Rising prices and the impact on the most financially vulnerable: A profile of those in the bottom family income quintile
This study uses the 2022 Portrait of Canadian Society Survey to examine the impact of rising inflation on the lowest income Canadians. Using multiple pre-pandemic data sources, the study takes a closer look at people living in the bottom family income quintile, examining their family income, debt and assets levels, as well as some indicators of economic hardship.
Research to help FSRA improve the lives of vulnerable consumers
Financial Services Regulatory Authority of Ontario commissioned a research study that focused on consumer attitudes, how consumers are engaging with financial services, and consumer characteristics such as vulnerability. Insights from the research are allowing FSRA to better understand the realities of consumers’ changing financial lives and helping to identify key opportunities to respond to the needs of vulnerable consumers. 2022 Consumer Research Study highlights. 2022 Consumer Research Study full report
Resources
Presentation slides, handouts, and video time-stamps
Read the presentation slides for this webinar.
Download the Overview of Financial vulnerability of Low-Income Canadians: A Rising Tide
Time-stamps for the video recording:
00:00 – Start
6:05 – Agenda and Introductions
8:24 – Overview of Financial vulnerability, of low-income Canadians: A rising tide (Speaker: Eloise Duncan)
25:40 – Panel discussion: how increasing financial vulnerability is playing out in community and how policy makers should respond.
45:35 – Q&A
Resources
Presentation slides, handouts, and video time stamps
Read the presentation slides for this webinar.
Download resources provided by webinar speakers:
Time-stamps for the video recording:
3:24 – Agenda and Introductions
6:36 – Audience poll questions
9:33 – FAIR Canada presentation (speaker: Tasmin Waley)
24:07 – Ontario Securities Commission presentation (speaker: Christine Allum)
39:10 – Investor Protection Clinic at Osgoode Hall Law School (speaker: Brigitte Catellier)
51:34 – Q&A
Resources
Presentation slides, handouts, and video time-stamps
Read the presentation slides for this webinar.
Download the handout for this webinar: Flyer for ‘Redefining Financial Vulnerability in Canada: The Embedded Experience of Households’.
Time-stamps for the video recording:
3:31 – Agenda and Introductions
7:15 – Redefining financial vulnerability in Canada (speaker: Jerry Buckland and Brenda Spotton Visano)
24:33 – Audience poll question 1
27:07– Audience poll questions 2 & 3
33:57 – Audience poll question 4
38:00 – Financial Empowerment (Speaker: Margaret Yu)
52:15– Q&A
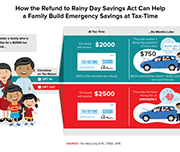
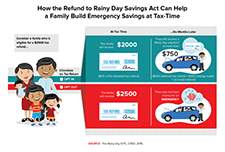
The impact of the enhanced child tax credit on lower-income households
The American Rescue Plan, one of the most significant policy responses to alleviate child poverty in decades, made fundamental changes in enhancing the Child Tax Credit (CTC). In response to the pandemic, the law expanded the CTC for tax year 2021 to ensure a minimum level of economic support to all families raising children. Commonwealth, SaverLife, and Neighborhood Trust Financial Partners followed up with CTC-eligible families after most filed their 2021 tax returns. We conducted interviews and surveys to assess the impact of the enhanced credit on families’ financial health. Although we focused on the second half of the CTC payment, which was delivered as a lump sum payment as part of the tax refund, we also asked recipients about their tax filing experience and what a continuation of an expanded credit would mean for their families.
Emergency savings features that work for employees earning low to moderate incomes
Workers earning low to moderate incomes (LMI) continue to face challenges in financial security. The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated the financial situation of many workers earning LMI. Along with the current macroeconomic environment, it has become even more challenging to build liquid savings for unexpected expenses. In this brief, we will share insights from our latest research with DCIIA Research Retirement Center on how employers and service providers can build and offer emergency savings solutions that are inclusively designed for workers earning LMI.
Turning aces into assets
Ontario has just become the first province to open its legal gambling market to private internet gaming providers. As of April 4, 2022, Ontarians can play casino-style games online and place bets on sports, including single games, through sites regulated by iGaming Ontario. According to the provincial regulator, the launch of iGaming marks the triumph “of a legal internet gaming market” over “its previous grey market standing.” But as with all forms of gambling, this development has a dark side. It was only a matter of time before Ontario expanded its gambling market—not because of popular demand, but because the provincial government is addicted to gambling money and is eager to seize any opportunity to get more of it, regardless of the costs to the people it is supposed to protect. This report provides the background of gambling in Ontario, outlines the new risks with iGaming and offers four policy options.
101 solutions for inclusive wealth building
Having wealth, or a family’s assets minus their debts, is important not just for the rich— everyone needs wealth to thrive. Yet building the amount of wealth needed to thrive is a major challenge. Nearly 13 million U.S. households have negative net worth. Millions more are low wealth; they do not have the assets or liquidity needed to maintain financial stability and invest in themselves in the present, nor are they on track to accumulate the amount of wealth they will need to have financial security in retirement. This report examines what it will take to create truly shared prosperity in the United States. It is focused on solutions that would grow the wealth of households in the bottom half of the wealth distribution, and it explores reparative approaches to building the wealth of Black, Indigenous, and other people of color (BIPOC).
Together, these groups represent at least half of all U.S. households.
Protecting aging investors through behavioural insights
This report identifies behaviourally informed techniques dealers and advisers can use to encourage their older clients to provide the necessary information for enhanced investor protection measures.
Hunger, Poverty, and Health Disparities During COVID-19 and the Federal Nutrition Programs’ Role in an Equitable Recovery
The health and economic crises brought on by the coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has made the federal nutrition programs more important than ever. An unacceptably high number of people in America do not have enough to eat, and it is likely that the economic recovery for families who struggle to put food on the table will take years.
Recovery will be particularly challenging for those groups that have suffered disproportionate harm from COVID-19. Inequities, also referred to as disparities, “adversely affect groups of people who have systematically experienced greater obstacles […] based on their racial or ethnic group; religion; socioeconomic status; gender; age; mental health; cognitive, sensory, or physical disability; sexual orientation or gender identity; geographic location; or other characteristics historically linked to discrimination or exclusion.”
Household Food Insecurity in Canada, 2017-2018
Food insecurity – inadequate or uncertain access to food because of financial constraints – is a serious public health problem in Canada, and all indications are that the problem is getting worse. Drawing on data for 103,500 households from Statistics Canada’s Canadian Community Health Survey conducted in 2017 and 2018, we found that 12.7% of households experienced some level of food insecurity in the previous 12 months. There were 4.4 million people, including more than 1.2 million children under the age of 18, living in food-insecure households in 2017-18. This is higher than any prior national estimate.
Recognizing and responding to economic abuse
With speakers from CCFWE, Johannah Brockie - Program Manager for Advocacy and System Change and Jessica Tran - Program Manager for Education and Awareness, this webinar will guide you through the definition of economic abuse, how to identify an economic abuser, impacts of economic abuse, Covid-19 impacts, tactics, what you should do if you are a victim of economic abuse, and key safety tips. Economic Abuse occurs when a domestic partner interferes with a partner’s access to finances, employment or social benefits, such as fraudulently racking up credit card debt in their partner’s name or preventing their partner from going to work has a devastating effect on victims and survivors of domestic partner violence, yet it’s rarely talked about in Canada. It’s experienced by women from all backgrounds, regions and income levels but women from marginalized groups, including newcomers, refugees, racialized and Indigenous women, are at a higher risk of economic abuse due to other systemic factors.
Economic Abuse: Coercive Control Tactics in Intimate Relationships
This infographic explores 3 forms of economic abuse and associated tactics used to coercively control intimate partners. These abusive tactics are compounded by economic systems that systemically oppress groups including Black, Indigenous, and people of colour; people with disabilities; people with precarious immigration status; and gender-oppressed people. Economic abuse consists of behaviours to control, exploit, and sabotage an individual’s resources. It limits the individual’s independence and autonomy. Compared to financial abuse which usually only focuses on money, economic abuse includes a more expansive range of behaviour that affects things like employment, food, medicine, and housing. Economic abuse is often used to coercively control individuals, such as intimate partners. It occurs in conjunction with further forms of abuse, like physical and sexual violence. Economic abuse can make it more difficult for survivors to escape violence since they may not have the resources to secure long-term housing and employment while meeting basic needs for themselves and potentially their children.
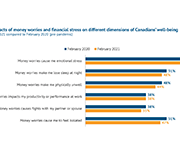
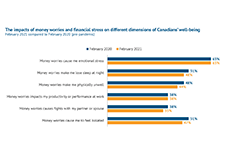
The Well-Being and Financial Well-Being of Canadians: financially vulnerable households the most challenged
This brief discusses how more financially vulnerable Canadians are most challenged based on the Seymour Financial Resilience Index TM. This E-Brief builds on Statistics Canada Canadians' Well-being in Year One of the COVID-19 Pandemic report and Seymour’s February 2021 Index Release Summary.
The Pivotal Role of Human Service Practitioners in Building Financial Capability
This report shares remarks by Mae Watson Grote, Founder and CEO of The Financial Clinic, at the Coin A Better Future conference in May 2018. The journey from financial insecurity to security, and eventually, mobility—what we conceptualize and even romanticize as the quintessential American experience—is one that far too often ensnares people at the insecurity stage, particularly those communities or neighborhoods that have historically been marginalized and deliberately excluded from the traditional pathway towards prosperity. Fraught with debt and credit crises, alongside a myriad of predatory products and lending practices, to a sense of stigma and shame many Americans feel because of their economic status, financial insecurity involves navigating a world on a daily basis where everyday needs are at the mercy of unjust and uncontrollable variables.
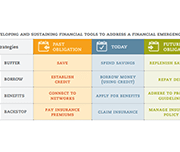
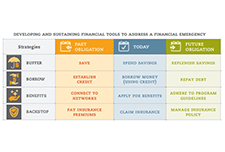
Achieving Financial Resilience in the Face of Financial Setbacks
Financial shocks like these happen to financially vulnerable families every day. Such shocks destabilize household finances and can create hardships that threaten overall well-being. Having tools to manage financial emergencies is critical for people’s long-run financial security. The Asset Funders Network (AFN) developed this primer to inform community-based strategies that can help economically-vulnerable families to better manage financial setbacks, shortfalls, and shocks. The goal of this brief is to provide a common understanding and language for funders and financial capability programs as part of a financial emergency toolkit.
Roadblock to Recovery: Consumer debt of low- and moderate-income Canadians in the time of COVID-19
Almost half of low-income households and 62 per cent of moderate-income households carry debt, with households on low incomes spending 31 per cent of their income on debt repayments, according to a new report published by national charity, Prosper Canada.
This report analyzes the distribution, amount and composition of non-mortgage debt held by low- and moderate-income Canadian households and explores implications for federal and provincial/territorial policy makers as they develop and implement COVID-19 economic recovery plans and fulfill their respective regulatory roles.
Hunger Lives Here: Risks and Challenges Faced by Food Bank Clients During COVID-19
This report provides quantitative and qualitative data about the experience of hunger and poverty in Toronto during COVID-19. Based on phone surveys with over 220 food bank clients in May and June 2020 and an analysis of food bank client intake data, the report demonstrates that COVID-19 has led to increased reliance on food banks. The rate of new clients accessing food banks has tripled since the pandemic began. Among new clients, 76% report that they began accessing food banks as a result of COVID-19 and the associated economic downturn.
From Emergency to Opportunity: Building a Resilient Alberta Nonprofit Sector After COVID-19
This report presents an analysis of the impact of COVID-19 on the nonprofit sector drawn from data collected in CCVO's Alberta Nonprofit Survey, data from surveys by the Alberta The analysis in this report shows that the effects on the nonprofit sector have been magnified through increased service demand, decreased revenue, and diminished organizational capacity coupled by delays in support and inadequate recognition for the leadership role that the sector is being called upon to play.
Nonprofit Network, Imagine Canada, and partner organizations across the country.
How Are the Most Vulnerable Households Navigating the Financial Impact of COVID-19?
The COVID-19 pandemic has already had an unprecedented impact on the financial lives of households across the United States. During June and July 2020, Prosperity Now conducted a national survey of lower-income households to better understand the circumstances these households are confronted with and the strategies they use to secure resources to navigate this crisis.
U.S. Financial Health Pulse: 2019 Trends Report
This report presents findings from the second annual U.S. Financial Health Pulse, which is designed to explore how the financial health of people in America is changing over time. The annual Pulse report scores survey respondents against eight indicators of financial health -- spending, bill payment, short-term and long-term savings, debt load, credit score, insurance coverage, and planning -- to assess whether they are “financially healthy,” “financially coping,” or “financially vulnerable”. The data in the Pulse report provide critical insights that go beyond aggregate economic indicators, such as employment and market performance, to provide a more accurate picture of the financial lives of people in the U.S.
Economic and Fiscal Snapshot 2020
The COVID-19 crisis is a public health crisis and an economic crisis. The Economic and Fiscal Snapshot 2020 lays out the steps Canada is taking to stabilize the economy and protect the health and economic well-being of Canadians and businesses across the country.
Advancing Health and Wealth Integration in the Earliest Years
Despite the well-documented connection between health and wealth, investing in this intersection is still a new approach for many grantmakers. With the goal of inspiring increased philanthropic attention, exploration, and replication, this new spotlight elevates responsive philanthropic strategies that support both health and wealth. This report focuses on the in utero-toddler stage of the life cycle (0-3 years). This age segment has some health-wealth integration activity, primarily through two-generation approaches. The goal is to inspire more philanthropic investment for this cohort by highlighting research and examples and offering recommendations.
Defining disability for social assistance in Ontario: Options for moving forward
Narrowing the definition of disability used by the Ontario Disability Support Program (ODSP) could have serious implications. Improving the program’s assessment process would yield better results for applicants, Ontario's social safety net, and the government. This report explores the role of ODSP, the risks of narrowing the definition of disability, models of disability assessment from other jurisdictions, and alternative ways that the government could reform the program. Most importantly, the paper recommends that the Ministry focus on improving ODSP’s initial application process. A simplified assessment system would save time and money for applicants, medical professionals, legal clinics, adjudicators, and the Social Benefits Tribunal. These savings should be reinvested back into social assistance.
Elder Fraud Prevention and Response Networks Development Guide
This guide provides step-by-step materials to help communities form networks to increase their capacity to prevent and respond to elder financial exploitation. The planning tools, templates and exercises offered in this guide help stakeholders plan a stakeholder retreat and training event, host a retreat, reconvene and establish their network, and expand network capabilities in order to create a new network or to refresh or expand an existing one.
Ageing and Financial Inclusion: 8 key steps to design a better future
The G20 Fukuoka Policy Priorities for Ageing and Financial Inclusion is jointly prepared by the GPFI and the OECD. The document identifies eight priorities to help policy makers, financial service providers, consumers and other actors in the real economy to identify and address the challenges associated with ageing populations and the global increase in longevity. They reflect policies and practices to improve the outcomes of both current generations of older people and future generations.
System transformation in Ontario Works: Considerations for Ontario
This paper focuses on proposed system transformation in Ontario Works, and explores the possibilities and limitations associated with the proposed changes in 2018. First, it looks at the broader context within which the government’s social assistance reforms are taking place. Second, it provides an overview of what is known about some of the structural changes in social assistance to date, as well as an overview of experiences in other jurisdictions that have undertaken similar reforms. In conclusion, the paper outlines some key considerations and unresolved questions that the government will need to address before it can move forward with a plan for reform.
Urban Spotlight: Neighbourhood Financial Health Index findings for Canada’s cities
This report examines the financial health and vulnerability of households in Canada’s 35 largest cities, using a new composite index of household financial health at the neighbourhood level, the Neighbourhood Financial Health Index or NFHI. The NFHI is designed to shine a light on the dynamics underlying national trends, taking a closer look at what is happening at the provincial/territorial, community and neighbourhood levels. Update July 22, 2022: Please note that the Neighbourhood Financial Health Index is no longer available
Helping Families Save to Withstand Emergencies
This brief identifies policy solutions to help American families build savings to withstand emergencies that threaten their financial stability.
Removing Savings Penalties for Temporary Assistance for Needy Families
This brief discusses the savings penalties in public assistance programs in the United States, also known as asset limits, and that actions that can be taken to eliminate these limits and the barriers towards building savings for families living on low income.
Running in Place: Why the Racial Wealth Divide Keeps Black and Latino Families From Achieving Economic Security
This report examines data from the Federal Reserve System’s 2016 Survey of Consumer Finances to understand how the wealth of median Black, Latino and White families have changed since the findings of its previous survey were released in 2013.
Money stories: Financial resilience among Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians
This report builds on previous work on financial resilience in Australia and represents the beginning of an exploration of the financial resilience of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples. Overall, we found significant economic disparity between Indigenous and non-Indigenous Australians. This is not surprising, given the histories of land dispossession, stolen wages and the late entry of Indigenous Australians into free participation in the economy (it is only 50 years since the referendum to include Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples as members of the Australian population). Specifically, we found: Severe financial stress is present for half the Indigenous population, compared with one in ten in the broader Australian population. Read the report to find out more about the financial barriers faced by Indigenous people in Australia, and the sharing economy in which money as a commodity can both help and hurt financial resilience.
Protecting vulnerable clients: A practical guide for the financial services industry
Firms and representatives in the financial services industry occasionally encounter situations where a client’s vulnerability causes the client to make decisions that are contrary to his or her financial interests, needs or objectives or that leave him or her exposed to potential financial mistreatment. Because of the relationships they develop with their clients and the knowledge they acquire about clients’ financial needs or objectives over time, firms and representatives in the financial sector can play a key role in helping people who are in a vulnerable situation protect their financial well-being. They are instrumental in preventing and detecting financial mistreatment among consumers of financial services. Firms and representatives can also help clients experiencing financial mistreatment get the assistance they need. This guide proposes possible courses of action to protect vulnerable clients. Its purpose is to provide financial sector participants with guidance on the steps they can take to help protect clients’ financial well-being, prevent and detect financial mistreatment, and assist clients who are experiencing this type of mistreatment.
State of Cities Reducing Poverty
How has the Vibrant Communities – Cities Reducing Poverty (VC – CRP) network contributed to poverty reduction in Canada? In seeking to answer this central question, the State of Cities Reducing Poverty paper highlights the network’s numerous and varied impacts.
Boosting the Earned Income Tax Credit for Singles
By providing a refundable credit at tax time, the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) is widely viewed as a successful public policy that is both antipoverty and pro-work. But most of its benefits have gone to workers with children. Paycheck Plus is a test of a more generous credit for low-income workers without dependent children. The program, which provides a bonus of up to $2,000 at tax time, is being evaluated using a randomized controlled trial in New York City and Atlanta. This report presents findings through three years from New York, where over 6,000 low-income single adults without dependent children enrolled in the study in late 2013. The findings are consistent with other research on the federal EITC, indicating that an effective work-based safety net program can increase incomes for vulnerable and low-income individuals and families while encouraging and rewarding work.
Gig Workers in America: Profiles, Mindset and Financial Wellness
The Gig Worker On-Demand Economy survey was conducted online by Harris Poll on behalf of Prudential from January 5 to February 18, 2017, among a nationally representative (U.S.) sample of 1,491 workers including 514 full-time and 256 part-time traditional employees and 721 gig workers. Gig work was defined as providing a service or labor, and did not include renting out assets. Survey respondents were selected from among adults aged 18+ who had agreed to participate in online surveys from the Harris Poll Online panel and preferred sample partners.
Unfinished Business Pension Reform in Canada
Since taking office in the fall of 2015, the Liberal government has made important changes to the publicly administered components of Canada’s retirement income system (RIS). It has restored the age of eligibility for benefits under Old Age Security (OAS) and the Guaranteed Income Supplement (GIS) to 65, it has increased the top-up on GIS benefits for single elderly persons, and it has agreed with the provinces to enhance Canada Pension Plan (CPP) benefits, starting in 2019.
Each of these changes, on its own, contributes to one of the two main objectives of the RIS: to minimize the people’s risk of poverty in old age and to enhance their ability to retain their standard of living as they move from employment to retirement. However, as Bob Baldwin and Richard Shillington show in this study, when examined together, the changes are problematic and incomplete.
The Ever Growing Gap: Without Change, African American and Latino Families Won’t Match White Wealth for Centuries
This report examines the growing racial wealth divide for Black and Latino and the ways that accelerating concentrations of wealth at the top compound and exacerbate this divide. It looks at trends in wealth accumulation from 1983 to 2013, as well as projections of what the next thirty years might bring. It also considers the impact public policy has had in contributing to the racial wealth divide and how new policies can close this gap.
We Tracked Every Dollar 235 U.S. Households Spent for a Year, and Found Widespread Financial Vulnerability
Income inequality in the United States is growing, but the most common economic statistics hide a significant portion of Americans’ financial instability by drawing on annual aggregates of income and spending. Annual numbers can hide fluctuations that determine whether families have trouble paying bills or making important investments at a given moment. The lack of access to stable, predictable cash flows is the hard-to-see source of much of today’s economic insecurity.
Financial Empowerment: Improving financial outcomes for low-income households
Financial Empowerment is a new approach to poverty reduction that focuses on improving the financial security of low-income people. It is an evidence-driven set of interventions that have proven successful at both eliminating systemic barriers to the full financial inclusion of low-income people and providing enabling supports that help them to acquire and practice the financial skills and behaviours that tangibly improve their financial outcomes and build their financial security. The Financial Empowerment approach focuses on community level strategies that encompass five main types of interventions that have been identified as both necessary for low-income households to improve their financial outcomes, and effective at helping them to do so.
The Real Cost of Payday Lending
Since the early 1990s payday lending businesses have become increasingly prolific in most parts of Canada, including Calgary. Social agencies and advocates working to reduce poverty view payday lenders and other fringe financial businesses as problematic for those looking to exit the cycle of poverty. Payday lenders charge interest rates that, when annualized, top 400%. The industry justifies this by stating that comparisons to an annual rate are unfair as loans are not meant to or allowed to last longer than two months. However, the fact remains that these businesses charge far more for credit than mainstream financial institutions and are more prevalent in lower income neighbourhoods.