Housing law: free legal information
This resource produced by Community Legal Education Ontario (CLEO) provides a list of free legal information about paying rent, eviction procedures and much more.
Housing conditions among racialized groups: A brief overview
In response to Canada's Anti-Racism Strategy, Statistics Canada's Centre for Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics is releasing a second set of five data tables on social inclusion. Over 20 new indicators, for a total of over 120 indicators, can now be used to examine various socioeconomic facets of racialized Canadians.
Non-Profit Organizations and Volunteering Satellite Account: Human Resources Module, 2010 to 2019
In 2019, non-profit organizations (NPOs)—serving households, businesses and governments—employed 2.5 million people, representing 12.8% of all jobs in Canada. The employment share ranged between 12.4% and 12.8%, increasing during the 2010-to-2019 period. While the economic and social landscape of Canada is very different at the time of this release than it was in 2019, these data provide a valuable baseline to better understand the potential impacts of COVID-19 in later reference years.
Impact of the COVID-19 Crisis on Montreal “Cultural Communities”
This exploratory study aims to better understand the challenges experienced by members of cultural communities in Montreal, particularly the most disadvantaged groups, during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Spring of 2020.
Longitudinal Immigration Database: Asylum claimant and immigrant economic region tables, 2018
Tables on the income and mobility of immigrants by economic region, and a table on asylum claimant economic outcomes, are now available. These tables use data from the Longitudinal Immigration Database.
Longitudinal Immigration Database: Immigrant children and census metropolitan area tables, 2018
The most recent 2018 data from the Longitudinal Immigration Database (IMDB) indicate that immigrant children make a significant contribution to Canadian society and the Canadian economy over time. Although immigrant children (32.2%) are more than twice as likely as non-immigrant children (15.4%) to live in low-income households, factors such as the opportunity to be educated in the Canadian system and an increased proficiency in the official languages help immigrant children attain wages in adulthood similar to those of their Canadian-born peers. This analysis connects the characteristics of immigrants who came to Canada as children with their adulthood socioeconomic outcomes in 2018, such as participation in postsecondary education and median wages. The IMDB provides a long-term perspective on immigrants and their socioeconomic outcomes in Canada, offering details on how immigration is shaping Canada's future. In addition, these data from 2018 contribute to baseline estimates in preparation for future research on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on immigrant children, including immigrant children admitted during the pandemic, their adjustment period and their long-term socioeconomic outcomes in adulthood.
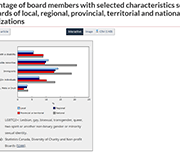
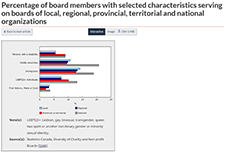
Diversity of charity and non-profit boards of directors: Overview of the Canadian non-profit sector
Charities and non-profit organizations play a vital role in supporting and enriching the lives of Canadians. A crowdsourcing survey of individuals involved in the governance of charities and non-profit organizations was conducted from December 4, 2020, to January 18, 2021. The objectives of the survey were to collect timely information on the activities of these organizations and the individuals they serve and to learn more about the diversity of those who serve on their boards of directors. A total of 8,835 individuals completed the survey, 6,170 of whom were board members.
Income and mobility of immigrants, 2018
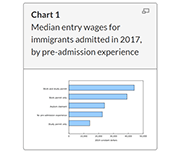
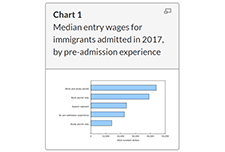
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected many aspects of Canadian immigration, including reduced permanent resident admissions and lower labour market outcomes. This article presents the latest economic and mobility outcomes of immigrants admitted to Canada using data from the 2019 Longitudinal Immigration Database, and provides baseline estimates prior to the pandemic for future analyses. In recent years, the profile of immigrants admitted to Canada has changed. The median entry wage for immigrants admitted to Canada in 2017 was the highest to date, reaching $30,100 in 2018. This value surpassed the previous high of $26,500 for 2017 outcomes of immigrants admitted in 2016. These new data also highlight a decreasing gap between the immigrant median entry wage and the Canadian median wage ($37,400). Factors such as pre-admission experience, knowledge of official languages, and category of admission, among other socioeconomic characteristics, could contribute to the rise in median entry wage compared with previous admission years.
Statistic Canada’s Longitudinal Immigration Database: Birth area and income table, 2018
Statistics Canada's Longitudinal Immigration Database (IMDB) Interactive Application has been updated to include data on citizenship intake rates and income by birth area, sex, pre-admission experience and admission category. This table includes income measures up to 2018 for immigrants admitted to Canada since 2008.
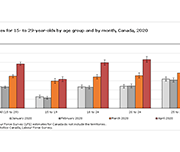
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the NEET (not in employment, education or training) indicator, March and April 2020
A fact sheet released by Statistics Canada shows that, in March and April 2020, the proportion of young Canadians who were not in employment, education or training (NEET) increased to unprecedented levels. The COVID-19 pandemic—and the public health interventions that were put in place to limit its spread—have affected young people in a number of ways, including high unemployment rates, school closures and education moving online.
Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics Hub
Launched by the Centre for Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics (CGDIS), the Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Hub focuses on disaggregated data by gender and other identities to support evidence-based policy development and decision making.
Transitions into and out of employment by immigrants during the COVID-19 lockdown and recovery
During the widespread lockdown of economic activities in March and April 2020, the Canadian labour market lost 3 million jobs. From May to July, as many businesses gradually resumed their operations, 1.7 million jobs were recovered. While studies in the United States and Europe suggest that immigrants are often more severely affected by economic downturns than the native born (Borjas and Cassidy 2020; Botric 2018), little is known about whether immigrants and the Canadian born fared differently in the employment disruption induced by the COVID-19 pandemic and, if so, how such differences are related to their socio-demographic and job characteristics. This paper fills this gap by comparing immigrants and the Canadian-born population in their transitions out of employment in the months of heavy contraction and into employment during the months of partial recovery. The analysis is based on individual-level monthly panel data from the Labour Force Survey and focuses on the population aged 20 to 64. Immigrants are grouped into recent immigrants who landed in Canada within 10 years or less, and long-term immigrants who landed in Canada more than 10 years earlier.
Changes in the socioeconomic situation of Canada’s Black population
This study provides disaggregated statistics on the socioeconomic outcomes of the Black population by generation status (and immigrant status), sex and country of origin, and is intended to illustrate and contribute to the relevance of disaggregation in understanding these populations and the diversity of their situation. This study sheds light on some of the issues faced by the Black population and shows differences that exist compared with the rest of the working-age population, by sex, generation and place of origin, from 2001 to 2016.
Legal Resources Catalogue: Free legal information
This resource provides a list of free legal information resources produced by Community Legal Education Ontario (CLEO).
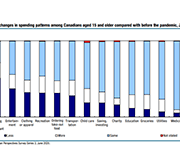
Expected changes in spending habits during the recovery period
Around mid-June, physical distancing measures began easing across the country, giving Canadians more opportunities to spend money. However, COVID-19 is still with us, shopping habits have changed and there are 1.8 million fewer employed Canadians now than there were prior to the pandemic. How our economy evolves going forward will largely depend upon the spending choices Canadians make over the coming weeks and months. This study presents results from a recent web panel survey conducted in June, looks at how spending habits may change.
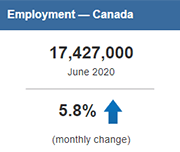
Labour Force Survey, June 2020
Labour Force Survey (LFS) results for June reflect labour market conditions as of the week of June 14 to June 20. A series of survey enhancements continued in June, including additional questions on working from home, difficulty meeting financial needs, and receipt of federal COVID-19 assistance payments. New questions were added to measure the extent to which COVID-19-related health risks are being mitigated through workplace adaptations and protective measures.
Providing one-on-one financial coaching to newcomers: Insights for frontline service providers
One-on-one financial help is a key financial empowerment (FE) intervention that Prosper Canada is working to pilot, scale and integrate into other social services, in collaboration with FE partners across the country. FE is increasingly gaining traction as an effective poverty reduction measure. FE interventions include financial coaching and supports that assist people to build money management skills, access income benefits, tackle debt, learn about safe financial products and services and find ways to save for emergencies. This report shares insights on providing one-on-one financial coaching to newcomers captured through two financial coaching pilot projects that Prosper Canada conducted in collaboration with several frontline community partners.
English
Benefits 101
What are tax credits and benefits
Reasons to file a tax return
List of common benefits
Getting government payments by direct deposit
Common benefits and credits Benefits pathways (for practitioner reference only – some illustrations presented are Ontario benefits)
Pathways to accessing government benefits
Overview of tax benefits and other income supports (adults, children, seniors)
Overview of tax benefits and other income supports (people with disabilities or survivors)
Income support programs for immigrants and refugees
Glossary of terms – Benefits 101
Resources – Benefits 101
Key benefits you may be eligible for
Make sure you maximize the benefits you are entitled to if you are First Nations, Inuit, or Métis
Benefits of Filing a Tax Return: Infographic
Common benefits and credits
Resource links:
Benefits and credits for newcomers to Canada – Canada Revenue Agency
Benefit Finder – Government of Canada
Electronic Benefits and credits date reminders – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Income Assistance Handbook – Government of Northwest Territories
What to do when you get money from the government – Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC)
Emergency benefits
General emergency government benefits information & navigation
Financial Relief Navigator tool (Prosper Canada)
Changes to taxes and benefits: CRA and COVID-19 – Government of Canada
Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB)
Apply for Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB) with CRA – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Questions & Answers on CERB – Government of Canada
What is the CERB? – Prosper Canada
FAQ: Canada Emergency Response Benefit – Prosper Canada (updated June 10th)
CERB: What you need to know about cashing your cheque – FCAC
COVID-19 Benefits (summary, includes Ontario) – CLEO/Steps to Justice
COVID-19 Employment and Work – CLEO/Steps to Justice
GST/HST credit and Canada Child Benefit
COVID-19 – Increase to the GST/HST amount – Government of Canada
Canada Child Benefit Payment Increase – Government of Canada
Benefits payments for eligible Canadians to extend to Fall 2020 – Government of Canada
Support for students
Support for students and recent graduates – Government of Canada
Canada Emergency Student Benefit (CESB) – Government of Canada
Benefits and credits for families with children
Benefits and credits for families with children
Resource links:
Child and family benefits – Government of Canada
Child and family benefits calculator – Government of Canada
Benefits and credits for people with disabilities
Benefits and credits for people with disabilities
RDSP, grants and bonds
Resource links:
Canada Pension Plan disability benefit toolkit – Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC)
Disability benefits – Government of Canada
Disability tax credit (DTC) – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Free RDSP Calculator for Canadians – Plan Institute
Future Planning Tool – Plan Institute
Creating Financial Security: Financial Planning in Support of a Relative with a Disability (handbook) – Partners for Planning
Nurturing Supportive Relationships: The Foundation to a Secure Future (handbook) – Partners for Planning
RDSP – Plan Institute
Disability Tax Credit Tool – Disability Alliance BC
ODSP Appeal Handbook – CLEO
Disability Inclusion Analysis of Government of Canada’s Response to COVID-19 (report and fact sheets) – Live Work Well Research Centre
Demystifying the Disability Tax Credit – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Benefits and credits for seniors
Benefits and credits for seniors
Resource links:
Canadian Retirement Income Calculator – Government of Canada
Comparing Retirement Savings Options – Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC)
Federal Provincial Territorial Ministers Responsible for Seniors Forum – Employment and Social Services Canada (ESDC)
Retiring on a low income – Open Policy Ontario
RRSP vs GIS Calculator – Daniela Baron
Sources of income for seniors handout – West Neighbourhood House
What every older Canadian should know about: Income and benefits from government programs – Employment and Social Services Canada (ESDC)
French
Comprendre les prestations
Que sont les crédits d’impôt et les prestations?
Pourquoi produire une déclaration de revenus?
Processus d’accès aux prestations (simple, complexe ou laborieux)
Aperçu des prestations et crédits d’impôt et des autres mesures d’aide au revenu
Aperçu des prestations et crédits d’impôt et des autres mesures d’aide au revenu : personnes handicapées ou survivants
Programmes d’aide au revenu pour immigrants et réfugiés – Admissibilité et processus de demande
Glossaire – Prestations et credits
Ressources : Prestations et credits
Principales mesures d’aide auxquelles vous pouvez être admissibles
Assurez-vous de maximiser les prestations auxquelles vous avez droit si vous êtes Autochtone,
Infographie sur les avantages de produire une déclaration de revenus
Prestations et crédits courants
Prestations et crédits pour familles avec enfants
Prestations et crédits pour personnes handicapées
Prestations et crédits pour les personnes âgées
Informations d’identification pour accéder aux prestations
Études de cas
COVID-19 and support for seniors: Do seniors have people they can depend on during difficult times?
In an effort to avoid the spread of COVID-19, Canadians are engaging in physical distancing to minimize their social contact with others. However, social support systems continue to play an important role during this time. In particular, seniors living in private households may depend on family, friends or neighbours to deliver groceries, medication and other essential items to their homes. This study examines the level of social support reported by seniors living in private households.
Results from the 2016 Census: Examining the effect of public pension benefits on the low income of senior immigrants
This is a study released by Insights on Canadian Society based on 2016 Census data. Census information on immigration and income is used to better understand the factors associated with low income among senior immigrants. This study examines the factors associated with the low-income rate of senior immigrants, with a focus on access to Old Age Security (OAS) and Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) benefits.
Trends in the Citizenship Rate Among New Immigrants to Canada
This Economic Insights article examines trends in the citizenship rate (the percent of immigrants who become Canadian citizens) among recent immigrants who arrived in Canada five to nine years before a given census. The citizenship rate among recent immigrants aged 18 and over peaked in 1996 and declined continuously to 2016. Most of this decline occurred after 2006. The citizenship rate declined most among immigrants with low family income, poor official language skills, and lower levels of education. There was also significant variation in the decline among immigrants from different source regions, with the decline largest among Chinese immigrants.
Resources
Handouts, slides, and time-stamps
Read the presentation slides for this webinar
Access the handouts for this webinar:
Poster presentation: Financial Empowerment for Newcomers project
Infographics: Newcomer settlement stages, money matters, and client personas
Time-stamps for the video recording:
3:11 – Agenda and introductions
5:21 – Audience poll
8:25 – Introduction to Financial Empowerment for Newcomers project (Speaker: Glenna Harris)
11:25 – AXIS financial coaching program (Speaker: Sheri Abbot)
30:05 – North York Community House financial coaching program (Speaker: Noemi Garcia)
45:40 – Q&A
Chronic Low Income Among Immigrants in Canada and its Communities
This study examines the rate of chronic low income among adult immigrants (aged 25 or older) in Canada during the 2000s. Data is taken from the Longitudinal Immigration Database (IMDB) for the period from 1993 to 2012, with regional adjustments used for the analysis. Chronic low income is categorized as having a family income under a low-income cut-off for five consecutive years or more. The study found that for immigrants were in in low-income in any given year, half were in chronic low-income. Including spells of low income which become chronic in later years, this number rises to two-thirds. The highest chronic rates were found in immigrant seniors and immigrants who were unattached or lone parents. Chronic low income is a large component of income disparity and overall low income among immigrants.
My money in Canada
This online tool will help you learn about the financial system in Canada and how to manage your money. Explore five money modules on banking, income and expenses, money goals and savings, credit, and taxes. Clients can do the modules in the order they appear, or just the ones they want to use. The tool is intended to be used with clients and settlement workers together, but can also be used by the client on their own if they are comfortable.
Evaluation of the Guaranteed Income Supplement
The Old Age Security program is the largest statutory program of the Government of Canada, and consists of the Old Age Security pension, the Guaranteed Income Supplement, and the Allowance. The Guaranteed Income Supplement is provided to low-income seniors aged 65 years and over who receive the Old Age Security pension and are below a low-income cut-off level. This evaluation examines take-up of the Guaranteed Income Supplement by various socioeconomic groups, the characteristics of those who are eligible for the Supplement but do not receive it, and barriers faced by vulnerable groups.