Benefits & credits: factsheets from the CRA
The CRA has compiled benefits and credits factsheets for: These are available in English and French.
Cyber security awareness
The Canadian Bankers Association has created a new Cyber Security Awareness Quiz site to test your knowledge and ability to spot a “phishy” email, message or text.
Cyber security & fraud prevention learning guide
Banks take fraud very seriously and have highly sophisticated security systems and teams of experts to protect you from financial fraud. As a banking customer, there are also simple steps you can take to recognize cyber crime and protect your personal information and your money. Educating yourself, your family and your employees about cyber safety can seem overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be that complicated and the CBA has developed a learning path to help.
Protecting aging investors through behavioural insights
This report identifies behaviourally informed techniques dealers and advisers can use to encourage their older clients to provide the necessary information for enhanced investor protection measures.
Let’s talk money- seniors edition
With a little preparation, talking about financial matters can help build trust, deepen connections, relieve stress and lead to greater peace of mind. Yet for many people, these conversations can be difficult. In some families, money is just not something you talk about. The same applies to wills, inheritances, senior living, end-of-life care and many more topics that matter most to seniors. Let's Talk About Money: Seniors' Edition -- wants to help you change that. There are tips to help parents talk with adult children and tips for adult children to have meaningful money conversations their parents. The most important thing is to have these conversations early, before there’s a crisis. So let's start talking.Open, honest conversations about money are one of the keys to building a healthy relationship with your family, across the generations.
Your trusted contact person and why they matter
The Trusted Contact Person initiative has been adopted across Canada. It is part of new regulatory measures to support advisors in their efforts to help investors, particularly older investors and vulnerable, protect themselves and their financial interests. Canadian seniors are increasingly called upon to make complex financial decisions, with higher stakes, later in life than ever before. For many, health, mobility, or cognitive changes that can occur with age, may affect their ability to make these decisions. This can make seniors more susceptible to financial exploitation and fraud. In fact, about half of the victims of investment fraud are over age 55. Watch this new video on understanding the importance of appointing a trusted contact person.
Fraud Prevention Toolkits
In 2021, losses reported to the Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre reached an all time high of 379 million with Canadian losses accounting for 275 million of this. Fraud Prevention Month is a campaign held each March to inform and educate the public on protecting yourself from being a victim of fraud. This year's theme is impersonation, and focuses on scams where fraudsters will claim to be government official, critical infrastructure companies, and even law enforcement officials. This collection of fraud prevention toolkits is available in English and French. In English: En Français:
Living your retirement
These resources from the Ontario Securities Commission are oriented towards planning for retirement. Resources include tips on insurance planning, government benefits, RRSP calculator, and more.
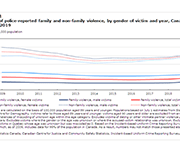
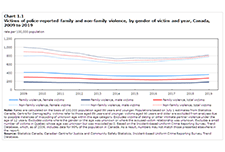
Family violence in Canada: A statistical profile, 2019
Family violence in Canada: A statistical profile is an annual report produced by the Canadian Centre for Justice and Community Safety Statistics at Statistics Canada as part of the Federal Family Violence Initiative. Since 1998, this report has provided data on the nature and extent of family violence in Canada, as well as an analysis of trends over time. The information presented is used extensively to monitor changes that inform policy makers and the public.
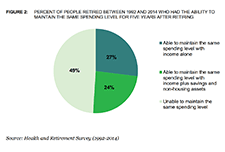
Retirement Security and Financial Decision-making: Research Brief
A growing number of retirees are not experiencing the expected gradual reduction in spending after they retire. This report summarizes the findings of a Bureau study into whether people who retired between 1992 and 2014 had the income, savings, and/or non-housing assets to maintain the same level of spending for at least five consecutive years after retiring. The study found that about half of people who retired between 1992 and 2014 had income, savings, and/or non-housing assets to maintain the same spending level for five consecutive years after retiring. In addition, the Bureau found that the ability to maintain the same spending level in the first five years in retirement was associated with large spending cuts in later years. The study helps identify ways to protect retirees from overspending their savings in early retirement.
Financial Life Stages of Older Canadians
This study, commissioned by the Ontario Securities Commission (OSC) and conducted by the Brondesbury Group, provides some insights on the knowledge that older Canadians have about the financial realities of retirement and how they would apply that knowledge earlier in life if they are able to do so. The top financial concerns and main financial risks of older Canadians are identified for each life stage and how they are being managed are discussed.
Low Income Measure: Comparison of Two Data Sources, T1 Family File and 2016 Census of Population
This study looks at the differences in after-tax low income measure (LIM) statistics from two data sources which both use administrative tax data as their principal inputs: the 2016 Census of Population and the T1 Family file (T1FF). It presents a summary of the two data sources and compares after-tax LIM statistics by focussing on unit of analysis, LIM thresholds and the percentage of population below the LIM. The study also explores what factors users may want to consider when choosing one data source over the other.
Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics Hub
Launched by the Centre for Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Statistics (CGDIS), the Gender, Diversity and Inclusion Hub focuses on disaggregated data by gender and other identities to support evidence-based policy development and decision making.
From Emergency to Opportunity: Building a Resilient Alberta Nonprofit Sector After COVID-19
This report presents an analysis of the impact of COVID-19 on the nonprofit sector drawn from data collected in CCVO's Alberta Nonprofit Survey, data from surveys by the Alberta The analysis in this report shows that the effects on the nonprofit sector have been magnified through increased service demand, decreased revenue, and diminished organizational capacity coupled by delays in support and inadequate recognition for the leadership role that the sector is being called upon to play.
Nonprofit Network, Imagine Canada, and partner organizations across the country.
Taxpayer Rights in the Digital Age
This paper explores the intersection of digital innovation, digital services, access, and taxpayer rights in the Canadian context, in light of the experiences of vulnerable populations in Canada, from the perspective of the Taxpayers’ Ombudsman. Many aspects of the CRA’s digitalization can further marginalize vulnerable populations but there are also opportunities for digital services to help vulnerable persons in accessing the CRA’s services.
Low Income Retirement Planning
This booklet contains information on retirement planning on a low income. Topics include four things to think about for low income retirement planning, a background paper on maximizing the Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS), and determining Old Age Security (OAS) and GIS eligibility for people who come to Canada as adults.
Elder Fraud Prevention and Response Networks Development Guide
This guide provides step-by-step materials to help communities form networks to increase their capacity to prevent and respond to elder financial exploitation. The planning tools, templates and exercises offered in this guide help stakeholders plan a stakeholder retreat and training event, host a retreat, reconvene and establish their network, and expand network capabilities in order to create a new network or to refresh or expand an existing one.
Virtual tax filing: Piloting a new way to file taxes for homebound seniors
WoodGreen Community Services, a large multi-service frontline social service agency in Toronto, provides free tax preparation services year-round to people living on low incomes. WoodGreen was interested in designing a novel solution to address the tax filing needs of homebound seniors who are unable to access WoodGreen’s free in-person tax-preparation services due to physical or mental health challenges. Specifically, WoodGreen wanted to know… How might we provide high-quality professional tax preparation services to all clients whether or not they are onsite? Prosper Canada and a leading commercial tax preparation software company partnered with WoodGreen Community Services in order to answer this design question.
English
Benefits 101
What are tax credits and benefits
Reasons to file a tax return
List of common benefits
Getting government payments by direct deposit
Common benefits and credits Benefits pathways (for practitioner reference only – some illustrations presented are Ontario benefits)
Pathways to accessing government benefits
Overview of tax benefits and other income supports (adults, children, seniors)
Overview of tax benefits and other income supports (people with disabilities or survivors)
Income support programs for immigrants and refugees
Glossary of terms – Benefits 101
Resources – Benefits 101
Key benefits you may be eligible for
Make sure you maximize the benefits you are entitled to if you are First Nations, Inuit, or Métis
Benefits of Filing a Tax Return: Infographic
Common benefits and credits
Resource links:
Benefits and credits for newcomers to Canada – Canada Revenue Agency
Benefit Finder – Government of Canada
Electronic Benefits and credits date reminders – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Income Assistance Handbook – Government of Northwest Territories
What to do when you get money from the government – Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC)
Emergency benefits
General emergency government benefits information & navigation
Financial Relief Navigator tool (Prosper Canada)
Changes to taxes and benefits: CRA and COVID-19 – Government of Canada
Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB)
Apply for Canada Emergency Response Benefit (CERB) with CRA – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Questions & Answers on CERB – Government of Canada
What is the CERB? – Prosper Canada
FAQ: Canada Emergency Response Benefit – Prosper Canada (updated June 10th)
CERB: What you need to know about cashing your cheque – FCAC
COVID-19 Benefits (summary, includes Ontario) – CLEO/Steps to Justice
COVID-19 Employment and Work – CLEO/Steps to Justice
GST/HST credit and Canada Child Benefit
COVID-19 – Increase to the GST/HST amount – Government of Canada
Canada Child Benefit Payment Increase – Government of Canada
Benefits payments for eligible Canadians to extend to Fall 2020 – Government of Canada
Support for students
Support for students and recent graduates – Government of Canada
Canada Emergency Student Benefit (CESB) – Government of Canada
Benefits and credits for families with children
Benefits and credits for families with children
Resource links:
Child and family benefits – Government of Canada
Child and family benefits calculator – Government of Canada
Benefits and credits for people with disabilities
Benefits and credits for people with disabilities
RDSP, grants and bonds
Resource links:
Canada Pension Plan disability benefit toolkit – Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC)
Disability benefits – Government of Canada
Disability tax credit (DTC) – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Free RDSP Calculator for Canadians – Plan Institute
Future Planning Tool – Plan Institute
Creating Financial Security: Financial Planning in Support of a Relative with a Disability (handbook) – Partners for Planning
Nurturing Supportive Relationships: The Foundation to a Secure Future (handbook) – Partners for Planning
RDSP – Plan Institute
Disability Tax Credit Tool – Disability Alliance BC
ODSP Appeal Handbook – CLEO
Disability Inclusion Analysis of Government of Canada’s Response to COVID-19 (report and fact sheets) – Live Work Well Research Centre
Demystifying the Disability Tax Credit – Canada Revenue Agency (CRA)
Benefits and credits for seniors
Benefits and credits for seniors
Resource links:
Canadian Retirement Income Calculator – Government of Canada
Comparing Retirement Savings Options – Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC)
Federal Provincial Territorial Ministers Responsible for Seniors Forum – Employment and Social Services Canada (ESDC)
Retiring on a low income – Open Policy Ontario
RRSP vs GIS Calculator – Daniela Baron
Sources of income for seniors handout – West Neighbourhood House
What every older Canadian should know about: Income and benefits from government programs – Employment and Social Services Canada (ESDC)
French
Comprendre les prestations
Que sont les crédits d’impôt et les prestations?
Pourquoi produire une déclaration de revenus?
Processus d’accès aux prestations (simple, complexe ou laborieux)
Aperçu des prestations et crédits d’impôt et des autres mesures d’aide au revenu
Aperçu des prestations et crédits d’impôt et des autres mesures d’aide au revenu : personnes handicapées ou survivants
Programmes d’aide au revenu pour immigrants et réfugiés – Admissibilité et processus de demande
Glossaire – Prestations et credits
Ressources : Prestations et credits
Principales mesures d’aide auxquelles vous pouvez être admissibles
Assurez-vous de maximiser les prestations auxquelles vous avez droit si vous êtes Autochtone,
Infographie sur les avantages de produire une déclaration de revenus
Prestations et crédits courants
Prestations et crédits pour familles avec enfants
Prestations et crédits pour personnes handicapées
Prestations et crédits pour les personnes âgées
Informations d’identification pour accéder aux prestations
Études de cas
COVID-19 and support for seniors: Do seniors have people they can depend on during difficult times?
In an effort to avoid the spread of COVID-19, Canadians are engaging in physical distancing to minimize their social contact with others. However, social support systems continue to play an important role during this time. In particular, seniors living in private households may depend on family, friends or neighbours to deliver groceries, medication and other essential items to their homes. This study examines the level of social support reported by seniors living in private households.
Seniors: tips to help you this tax season
As a senior, you may be eligible for benefits and credits when you file your taxes. The Canada Revenue Agency has tips to help you get all of them! This page includes tips for seniors at tax time and links to relevant Government of Canada resources.
Ageing and Financial Inclusion: 8 key steps to design a better future
The G20 Fukuoka Policy Priorities for Ageing and Financial Inclusion is jointly prepared by the GPFI and the OECD. The document identifies eight priorities to help policy makers, financial service providers, consumers and other actors in the real economy to identify and address the challenges associated with ageing populations and the global increase in longevity. They reflect policies and practices to improve the outcomes of both current generations of older people and future generations.
Results from the 2016 Census: Examining the effect of public pension benefits on the low income of senior immigrants
This is a study released by Insights on Canadian Society based on 2016 Census data. Census information on immigration and income is used to better understand the factors associated with low income among senior immigrants. This study examines the factors associated with the low-income rate of senior immigrants, with a focus on access to Old Age Security (OAS) and Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) benefits.
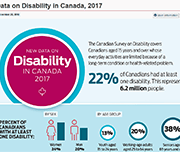
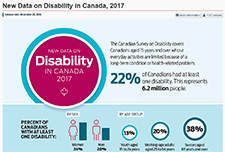
Infographic: New Data on Disability in Canada, 2017
This infographic released from Statistics Canada compiles some of the data collected from the 2017 Canadian Survey on Disability. 22% of Canadians had at least one disability, representing 6.2 million people.
Retirement 20/20: The 2019 Fidelity Retirement Survey
The Fidelity Retirement Survey is focused on how Canadians near, and already in, retirement approach the next stage of their lives. This is the 14th year of the survey. The results indicate Canadians are retiring earlier than expected. They also show 46% of pre-retirees expect to have some long-term debt when they retire, and that 70% believe they will be working in retirement, among other results.
Evaluation of the Guaranteed Income Supplement
The Old Age Security program is the largest statutory program of the Government of Canada, and consists of the Old Age Security pension, the Guaranteed Income Supplement, and the Allowance. The Guaranteed Income Supplement is provided to low-income seniors aged 65 years and over who receive the Old Age Security pension and are below a low-income cut-off level. This evaluation examines take-up of the Guaranteed Income Supplement by various socioeconomic groups, the characteristics of those who are eligible for the Supplement but do not receive it, and barriers faced by vulnerable groups.
Debt and assets among senior Canadian families
Using data from the Survey of Financial Security (SFS), this article looks at changes in debt, assets and net worth among senior Canadian families over the period from 1999 to 2016. It also examines changes in the debt-to income ratio and the debt to-asset ratio of senior families with debt. This study finds that the proportion of senior families with debt increased from 27% to 42% between 1999 and 2016.
Are Low-Income Savers Still in the Lurch? TFSAs at 10 Years
The introduction of Tax-Free Savings Accounts (TFSAs) in 2009 transformed how Canadians save. One of the main reasons for creating TFSAs was to provide a taxassisted savings instrument for low-income Canadians to enable them to improve their retirement income. Now, 10 years later, many low-income savers are still not using TFSAs in ways that would allow them to benefit fully from the government transfer programs intended for them in retirement, such as the Guaranteed Income Supplement. Consequently, intended benefits from TFSAs are going untapped. Improving public education and financial literacy may be part of the solution to this problem, but built-in policy nudges and tax adjustments will be more effective.
Debt and assets among senior Canadian families, 1999 to 2016
These results are from the new study "Debt and assets among senior Canadian families." released in April 2018. The study examines changes in debt, assets and net worth among Canadian families whose major income earner was 65 years of age or older. In recent years, household debt has increased. The level of debt and value of assets are especially important for the financial security of seniors. Because income typically declines during the retirement years, seniors often need accumulated assets to finance their consumption, especially if they do not benefit from a private pension plan. Debt can also be particularly problematic for seniors as repayment can be more difficult on a reduced income.
The Economic Well-Being of Women in Canada
Economic well-being has both a present component and a future component. In the present, economic well-being is characterized by the ability of individuals and small groups, such as families or households, to consistently meet their basic needs, including food, clothing, housing, utilities, health care, transportation, education, and paid taxes. It is also characterized by the ability to make economic choices and feel a sense of security, satisfaction, and personal fulfillment with respect to finances and employment pursuits. Using Statistics Canada data from a variety of sources, including the Survey of Labour and Income Dynamics, the Canadian Income Survey, the Survey of Financial Security, and the 2016 Census of Population, this chapter of Women in Canada examines women’s economic well-being in comparison with men’s and, where relevant, explores how it has evolved over the past 40 years. In addition to gender, age and family type (i.e., couple families with or without children; lone mothers and fathers; and single women and men without children) are important determinants of economic well-being. Hence, many of the analyses distinguish between women and men in different age groups and/or types of families.
Get Your Benefits! Diagnose and Treat Poverty
In this presentation, Noralou P. Roos, Co-Director, GetYourBenefits! and Professor, Manitoba Centre for Health Policy, explains how access to tax filing and benefits is an important poverty intervention. This presentation is from the panel discussion 'National and regional strategies to boost tax filing', at the tax research symposium hosted by Prosper Canada and Intuit, February 7, 2019, in Ottawa.
Strengthening retirement security for low- and moderate-income workers
In this video presentation Johnathan Weisstub from Common Wealth discusses recent improvements in senior Canadians' poverty levels due to benefits such as OAS and GIS, and the challenges that still remain in ensuring retirement security for modest-earning and low-income Canadians. This presentation was given at the Prosper Canada Policy Research Symposium on March 9, 2018. Read the slide deck that accompanies this presentation. View the full video playlist of all presentations from this symposium.
Unfinished Business Pension Reform in Canada
Since taking office in the fall of 2015, the Liberal government has made important changes to the publicly administered components of Canada’s retirement income system (RIS). It has restored the age of eligibility for benefits under Old Age Security (OAS) and the Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) to 65, it has increased the top-up on GIS benefits for single elderly persons, and it has agreed with the provinces to enhance Canada Pension Plan (CPP) benefits, starting in 2019.
Each of these changes, on its own, contributes to one of the two main objectives of the RIS: to minimize the people’s risk of poverty in old age and to enhance their ability to retain their standard of living as they move from employment to retirement. However, as Bob Baldwin and Richard Shillington show in this study, when examined together, the changes are problematic and incomplete.