number of reliable and accessible information sources could lead to information overload, also known as “infobesity, where there is so much information that the consumer cannot process it all. Infobesity can lead to decision paralysis. In this paper the AMF make the most of their 360-degree view on the financial industry’s digital transformation to review the main changes that occurred in each of their areas of focus, describe the risk of digitalization for the consumers of financial products and services and present the potential opportunities that have been identified to mitigate these risks.
National Indigenous Economic Strategy 2022
This National Indigenous Economic Strategy for Canada is the blueprint to achieve the meaningful engagement and inclusion of Indigenous Peoples in the Canadian economy. It has been initiated and developed by a coalition of national Indigenous organizations and experts in the field of economic development. The Strategy is supported by four Strategic Pathways: People, Lands, Infrastructure, and Finance. Each pathway is further defined by a Vision that describes the desired outcomes for the actions and results of individual Strategic Statements. The Calls to Economic Prosperity recommend specific actions to achieve the outcomes described in the Strategic Statements. This document is not intended as a strategic plan specifically, but rather a strategy that others can incorporate into their own strategic plans.
Multicultural and newcomer charitable giving study
While much research has been conducted on how giving is correlated to factors like educational attainment or income level, the influence of ethnicity has been elusive. This research attempts to better understand how newcomers to Canada and second-generation Canadians perceive and approach giving and volunteerism.
Introduction to behavioural insights for the social sector: a capacity building course
This self-paced online course will help you learn about behavioural insights and how they can help you increase impact in simple, practical ways. In this self-paced learning experience, you will learn foundational skills and tools that you can apply immediately to your work, creating a long-lasting social impact.
Protecting aging investors through behavioural insights
This report identifies behaviourally informed techniques dealers and advisers can use to encourage their older clients to provide the necessary information for enhanced investor protection measures.
Recognizing and responding to economic abuse
With speakers from CCFWE, Johannah Brockie - Program Manager for Advocacy and System Change and Jessica Tran - Program Manager for Education and Awareness, this webinar will guide you through the definition of economic abuse, how to identify an economic abuser, impacts of economic abuse, Covid-19 impacts, tactics, what you should do if you are a victim of economic abuse, and key safety tips. Economic Abuse occurs when a domestic partner interferes with a partner’s access to finances, employment or social benefits, such as fraudulently racking up credit card debt in their partner’s name or preventing their partner from going to work has a devastating effect on victims and survivors of domestic partner violence, yet it’s rarely talked about in Canada. It’s experienced by women from all backgrounds, regions and income levels but women from marginalized groups, including newcomers, refugees, racialized and Indigenous women, are at a higher risk of economic abuse due to other systemic factors.
Who Doesn’t File a Tax Return? A Portrait of Non-Filers
The Canada Revenue Agency administers dozens of cash transfer programs that require an annual personal income tax return to establish eligibility. Approximately 10–12 percent of Canadians, however, do not file a return; as a result, they will not receive the benefits for which they are otherwise eligible. In this article, we provide the first estimates of the number and characteristics of non-filers. We also estimate that the value of cash benefits lost to working-age non-filers was $1.7 billion in 2015. Previous literature suggests either a rational choice model of tax compliance (in which the costs of filing are weighed against its benefits) or a more complex behavioural model. Our study has important consequences for policy-making in terms of the administrative design and fiscal costs of public cash benefits attached to tax filing, the measurement of household incomes, and poverty rates.
Investing and The COVID-19 Pandemic: Survey of Canadian Investors
The Investor Office conducted this study to further our understanding of the experiences and behaviours of retail investors during the COVID-19 Pandemic. The study explored several topics including the financial preparedness, savings behaviour, financial situations, changing preference, and trading activity of retail investors. Key findings include that 32 per cent of investors have experienced a decline in their financial situation during the pandemic while 16 per cent have experienced an improvement. Half of investors have not done any trading during the pandemic, but of those who have been trading, 63 per cent have increased their holdings.
Financial Well-Being: A Conceptual Model and Preliminary Analysis
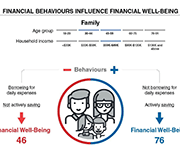
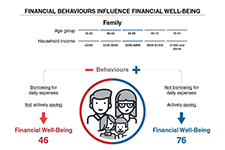
Based on an extensive literature review and re-analysis of existing qualitative data, this report offers a working definition and an a priori conceptual model of financial well-being and its possible determinants. Using survey data from Norway (2016), ten regression models have been conducted to identify the key drivers of financial well-being and enhance the understanding of the underlying mechanisms responsible for the unequal spread of well-being across the population. The preliminary analyses in this report were consistent with both the definition and the model, albeit with some nuances and unexplained effects. The empirical analysis identified three sub-domains of financial well-being. It was found that all three measures share three behaviours as their main drivers: ‘active saving’, ‘spending restraints’ and ‘not borrowing for daily expenses’. Also, ‘locus of control’ stood out as an important explanatory variable, with significant impacts on all three levels of well-being. Beyond that, some distinguishing characteristics were identified for each of the measures.
Encouraging Retirement Planning through Behavioural Insights
This research report identifies behaviourally informed ways that government, regulators, employers, and financial institutions can encourage retirement planning. Thirty different initiatives and tactics that could be implemented by a variety of stakeholders to encourage retirement planning are proposed, and interventions are organized around four primary challenges people face in moving from having the intention to create a retirement plan to the action of making a plan: (1) it’s hard to start, (2) it’s easy to put off, (3) it’s easy to get overwhelmed and drop out, and (4) it’s hard to get the right advice. The report also includes the results of a randomized experiment that evaluated several of the approaches proposed in the report. This report was published as part of the Ontario Securities Commission’s strategy and action plan to respond to the needs and priorities of Ontario seniors.
How to really build financial capability
Recent years have seen an explosion in interventions designed to improve financial outcomes of participants. Yet on-the-ground evidence suggests that not all financial education programs are equally successful at achieving this aim. This paper examines the difference between interventions that work, and those than do not. It attempts to answer the question: “How do you actually build financial capability?” In doing so, we aim to help interested parties enhance the effectiveness of their programs and policies by providing them with evidence-based recommendations to drive positive outcomes in participants.
The Impact of Matched Savings Programs: Building Assets & Lasting Habits
Matched Savings programs, or Individual Development Accounts, are a financial empowerment strategy that aim to build financial stability and reduce poverty. These programs build sustainable livelihoods by working with participants to earn savings while learning about money management, build regular savings habits, self-confidence, and hope for the future. Matching This brief presents key findings from Momentum's Matched Saving programs and the impact on program graduates' saving habits, establishment of emergency savings, and contribution to registered savings.
funds act as a power boost to the participants’ own savings, allowing them to purchase productive assets to move their lives forward.
Smarter Financial Education: Key lessons from behavioural insights for financial literacy initiatives
This publication presents key findings for financial education, drawn from the IOSCO/OECD joint report “The Application of Behavioural Insights to Financial Literacy and Investor Education Programmes and Initiatives”. It gives a short overview of the ways in which behavioural insights are relevant for financial education and then summarises five key lessons that policy makers can follow, illustrated with the experiences of OECD/INFE members.
How personality traits and economic beliefs shape financial capability and literacy
An emerging body of international literature is beginning to reveal a significant connection between financial capability metrics and personality, suggesting that what influences our financial well-being may be more nuanced than we previously thought. This report investigates how the inclusion of personality traits impacts the analysis of the gender difference in financial capability scores.
Creating a Strong Foundation for Change
This guide is designed to be a resource for programs working with low income families to use when anticipating or implementing a new approach, such as coaching, to doing business. It helps you to systematically – and honestly – look at your foundational readiness for change, so that the improvements you want to make will take root and grow in fertile ground. Making time and space to look deeply into your organization can offer the opportunity to reconsider what quality service delivery looks like, help you discover how coaching (or other techniques) could be a tool, and plan efficiently on where it fits best into your existing context.
The Effects of Education on Canadians’ Retirement Savings Behaviour
This paper assesses the extent to which education level affects how Canadians save and accumulate wealth for retirement. Data from administrative income-tax records and responses from the 1991 and 2006 censuses of Canada show that individuals with more schooling are more likely to contribute to a tax-preferred savings account and have higher saving rates, have higher home values, and are less likely to rent housing.
Backgrounder: Preliminary findings from Canada’s Financial Well-Being Survey
This backgrounder reports preliminary findings from a survey of financial well-being among Canadian adults. Preliminary analysis of the survey data indicates that two behaviours are particularly important in supporting the financial well-being of Canadians. First, our analysis indicates that Canadians who practice active savings behaviour have higher levels of financial resilience as well as higher levels of overall financial well-being. In other words, regardless of the amount of money someone makes, regular efforts to save for unexpected expenses and other future priorities appears to be the key to feeling and being in control of personal finances. Secondly, Canadians who often use credit to pay for daily expenses because they have run short of money have lower levels of financial well-being. While this behaviour is likely symptomatic of low levels of financial well-being, our analysis indicates that a person can substantially improve their financial resilience and financial well-being by implementing strategies to reduce the frequency of running out of money and of having to rely on credit to get by.
Protecting vulnerable clients: A practical guide for the financial services industry
Firms and representatives in the financial services industry occasionally encounter situations where a client’s vulnerability causes the client to make decisions that are contrary to his or her financial interests, needs or objectives or that leave him or her exposed to potential financial mistreatment. Because of the relationships they develop with their clients and the knowledge they acquire about clients’ financial needs or objectives over time, firms and representatives in the financial sector can play a key role in helping people who are in a vulnerable situation protect their financial well-being. They are instrumental in preventing and detecting financial mistreatment among consumers of financial services. Firms and representatives can also help clients experiencing financial mistreatment get the assistance they need. This guide proposes possible courses of action to protect vulnerable clients. Its purpose is to provide financial sector participants with guidance on the steps they can take to help protect clients’ financial well-being, prevent and detect financial mistreatment, and assist clients who are experiencing this type of mistreatment.
The Financial Health Check: Scalable Solutions for Financial Resilience
A large majority of American households live in a state of financial vulnerability. Across a range of incomes, people struggle to build savings, pay down debt, and manage irregular cash flows. Even modest savings cushions could help households take care of unexpected expenses or disruptions in income without relying on costly credit. But in practice, setting aside savings can be difficult. Research from the field of behavioral science shows that light-touch interventions can help address these barriers. For example, changing default settings or bringing financial management to the forefront of everyday life have had powerful effects on savings activity. The Financial Health Check (FHC) draws on such insights to offer a new model of scalable support for achieving financial goals.
VITA: A step-by-step guide to increase your impact
In this report, The Common Cents Lab and MetLife Foundation share findings from the experiments we have run over the past several years with VITA providers to improve tax-related outcomes. We encourage you to consider implementing these ideas and engaging in additional conversations about how to use behavioral science to increase financial capability for all taxpayers. The report outlines a series of interventions that exemplify
ways these best practices have been implemented in the field and
how to use behavioral science to further extend their impact. We’ve
organized these interventions into two categories:
Habit Change: Literature Review
Habits are incredibly powerful. Good habits can make people highly successful, and bad habits can ruin people’s lives. Still, it is important to go beyond the anecdotal evidence of the many self-help books on habit, and to take stock of the scientific evidence. This literature review discusses we discuss how habits are formed, how bad habits can be abandoned, how approach-avoidance training can help adopting good habits and abandoning bad habits, and, finally, how habits can be measured properly.
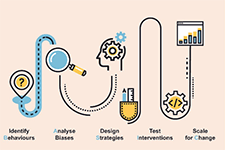
Tools and Ethics for Applied Behavioural Insights: The BASIC Toolkit
A better understanding of human behaviour can lead to better policies. If you are looking for a more data-driven and nuanced approach to policy making, then you should consider what actually drives the decisions and behaviours of citizens rather than relying on assumptions of how they should act. You can start applying behavioural insights (BI) to policy now. No matter where you are in the policy cycle, policies can be improved with BI through a process that looks at Behaviours, Analysis, Strategies, Interventions, Change (BASIC). This allows you to get to the root of the policy problem, gather evidence on what works, show your support for government innovation, and ultimately improve policy outcomes. This toolkit guides policy officials through these BASIC stages to start using an inductive and experimental approach for more effective policy making.
Increasing Take-Up of the Canada Learning Bond
The Canada Learning Bond (CLB) is an educational savings incentive that provides children from low income families born in 2004 or later with financial support for post-secondary education. Personal contributions are not required to receive the CLB, however take-up remains low among the eligible population. The Impact and Innovation Unit (IIU), in collaboration with the Learning Branch and the Innovation Lab at Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) conducted a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of behavioural insights (BI) in correspondence sent to primary caregivers of children eligible for the CLB. This trial demonstrates the effectiveness of BI interventions tailored to the particular behavioural barriers that affect specific populations in increasing take-up of programs like the CLB. If scaled across the eligible population, the best performing letter would result in thousands more children receiving this education savings incentive on an annual basis.