Income in retirement: Expectations versus reality
In 2014, a group of non-retired Canadians aged 55 or older was asked about their financial expectations for retirement. New data from 2020 reveal how this same group of Canadians - now retired- is doing financially.
Benefits & credits: factsheets from the CRA
The CRA has compiled benefits and credits factsheets for: These are available in English and French.
Canada workers benefit
The Canada workers benefit (CWB) is a refundable tax credit to help individuals and families who are working and earning a low income. The CWB has two parts: a basic amount and a disability supplement. You can claim the CWB when you file your income tax return. Learn more including eligibility requirements, how to apply and how much you can expect to receive by clicking on the Get It button below.
Resources
Presentation slides and video time stamps
Read the presentation slides for this webinar.
Time stamps for the video recording:
-
- 5:20 – Start
- 6:12 – Land acknowledgement
- 7:24 – Introduction of speakers
- 9:42 – Today’s presentation
- 10:45 – Barriers to access to benefits
- 15:12 – Designing for benefit accessibility
- 21:53 – ESDC pilot project
- 32:46 –Demo of the disability benefit compass
- 44:36 – Importance of evaluation
- 50:58 – What’s next? What’s possible?
- 58:55 – Questions
Welfare in Canada, 2021
Using data provided by provincial and territorial government sources, Welfare in Canada, 2021 describes the components of welfare incomes, how they have changed from previous years, and how they compared to low-income thresholds. Access the report here. During the launch event, the report’s authors, Jennefer Laidley and Mohy Tabbara, broke down the latest welfare income data from all 13 provinces and territories and presented the key takeaways. Recorded on November 24, the Welfare in Canada, 2021 launch event started with a brief presentation of the report’s key findings, followed by a panel discussion. Presenters: Moderator:
Canada’s Disability Inclusion Action Plan
Canada’s Disability Inclusion Action Plan is a comprehensive, whole-of-government approach to disability inclusion. It embeds disability considerations across our programs while identifying targeted investments in key areas to drive change. It builds on existing programs and measures that have sought to improve the inclusion of persons with disabilities, and establishes new and meaningful actions.
Financial wellness tools
The National Disability Institute's Financial Wellness Toolkit is full of free resources for disability service providers, nonprofits, financial professionals and municipalities, including Financial Education Handouts and Quick Reference Guides. This infographic highlights income, banking and credit inequality based on disability, race and ethnicity.
Survey on savings for persons with disabilities
Residents in Canada who have a severe and prolonged mental or physical disability are eligible for the Disability Tax Credit (DTC). This opens the door to other programs, one of which is the RDSP. Less than one-third of eligible residents in Canada (up to age 59) have a Registered Disability Savings Plan (RDSP)—about 31.5% in 2020. To understand why more eligible residents in Canada do not have an RDSP, Employment and Social Development Canada asked Statistics Canada to conduct the Survey on Savings for Persons with Disabilities. Its goal was to collect data from residents in Canada who were eligible for an RDSP but did not open one. These respondents included both persons with disabilities and family members or others who care for persons with disabilities, since the holder of the plan may not be the same person as the beneficiary in all cases. These data show that, in general, eligible residents in Canada lack information about the RDSP, with many not being aware it exists and a substantial portion reporting not having enough information or money to open one.
Early Planning Toolkit
A toolkit for parents/caregivers with a child with a disability ages 2 to 10, containing:
Nurturing Supporting Relationships: The Foundation to a Secure Future
This handbook provides a guide for actions to take when nurturing supporting relationships for people living with a disability.
Intersectionality and Economic Justice
Widespread financial precarity for women of color with disabilities existed before the pandemic. Rooted in existing systemic inequities, COVID worsened the situation and created new access barriers. Race, gender, and disability impact financial stability in complex ways. Having a disability may increase living costs and limit economic opportunities. At the same time, women of color face significant disparities in education, income, employment, financial services, and wealth. Faced with institutional barriers that limit earning and wealth building, disabled women of color are more likely to be unbanked, use alternative financial services, have medical debt, lack access to affordable health care, and experience food insecurity. Given these challenges and the dire need to address them, this webinar explored:
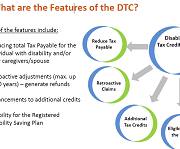
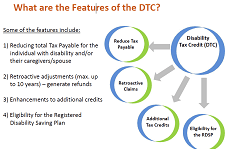
Disability Tax Credit Tool
The Canadian Disability Tax Credit (DTC) can help reduce the taxes you or someone who supports you owe. It also offers a lot of other great benefits. To apply for the DTC, your healthcare provider will need to fill out the Disability Tax Credit Certificate (form T2201). This tool is designed to give them the information they need to fill out that form
2019 Financial Coaching Network Bi-Monthly Peer Call Series
These calls, featuring guest practitioners, cover a variety of topics most pressing to the financial coaching field, provide useful tips and resources and serve as a peer-learning platform. Topics include:
2020 Second Annual Report of the Disability Advisory Committee
In November 2017, the Minister of National Revenue, the Honourable Diane Lebouthillier, announced the creation of the Disability Advisory Committee to provide advice to the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) on interpreting and administering tax measures for persons with disabilities in a fair, transparent and accessible manner. The committee’s full mandate is attached as Appendix A. Key disability tax measures are described in Appendix B. Our first annual report, Enabling access to disability tax measures, was published in May 2019. Since that time, we believe there has been important progress with respect to the administration of and communications about the disability tax credit (DTC). Our second annual report describes in detail the many improvements that the CRA has introduced over the past year in response to the recommendations in our 2019 report. These changes are summarized in “The Client Experience” on the following pages. Section 1 of this second annual report presents a review of the 42 recommendations made in our first annual report. Each recommendation summarizes the relevant context and associated follow-up actions. Section 2 covers the new areas of conversation during the second year of our mandate. Selected topics focus, for example, on DTC data, concerns of Indigenous peoples and eligibility for a registered disability savings plan. Section 3 includes the appendices, which provide details not covered in the text.
Creating Financial Security: Financial Planning in Support of a Relative with a Disability
This handbook covers the following topics:
Roadblocks and Resilience
This report, Roadblocks and Resilience Insights from the Access to Benefits for Persons with Disabilities project, provides insights on the barriers people with disabilities in British Columbia face in accessing key income benefits. These insights, and the accompanying service principles that participants identified, were obtained by reviewing existing research, directly engaging 16 B.C. residents with disabilities and interviewing 18 researchers and service providers across Canada. We will use these insights to inform development and testing of a pilot service to support people with disabilities to access disability benefits. The related journey map Common steps to get disability benefits also illustrates the complexities of this benefits application process. This journey map illustrates the process of applying for the Disability Tax Credit. The journey map Persons with Disability (PWD) status illustrates the process of preparing for and applying for and maintaining Persons with Disabilities Status and disability assistance in B.C.
Disability Inclusion Analysis of Lessons Learned and Best Practices of the Government of Canada’s Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic
This report provides the findings of research conducted to assist Employment and Social Development Canada in identifying good or best practices and lessons learned from the response to the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. Conducted in partnership with the DisAbled Women’s Network of Canada (DAWN), this research helps us better understand how diverse people with disabilities in Canada have been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic and the effects of government COVID-19 measures on diverse people with disabilities in Canada.
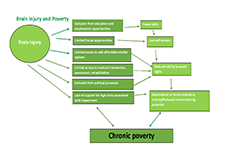
The Inequality of Poverty
This report explores the connections between low income, poverty and protected characteristics, how these can shape the experience of poverty, and whether this can result in a similar inequality in terms of when and how poverty premiums are incurred. COVID-19 has thrown light on the link between insecure work, low incomes and protected characteristics, with an opportunity for this link to be formally recognised. The pandemic, and the economic consequences look likely to throw many more people into poverty, and this poverty is falling hardest on those with protected characteristics.
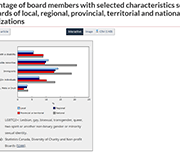
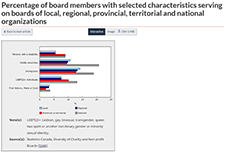
Diversity of charity and non-profit boards of directors: Overview of the Canadian non-profit sector
Charities and non-profit organizations play a vital role in supporting and enriching the lives of Canadians. A crowdsourcing survey of individuals involved in the governance of charities and non-profit organizations was conducted from December 4, 2020, to January 18, 2021. The objectives of the survey were to collect timely information on the activities of these organizations and the individuals they serve and to learn more about the diversity of those who serve on their boards of directors. A total of 8,835 individuals completed the survey, 6,170 of whom were board members.
The COVID-19 pandemic and Indigenous people with a disability or long-term condition
This paper uses crowdsourced data to provide an overview of the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the health, service access, and ability to meet basic needs of Indigenous participants with disabilities or long-term conditions. Changes in overall health and mental health are examined by disability type, age group and sex. The most commonly reported service disruptions since the start of the pandemic are also presented. The crowdsourcing data reflected health and other disparities between Indigenous and non-Indigenous participants with a disability or long-term condition. Indigenous participants were more likely to report worsened overall health and mental health, service disruption, and a greater impact on their ability to meet essential needs.
One in five Canadians with mental health-related disabilities lives in core housing need
Canadians with mental health-related disabilities were more than twice as likely as those without disabilities to live in households considered to be in core housing need in 2017. Canadians with mental health-related disabilities were also more likely than those without disabilities to live alone, to rent their homes and to live in subsidized housing, according to the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability (CSD). The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) has identified those living with pre-existing mental health-related disabilities as a particularly vulnerable population because of the impacts of isolation and disruptions to mental health-related services during the COVID-19 pandemic. A recent crowdsourcing survey by Statistics Canada found that almost three-quarters (73%) of participants with mental health-related disabilities stated that their mental health had worsened since the beginning of the pandemic. In addition, PHAC has indicated that those living with inadequate or unsuitable housing are also more vulnerable during the pandemic and are at higher risk of contracting COVID-19. This infographic presents pre-existing living situations and housing conditions among Canadians with mental health-related disabilities that may put them at greater risk of contracting COVID-19, as well as the emotional and psychosocial impacts of living through a pandemic.
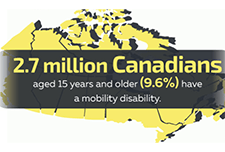
A profile of Canadians with a mobility disability and groups designated as visible minorities with a disability
Results from the 2017 Canadian Survey of Disability (CSD) have shown that over half of Canadians with a mobility disability need at least one workplace accommodation. Among population groups designated as visible minorities who have a disability, one-quarter considered themselves to be disadvantaged in employment because of their condition. In recognition of the International Day of Persons with Disabilities, Statistics Canada released three new data products based on findings from the 2017 CSD. One infographic focuses on disabilities related to mobility and another takes a look at visible minorities with disabilities. In addition, two data tables, on industry and occupation of those with and without disabilities, are now available.
COVID-19 Resources for people with disabilities
National Disability Institute (NDI)'s Financial Resilience Center offers resources and assistance to help those with disabilities and chronic health conditions navigate financially through the COVID-19 crisis. Resource topics include:
The Impact of COVID-19 on Women living with Disabilities in Canada
DisAbled Women’s Network (DAWNRAFH) Canada is a national, feminist, cross-disability organization whose mission is to end the poverty, isolation, discrimination and violence experienced People with disabilities, specifically women with disabilities face unique barriers related to Covid-19. This includes both the increased risk oftransmission and death from COVID-19, as well as the unique ways policies targeting COVID-19 impact this group. Prior to COVID-19 more than 50% of human rights complaints at the Federal, Provincial and Territorial levels in Canada for the last four years have been disability related, which speaks to systemic failures that have been exacerbated under COVID-19. In this brief, DAWN Canada highlights these unique considerations, as well as significant and existing policy gaps facing this group.
by Canadian women with disabilities and Deaf women.
The changes in health and well-being of Canadians with long-term conditions or disabilities since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic
This article examines how the self-reported health and mental health of people with long-term health conditions or disabilities has changed since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic explored by age, sex and type of reported difficulty. Additionally, the rates of health service disruptions are explored by type of service and region.
How are Canadians with long-term conditions and disabilities impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic?
This infographic focuses on self-reported health, unmet needs for services and therapies, and difficulties meeting certain financial obligations and essential needs since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic among participants aged 15 and older living with long-term conditions and disabilities. Results are based on the recent Statistics Canada crowdsourcing data collection completed by over 13,000 Canadians with long-term conditions or disabilities between June 23 and July 6, 2020.
Disability Alliance BC
Disability Alliance BC supports people in British Columbia with disabilities through direct services, community partnerships, advocacy, research and publications. Their website provides information on disability benefits including the Disability Tax Credit (DTC), CPP Disability, Registered Disability Savings Plans (RDSP) and more.
Plan Institute Learning Centre
The Plan Institute Learning Centre presents workshops, webinars, publications and other resources for individuals and/or families of a person with a disability, support-care workers, and organizations.
Serving Individuals With Disabilities – A Day in the Life of an American Job Center
The Disability and Employment eLearning Task Force in collaboration with the Employment and Training Administration (ETA) released three eLearning Training Modules to help support the professional development needs of the workforce development staff across the United States. The first module provide tools and resources to support front-line American Job Center staff effectively serve customers with disabilities, covering strategies for effective communication and interaction with individuals with disabilities.
Questions and answers to legal topics in Ontario
The Community of Legal Education Ontario (CLEO) website contains answers to common questions pertaining to a number of legal topics, including: COVID-19, debt and consumer rights, and employment and work.
Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics Hub
Launched by the Centre for Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics (CGDIS), the Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Hub focuses on disaggregated data by gender and other identities to support evidence-based policy development and decision making.
Impacts of COVID-19 on persons with disabilities
This article provides a general snapshot of the employment and income impacts of COVID-19 on survey participants aged 15 to 64 living with long-term conditions and disabilities.
From Emergency to Opportunity: Building a Resilient Alberta Nonprofit Sector After COVID-19
This report presents an analysis of the impact of COVID-19 on the nonprofit sector drawn from data collected in CCVO's Alberta Nonprofit Survey, data from surveys by the Alberta The analysis in this report shows that the effects on the nonprofit sector have been magnified through increased service demand, decreased revenue, and diminished organizational capacity coupled by delays in support and inadequate recognition for the leadership role that the sector is being called upon to play.
Nonprofit Network, Imagine Canada, and partner organizations across the country.
Legal Resources Catalogue: Free legal information
This resource provides a list of free legal information resources produced by Community Legal Education Ontario (CLEO).
Prosperity Now Scorecard
The Prosperity Now Scorecard is a comprehensive resource featuring data on family financial health and policy recommendations to help put all U.S. households on a path to prosperity. The Scorecard equips advocates, policymakers and practitioners with national, state, and local data to jump-start a conversation about solutions and policies that put households on stronger financial footing across five issue areas: Financial Assets & Income, Businesses & Jobs, Homeownership & Housing, Health Care and Education.
Taxpayer Rights in the Digital Age
This paper explores the intersection of digital innovation, digital services, access, and taxpayer rights in the Canadian context, in light of the experiences of vulnerable populations in Canada, from the perspective of the Taxpayers’ Ombudsman. Many aspects of the CRA’s digitalization can further marginalize vulnerable populations but there are also opportunities for digital services to help vulnerable persons in accessing the CRA’s services.
Infographic: An overview of Canadian financial programs for people with disabilities
One in five Canadians are currently living with a disability. This infographic provides an overview of financial programs for people with disabilities in Canada based on findings in Morris et al. (2018) "A demographic, employment and income profile of Canadians with disabilities aged 15 years and over, 2017".
Defining disability for social assistance in Ontario: Options for moving forward
Narrowing the definition of disability used by the Ontario Disability Support Program (ODSP) could have serious implications. Improving the program’s assessment process would yield better results for applicants, Ontario's social safety net, and the government. This report explores the role of ODSP, the risks of narrowing the definition of disability, models of disability assessment from other jurisdictions, and alternative ways that the government could reform the program. Most importantly, the paper recommends that the Ministry focus on improving ODSP’s initial application process. A simplified assessment system would save time and money for applicants, medical professionals, legal clinics, adjudicators, and the Social Benefits Tribunal. These savings should be reinvested back into social assistance.
English
Benefits 101
What are tax credits and benefits
Reasons to file a tax return
List of common benefits
Getting government payments by direct deposit
Common benefits and credits Benefits pathways (for practitioner reference only – some illustrations presented are Ontario benefits)
Pathways to accessing government benefits
Overview of tax benefits and other income supports (adults, children, seniors)
Overview of tax benefits and other income supports (people with disabilities or survivors)
Income support programs for immigrants and refugees
Glossary of terms – Benefits 101
Resources – Benefits 101
Key benefits you may be eligible for
Make sure you maximize the benefits you are entitled to if you are First Nations, Inuit, or Métis
Benefits of Filing a Tax Return: Infographic
Common benefits and credits
Resource links:
Benefits and credits for newcomers to Canada – Canada Revenue Agency
Benefit Finder – Government of Canada
Electronic Benefits and credits date reminders – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Income Assistance Handbook – Government of Northwest Territories
What to do when you get money from the government – Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC)
Emergency benefits
General emergency government benefits information & navigation
Financial Relief Navigator tool (Prosper Canada)
Changes to taxes and benefits: CRA and COVID-19 – Government of Canada
Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB)
Apply for Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB) with CRA – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Questions & Answers on CERB – Government of Canada
What is the CERB? – Prosper Canada
FAQ: Canada Emergency Response Benefit – Prosper Canada (updated June 10th)
CERB: What you need to know about cashing your cheque – FCAC
COVID-19 Benefits (summary, includes Ontario) – CLEO/Steps to Justice
COVID-19 Employment and Work – CLEO/Steps to Justice
GST/HST credit and Canada Child Benefit
COVID-19 – Increase to the GST/HST amount – Government of Canada
Canada Child Benefit Payment Increase – Government of Canada
Benefits payments for eligible Canadians to extend to Fall 2020 – Government of Canada
Support for students
Support for students and recent graduates – Government of Canada
Canada Emergency Student Benefit (CESB) – Government of Canada
Benefits and credits for families with children
Benefits and credits for families with children
Resource links:
Child and family benefits – Government of Canada
Child and family benefits calculator – Government of Canada
Benefits and credits for people with disabilities
Benefits and credits for people with disabilities
RDSP, grants and bonds
Resource links:
Canada Pension Plan disability benefit toolkit – Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC)
Disability benefits – Government of Canada
Disability tax credit (DTC) – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Free RDSP Calculator for Canadians – Plan Institute
Future Planning Tool – Plan Institute
Creating Financial Security: Financial Planning in Support of a Relative with a Disability (handbook) – Partners for Planning
Nurturing Supportive Relationships: The Foundation to a Secure Future (handbook) – Partners for Planning
RDSP – Plan Institute
Disability Tax Credit Tool – Disability Alliance BC
ODSP Appeal Handbook – CLEO
Disability Inclusion Analysis of Government of Canada’s Response to COVID-19 (report and fact sheets) – Live Work Well Research Centre
Demystifying the Disability Tax Credit – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Benefits and credits for seniors
Benefits and credits for seniors
Resource links:
Canadian Retirement Income Calculator – Government of Canada
Comparing Retirement Savings Options – Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC)
Federal Provincial Territorial Ministers Responsible for Seniors Forum – Employment and Social Services Canada (ESDC)
Retiring on a low income – Open Policy Ontario
RRSP vs GIS Calculator – Daniela Baron
Sources of income for seniors handout – West Neighbourhood House
What every older Canadian should know about: Income and benefits from government programs – Employment and Social Services Canada (ESDC)
French
Comprendre les prestations
Que sont les crédits d’impôt et les prestations?
Pourquoi produire une déclaration de revenus?
Processus d’accès aux prestations (simple, complexe ou laborieux)
Aperçu des prestations et crédits d’impôt et des autres mesures d’aide au revenu
Aperçu des prestations et crédits d’impôt et des autres mesures d’aide au revenu : personnes handicapées ou survivants
Programmes d’aide au revenu pour immigrants et réfugiés – Admissibilité et processus de demande
Glossaire – Prestations et credits
Ressources : Prestations et credits
Principales mesures d’aide auxquelles vous pouvez être admissibles
Assurez-vous de maximiser les prestations auxquelles vous avez droit si vous êtes Autochtone,
Infographie sur les avantages de produire une déclaration de revenus
Prestations et crédits courants
Prestations et crédits pour familles avec enfants
Prestations et crédits pour personnes handicapées
Prestations et crédits pour les personnes âgées
Informations d’identification pour accéder aux prestations
Études de cas
The Dynamics of Disability: Progressive, Recurrent or Fluctuating Limitations
Different from common perception, many disabilities do not follow a stable pattern. Persons with disabilities may experience periods of good health in between periods of their limitations and/or experience changes in the severity of their limitations over time. These types of disabilities may be characterized as dynamic because the very nature of the disability is one of change with different possible trajectories over time. As a consequence, the collective experiences of those with disability dynamics are likely to be different than those with so-called “continuous” disabilities. In this paper, four groups of persons with different disability dynamics (or lack of dynamics) are profiled based on data from the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability. Each group has their own unique demographic, employment, and workplace accommodation profile based on the length of time between periods of their limitations, as well as changes in their limitations over time.
Registered Disability Savings Plans (RDSPs) and Financial Empowerment
This policy brief discusses issues surrounding access to Registered Disability Savings Plans (RDSPs) in the province of Alberta and recommended solutions for increasing RDSP uptake. With the Government of Alberta's commitment to improving financial independence for people in the province, suggestions are provided on how to link the government RDSP strategy with financial empowerment collaboratives and champions existing in the province to maximize effectiveness and efficiency.
RDSP calculator
Enhance the quality of life for a family member with a disability. By answering a few simple questions, the RDSP Calculator can help you project the estimated future value of an RDSP, and the approximate value of future withdrawal payments. Run various scenarios to see how it would affect the value of your RDSP. The RDSP Calculator is a tool to help you assess the potential of opening and contributing to an RDSP. The estimates provided by the Calculator are for information purposes only. The profile of your RDSP may differ from the RDSP Calculator projection.
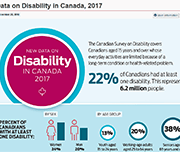
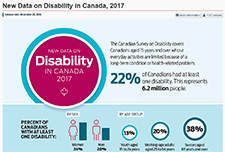
Infographic: New Data on Disability in Canada, 2017
This infographic released from Statistics Canada compiles some of the data collected from the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability. 22% of Canadians had at least one disability, representing 6.2 million people.
Low income among persons with a disability in Canada
Persons with a disability face a higher risk of low income compared to the overall population. This report uses data from the 2014 Longitudinal and International Study of Adults (LISA) to study the relationship between low income and characteristics of people aged 25 to 64 with a disability, including disability type, severity class, age of onset of disability, family composition, and other risk factors associated with low income. It also examines the composition of the low-income population in relation to disability, and provides information on the relationship between employment and low income for this population.
Income tax filing and benefits take-up: Challenges and opportunities for Canadians living on low incomes
In this presentation, Uttam Bajwa, Global Health and Research Associate with the Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, reports on tax filing challenges and opportunities for Canadians living on low incomes. This includes the challenges of not knowing what to do, fear and mistrust, and challenges accessing supports. This presentation is based on the research conducted for the Prosper Canada report 'Tax time insights: Experiences of people living on low incomes in Canada'. This presentation is from the session 'Barriers to tax filing experienced by people with low incomes', at the research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
Your Money, Your Goals: Focus on People with Disabilities
This is a companion guide to the 'Your Money, Your Goals' curriculum by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) in the United States. This guide- Your Money, Your Goals: Focus on People with Disabilities—contains information, tips, and tools based on the insights from people with disabilities and from organizations that serve the disability community. It is based on the core philosophy that everyone has the right to control their money and make their own financial decisions. Its specialized information and tools equip staff and volunteers to adapt training on and use of the toolkit and other resources to meet the needs of people with disabilities. It also includes information and tools to enable staff and volunteers to choose accessible locations, develop appropriate and considerate training activities, and plan to provide accommodations for diverse learning styles and other needs.
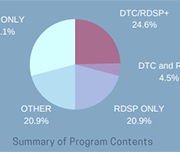
Breaking down barriers: A critical analysis of the Disability Tax Credit and the Registered Disability Savings Plan
The Disability Tax Credit helps Canadians by reducing the amount of income tax they are required to pay. The Registered Disability Savings Plan helps people with a disability or their caregiver save for the future by putting money into a fund that grows tax free until the beneficiary makes a withdrawal. This report, released by the Senate Committee on Social Affairs, Science and Technology, makes 16 recommendations aimed at improving both programs. They are divided into short-term objective to make the process for the two programs simpler and clearer, and a long-term philosophical shift in the way Canada deals with people who are in financial distress but cannot advocate for themselves. Recommendations include removing barriers that prevent people from taking advantage of the Disability Tax Credit and making enrolment in the Registered Disability Savings Plan automatic for eligible people under 60 years of age.
Policy Brief – Why is Uptake of the Disability Tax Credit Low in Canada?
Disability supports should be designed to provide benefit and not burdens to eligible recipients. Unfortunately, this is not a reality when it comes to one of the main benefits open to Canadians with disability: the federal Disability Tax Credit (DTC). Designed to recognize some of the higher costs faced by people with severe disabilities and their caregivers, the DTC appears to be more of a burden for many, with estimated utilisation unacceptably low at around 40 per cent of working-aged adults with qualifying disabilities. Low uptake is a concern not only because people are missing out on the credit itself but also because eligibility to the DTC – which is not automatic – is a gateway to other important and more valuable benefits such as the Child Disability Benefit and Registered Disability Savings Plans (RDSP).