Resources
Handouts, videos and time stamps
Women living in subsidized housing in Canada
Using data primarily from the 2021 Canadian Housing Survey, this study applies a gender lens to examine the characteristics of Canadians living in subsidized housing. It examines the experiences of renters in subsidized housing and their satisfaction with their dwelling and neighbourhood, drawing comparisons with their counterparts living in non-subsidized rental housing.
Benefits & credits: factsheets from the CRA
The CRA has compiled benefits and credits factsheets for: These are available in English and French.
Consumer Vulnerability: Evidence from the Monthly COVID-19 Financial Well-being Survey
The Financial Consumer Agency of Canada’s (FCAC) COVID-19 Financial Well-being Survey, which began in August 2020, is a nationally representative hybrid online-phone survey fielded monthly, with approximately 1,000 respondents per month. The survey collects information on Canadians’ day-to-day financial management and financial well-being. As of September 2022, the survey results show that over the past several months, financial hardships have increased for many Canadians due to the rapidly evolving economic environment. While financial vulnerability can affect anyone regardless of income, background or education, hardships have increased more for those living on a low income, Indigenous peoples, recent immigrants, and women, due to the disproportionate financial impact of the pandemic on these groups (households with low income, Indigenous people, new immigrants, and women.) This brief report provides an overview of survey results collected between August 2020 and September 2022. In publishing this report, FCAC’s goal is to provide insight into the financial well-being of Canadians, to identify which groups are experiencing greater vulnerabilities and hardships, and to inform and target our collective response as financial ecosystem stakeholders.
Rising prices and the impact on the most financially vulnerable: A profile of those in the bottom family income quintile
This study uses the 2022 Portrait of Canadian Society Survey to examine the impact of rising inflation on the lowest income Canadians. Using multiple pre-pandemic data sources, the study takes a closer look at people living in the bottom family income quintile, examining their family income, debt and assets levels, as well as some indicators of economic hardship.
National Indigenous Economic Strategy 2022
This National Indigenous Economic Strategy for Canada is the blueprint to achieve the meaningful engagement and inclusion of Indigenous Peoples in the Canadian economy. It has been initiated and developed by a coalition of national Indigenous organizations and experts in the field of economic development. The Strategy is supported by four Strategic Pathways: People, Lands, Infrastructure, and Finance. Each pathway is further defined by a Vision that describes the desired outcomes for the actions and results of individual Strategic Statements. The Calls to Economic Prosperity recommend specific actions to achieve the outcomes described in the Strategic Statements. This document is not intended as a strategic plan specifically, but rather a strategy that others can incorporate into their own strategic plans.
101 solutions for inclusive wealth building
Having wealth, or a family’s assets minus their debts, is important not just for the rich— everyone needs wealth to thrive. Yet building the amount of wealth needed to thrive is a major challenge. Nearly 13 million U.S. households have negative net worth. Millions more are low wealth; they do not have the assets or liquidity needed to maintain financial stability and invest in themselves in the present, nor are they on track to accumulate the amount of wealth they will need to have financial security in retirement. This report examines what it will take to create truly shared prosperity in the United States. It is focused on solutions that would grow the wealth of households in the bottom half of the wealth distribution, and it explores reparative approaches to building the wealth of Black, Indigenous, and other people of color (BIPOC).
Together, these groups represent at least half of all U.S. households.
Understanding Systems: The 2021 report of the National Advisory Council on Poverty
Canada’s National Advisory Council on Poverty’s second Annual Report, Understanding Systems, is the first report to provide a glimpse into poverty since COVID-19. Based on community engagements with Canadians and provinces/territories over the last year, the Council has recommended five broad strategies to reduce poverty in Canada. The pillars of the strategy are as follows: In a recent webinar, three Council members shared what strategies can make the greatest impact. Read more to learn about the key takeaways from the discussion.
Gathering a Bundle for Indigenous Evaluation
This guide brought together by the Indigenous Learning Circle (ILC) in Winnipeg's North End details how to conduct an Indigenous-grounded evaluation process. While not a comprehensive guide to complete an evaluation, the Bundle builds upon what is understood about evaluation and provides a guide that can be used in planning, designing, implementing and reporting based upon Indigenous values and principles. The Bundle provides a common understanding of the purpose of evaluation; how it can be beneficial for community; and Indigenous principles, values, considerations, and methods that could be used in the design and implementation of evaluation. It can be used by community organizations and staff to understand evaluation and increase community members’ capacity to actively participate in evaluation efforts in their programs and organizations.
Ganohonyohk (Giving Thanks): Indigenous Prosperity
The Ganohonyohk/Prosperity Research Project explored how seven Indigenous Friendship Centre communities in Ontario understood the concept of prosperity. The guiding research question of “How do urban Indigenous Friendship Centre communities in Ontario view a prosperous/wealthy life?” was used to gauge the meaning of prosperity through a community driven lens. This strength-based research explores culturally appropriate approaches to urban Indigenous prosperity and considers the role of Friendship Centres in promoting prosperity. It concludes that approaches to Indigenous prosperity need to be context-specific and allow for self-determination in establishing communities’ priorities.
Economic impact of COVID-19 among Indigenous people
This article uses data from a recent crowdsourcing data initiative to report on the employment and financial impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on Indigenous participants. It also examines the extent to which Indigenous participants applied for and received federal income support to alleviate these impacts. As Canada gradually enters a recovery phase, the article concludes by reporting on levels of trust among Indigenous participants on decisions to reopen workplaces and public spaces.
National Indigenous History Month 2021
In June, we commemorate National Indigenous History Month 2021 to recognize the history, heritage and diversity of First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples in Canada. The Crow-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada website contains resources on Indigenous history, promotional and educational materials, and information on how the Government of Canada is responding to the Truth and Reconciliation Commission's Calls to Action.
Introduction to Indigenous Peoples’ cultures online course
This free, on-demand, introductory course provides learners with insight into the history of First Nations, Métis and Inuit Peoples; an understanding of the devastation of colonialism on Indigenous communities and economies from an Indigenous perspective and how it is critical to reconciliation; and how culturally sensitive health care models help inform how accounting and finance education can be inclusive and supportive. This course was developed to provide the writers and facilitators of CPA education programs, cases and examinations with insight, knowledge and skills to better understand the perspectives of Indigenous students, to help support their success. It will provide all learners with a valuable introduction into the deep cultural and historical foundations upon which the future prosperity of Indigenous communities must be built.
Federal Spending on First Nations and Inuit Health Care
An analysis of provincial/territorial health care funding and funding for First Nations and Inuit by Indigenous Services Canada through the First Nations and Inuit Health Branch. This report provides an analytical overview of federal and provincial/territorial government health spending for the First Nations and Inuit population.
Cash Back: A Yellowhead Institute Red Paper
This report looks at how the dispossession of Indigenous lands nearly destroyed Indigenous economic livelihoods and discusses restitution from the perspective of stolen wealth.
San’yas Indigenous Cultural Safety Training
Cultural safety is about fostering a climate where the unique history of Indigenous peoples is recognized and respected in order to provide appropriate care and services in an equitable and safe way, without discrimination. This website includes information about the San’yas: Indigenous Cultural Safety Training Program delivered by the Provincial Health Services Authority of British Columbia.
Non-Profit Organizations and Volunteering Satellite Account: Human Resources Module, 2010 to 2019
In 2019, non-profit organizations (NPOs)—serving households, businesses and governments—employed 2.5 million people, representing 12.8% of all jobs in Canada. The employment share ranged between 12.4% and 12.8%, increasing during the 2010-to-2019 period. While the economic and social landscape of Canada is very different at the time of this release than it was in 2019, these data provide a valuable baseline to better understand the potential impacts of COVID-19 in later reference years.
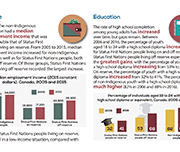
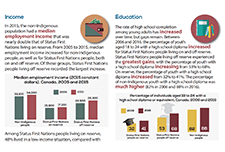
A snapshot: Status First Nations people in Canada
This is a custom report produced in collaboration between the Assembly of First Nations and Statistics Canada. It includes a variety of social and economic statistics for Status First Nations people living on and off reserve and includes comparisons with the non-Indigenous population.
Urban, Rural, and Northern Indigenous Housing
This report examines Indigenous housing in urban, rural, and northern areas, an expression which is taken to refer to Indigenous housing in all areas of Canada other than on reserves. This report is intended to provide an analysis of unmet Indigenous housing need and homelessness in these areas, and of government spending to address those issues. The report ends with a range
of estimated costs for addressing housing need to various extents under various programs.
This report was prepared at the request of the House of Commons Standing Committee on Human Resources, Skills and Social Development and the Status of Persons with Disabilities (HUMA).
Aboriginal Peoples Survey: Data tables, 2017
New data tables on the labour activities of Indigenous Peoples are now available. Data are from the 2017 Aboriginal Peoples Survey and include information on labour force status, job satisfaction, skills training, skills that limit job opportunities, job permanency, part-time or full-time job status, mismatch of skills for current job, disability status and disability severity class, by Indigenous identity, age group and sex. Data are available for Canada, the provinces (Atlantic provinces combined) and the territories.
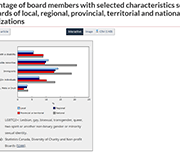
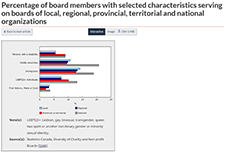
Diversity of charity and non-profit boards of directors: Overview of the Canadian non-profit sector
Charities and non-profit organizations play a vital role in supporting and enriching the lives of Canadians. A crowdsourcing survey of individuals involved in the governance of charities and non-profit organizations was conducted from December 4, 2020, to January 18, 2021. The objectives of the survey were to collect timely information on the activities of these organizations and the individuals they serve and to learn more about the diversity of those who serve on their boards of directors. A total of 8,835 individuals completed the survey, 6,170 of whom were board members.
The COVID-19 pandemic and Indigenous people with a disability or long-term condition
This paper uses crowdsourced data to provide an overview of the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the health, service access, and ability to meet basic needs of Indigenous participants with disabilities or long-term conditions. Changes in overall health and mental health are examined by disability type, age group and sex. The most commonly reported service disruptions since the start of the pandemic are also presented. The crowdsourcing data reflected health and other disparities between Indigenous and non-Indigenous participants with a disability or long-term condition. Indigenous participants were more likely to report worsened overall health and mental health, service disruption, and a greater impact on their ability to meet essential needs.
Statistics on Indigenous peoples
This data hub includes data on the following subjects:
Achieving financial resilience in the face of financial setbacks
The Asset Funders Network (AFN) developed this primer to inform community-based strategies that can help economically-vulnerable families to better manage financial setbacks, shortfalls, and shocks. The goal of this brief is to provide a common understanding and language for funders and financial capability programs as part of a financial emergency toolkit.
The Canadian Housing Survey, 2018: Core housing need of renter households living in social and affordable housing
This article provides a high level overview of those living in social and affordable housing by painting a portrait of them based on the results of the 2018 CHS. Socio-demographic and household characteristics are examined using housing indicators such as core housing need.
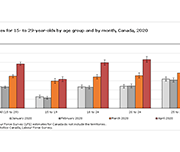
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the NEET (not in employment, education or training) indicator, March and April 2020
A fact sheet released by Statistics Canada shows that, in March and April 2020, the proportion of young Canadians who were not in employment, education or training (NEET) increased to unprecedented levels. The COVID-19 pandemic—and the public health interventions that were put in place to limit its spread—have affected young people in a number of ways, including high unemployment rates, school closures and education moving online.
Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics Hub
Launched by the Centre for Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics (CGDIS), the Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Hub focuses on disaggregated data by gender and other identities to support evidence-based policy development and decision making.
Shelters for victims of abuse with ties to Indigenous communities or organizations in Canada, 2017/2018
There were 85 shelters for victims of abuse that had ties to First Nations, Métis or Inuit communities or organizations operating across Canada in 2017/2018. These Indigenous shelters, which are primarily mandated to serve victims of abuse, play an important role for victims leaving abusive situations by providing a safe environment and basic living needs, as well as different kinds of support and outreach services. Over a one-year period, there were more than 10,500 admissions to Indigenous shelters; the vast majority of these admissions were women (63.7%) and their accompanying children (36.1%). This article uses data from the Survey of Residential Facilities for Victims of Abuse (SRFVA). Valuable insight into shelter use in Canada and the challenges that shelters and victims of abuse were facing in 2017/2018 is presented.
Taxpayer Rights in the Digital Age
This paper explores the intersection of digital innovation, digital services, access, and taxpayer rights in the Canadian context, in light of the experiences of vulnerable populations in Canada, from the perspective of the Taxpayers’ Ombudsman. Many aspects of the CRA’s digitalization can further marginalize vulnerable populations but there are also opportunities for digital services to help vulnerable persons in accessing the CRA’s services.
English
Download in English
French
Download in French
Money stories: Financial resilience among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians
This report builds on previous work on financial resilience in Australia and represents the beginning of an exploration of the financial resilience of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Overall, we found significant economic disparity between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. This is not surprising, given the histories of land dispossession, stolen wages and the late entry of Indigenous Australians into free participation in the economy (it is only 50 years since the referendum to include Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples as members of the Australian population). Specifically, we found: Severe financial stress is present for half the Indigenous population, compared with one in ten in the broader Australian population. Read the report to find out more about the financial barriers faced by Indigenous people in Australia, and the sharing economy in which money as a commodity can both help and hurt financial resilience.
Accessing the Canada Learning Bond: Meeting Identification and Income Eligibility Requirements
Introduced in 1998, the Canadian Education Savings Program (CESP) was designed as an incentive to encourage education savings for the post-secondary education of a child. The program is centred on Registered Education Savings Plans (RESPs), where savings accumulate tax-free until withdrawn, to pay for full- or part-time postsecondary studies such as a trade school, CEGEP, college, or university, or in an apprenticeship program. The CLB was introduced in 2004 specifically for children from low income families. CLB provides, without family contribution being required, eligible families with an initial RESP payment which may be followed by annual payments up until the child is aged 15 years old. The objective of this paper is to assess the extent to which not tax-filing and not having a SIN for a child could pose a challenge to accessing the CLB and the CESG. This study will address the knowledge gap by analyzing overall differences in SIN and tax-filing uptake by family income, levels of parental education, family type and Indigenous identity of the child. The findings will help understand access issues related to the CLB but also to other programs with similar administrative conditions. En francais: Accéder au Bon d’études canadien: l’atteinte des critères d’identification et d’éligibilité selon le revenu.
Providing tax filing and benefits assistance to Indigenous communities
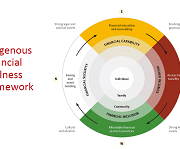
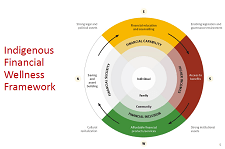
In this presentation, Simon Brascoupé, Vice President, Education and Training, AFOA Canada, explains the financial wellness framework and how tax filing presents opportunities for building financial wellness in Indigenous communities. This presentation is from the session 'Closing the tax-filing gap: Challenges and opportunities', at the tax research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
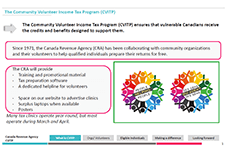
The Community Volunteer Income Tax Program (CVITP)
In this presentation, Nancy McKenna, Manager, CVITP, Canada Revenue Agency, explains how the Community Volunteer Income Tax Program (CVITP) works. This includes eligibility requirements, the size of the program in 2017/2018, and partnerships. This presentation is from the session 'Closing the tax-filing gap: Challenges and opportunities', at the tax research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
Stories from the field: Contextualizing the barriers Indigenous People face
In this presentation, Erin Jeffery, Outreach Officer with Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) shares what the CRA Outreach team has learned about tax filing barriers facing Indigeous People in Canada. These barriers include lack of documentation, lack of trust, access to services, and challenges around accessing Canada Child Benefit. This presentation is from the session 'Barriers to tax filing experienced by people with low incomes', at the research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
Tax time insights: Experiences of people living on low income in Canada
In this presentation, Nirupa Varatharasan, Research & Evaluation Officer with Prosper Canada, explains the research methods and insights gathered in the report 'Tax time insights: Experiences of people living on low income in Canada.' This includes demographic information, the type of tax filing resources accessed by this population, and insights on the types of challenges and opportunities that result from their tax filing processes. This presentation is from the session 'Barriers to tax filing experienced by people with low incomes', at the research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
Income tax filing and benefits take-up: Challenges and opportunities for Canadians living on low incomes
In this presentation, Uttam Bajwa, Global Health and Research Associate with the Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, reports on tax filing challenges and opportunities for Canadians living on low incomes. This includes the challenges of not knowing what to do, fear and mistrust, and challenges accessing supports. This presentation is based on the research conducted for the Prosper Canada report 'Tax time insights: Experiences of people living on low incomes in Canada'. This presentation is from the session 'Barriers to tax filing experienced by people with low incomes', at the research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
Indigenous Financial Literacy – AFOA 2014 Conference panel
This is the video recording of the AFOA 2014 Conference panel on Indigenous Financial Literacy. In this session, Liz Mulholland, Dr. Paulette Tremblay, Simon Brascoupe, and Darren Googoo discuss Indigneous financial wellness, financial literacy, and community education.
2018 Report Card on Child and Family Poverty in Canada: Bold Ambitions for Child and Family Poverty Eradication
The 2018 national report card “Bold Ambitions for Child Poverty Eradication in Canada,” provides a current snapshot of child and family poverty and demonstrates the need for a costed implementation plan to eradicate child poverty in this generation. In advance of the 30th year of the all-party commitment to eliminate child poverty by the year 2000 and the federal election in 2019, our spotlight is on the central role of universal childcare in the eradication of child poverty. The lack of affordable, high quality childcare robs children of valuable learning environments and keeps parents, mainly women, out of the workforce, education and training. Without childcare, parents cannot lift themselves out of poverty and improve their living standards.
Integrating Financial Capability Services into Tribal LIHEAP
This brief is a companion resource to Building Financial Capability: A Planning Guide for Integrated Services (also known as the Guide) and provides real-world examples of financial capability integration efforts. The brief shares lessons and approaches for how tribal-serving organizations can integrate financial capability services into LIHEAP and other emergency assistance services. The brief highlights the experiences of two tribal serving organizations in Alaska that integrated financial capability services: the Kenaitze Indian Tribe and the Aleutian Pribilof Island Association (APIA). It is organized into three sections: understanding households’ financial lives, deciding which financial capability services to integrate, and assessing organizational and community capacity to plan for how to deliver services.
Insights on planning free tax clinics in Indigenous communities
This infographic by Prosper Canada features advice to help Indigenous communities and organizations set up free income tax clinics. Advice was shared by clinic volunteers through a roundtable and interviews as part of the First Nations Financial Wellness project.
Complaints Related to Service from the CRA: Lessons Learned and Working Towards Better Service
Operating at arm’s length from the Canada Revenue Agency, the Office of the Taxpayers' Ombudsman (OTO) works to enhance the Canada Revenue Agency's (CRA) accountability in its service to, and treatment of, taxpayers through independent and impartial reviews of service-related complaints and systemic issues. OTO receives complaints and concerns from members of First Nations, Inuit and Métis communities. In this conference presentation, the Taxpayers’ Ombudsman provides examples of the types of issues her Office receives in order to provide community leaders with her insights in helping Indigenous people get better service from the CRA. In support of the AFOA Canada 2018 National Conference theme of Human Capital – Balancing Indigenous Culture and Creativity with Modern Workplaces, this presentation will provide participants with information on the types of issues and trends her office sees from members of the Indigenous communities and on better ways of serving these populations.
Financial Literacy of Indigenous Secondary Students in the Atlantic Provinces
Research conducted by agencies such as AFOA, Native Women’s Association of Canada, and various other Canadian entities, has identified the need for improved financial literacy education in Indigenous communities, particularly among youth and Elders. Such research reports are often equipped with a list of recommendations for improving and addressing the gaps in education around financial literacy. In the spirit of building upon this research into financial literacy and Indigenous peoples, the Purdy Crawford Chair in Aboriginal Business Studies (PCC) proposed a project focused on Atlantic Canada’s 14-18 year old Indigenous population and their levels of financial literacy. The results reveal that the majority of respondents would like to learn more about money. As well, they affirm that face-to-face learning from family members and in classroom settings remain the preferred way to learn about financial issues. Finally, based on the literature review, the environmental scan, survey data, and feedback from the community consultation process, a web application titled Seven Generations Financial Literacy was developed and is located at www.sevengenerationsfinancial.com.
Managing your money: Tools and tips to help you meet your goals (English)
MYM Worksheet 1: Your money goals
MYM Worksheet 1: Your money goals – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 2: Tracking your regular income
MYM Worksheet 2: Tracking your regular income – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 3: Tracking your spending
MYM Worksheet 3: Tracking your spending – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 4: Tracking your bills
MYM Worksheet 4: Tracking your bills – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 5: Monthly budgeting
MYM Worksheet 5: Monthly budgeting – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 6: Setting a savings goal
MYM Worksheet 6: Setting a savings goal – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 7: Preparing for tax filing
MYM Worksheet 7: Preparing for tax filing
About the ‘Managing your money’ resource
All ‘Managing your money’ worksheets
Facilitator resources (English)
Gérer votre argent: Outils et conseils pour vous aider à atteindre vos objectifs (French)
Feuille de travail #1: Vos objectifs en lien à l’argent (MYM)
Feuille de travail #2: Suivi de votre revenu régulier (MYM)
Feuille de travail #3: Suivi de vos dépenses (MYM)
Feuille de travail #4: Suivi de vos factures (MYM)
Feuille de travail #5: Budget mensuel (MYM)
Feuille de travail #6: Fixer un objectif d’épargne (MYM)
Feuille de travail #7: Préparation pour la déclaration de revenus (MYM)
Note pour les communautés et les organismes (MYM)
Feuilles de travail complètes
Ka-paminit kisôniyâm (Plains Cree)
Managing your money #7: Preparing for tax filing
Even if you make no money, you should file a tax return each year. You may be eligible for a refund (money back). Filing your taxes triggers access to government benefits that you can’t get any other way. This worksheet will help you gather the information you will need at tax time. You will need a file folder, an envelope, or a small box to put all of your paperwork in. This is worksheet #7 from the booklet 'Managing your money'.
Managing your money #6: Setting a savings goal
Setting a savings goal means that you have decided how much money you can put away, and what you are going to save for. This activity can help you write down some money goals and when you would like to achieve them. You can build savings by putting aside small amounts on a regular basis. This is worksheet #6 from the booklet 'Managing your money'.
Managing your money #5: Monthly budgeting
When you make a budget, you give yourself a clear picture of your financial situation. A budget compares your income to your expenses, all in one place. This is worksheet #5 from the booklet 'Managing your money'.
Managing your money #4: Tracking your bills
Knowing what bills you have and when they are due can help you plan your spending. This activity will help you to be aware of two things: how much you owe each month, and at what time of the month that money is due. This will help you to pay bills on time, and avoid late fees. This is worksheet #4 from the booklet 'Managing your money.'
Managing your Money #3: Tracking your spending
Keeping track of where your money goes during the month is another helpful step towards making a budget. Then you will be able to compare your spending with your income. This is worksheet #3 from the booklet 'Managing your money.'
Managing your money #2: Tracking your regular income
Income is the money that comes into your household. This worksheet will help you see the ‘big picture’ of your income and other resources. Then you can think about how to plan your expenses. This is worksheet #2 from the booklet 'Managing your money.'