How to build financial health in Native communities
American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) peoples have long faced barriers to asset building. More than half of AI/AN populations are un- or underbanked, financial services often don’t operate on reservations, and access to capital is difficult. Native peoples have been excluded from financial wealth accumulation through government asset stripping, industry redlining, and simple neglect, thanks to historic (and ongoing) discrimination, exclusion, and racism baked into government and private-sector policies. Solutions are within reach. Recently, the Financial Security Program, the Oklahoma Native Assets Coalition, Inc (ONAC), and the Center for Native American Youth hosted an event featuring Native leaders representing various geographies, experiences, and tribal affiliations. The group discussed experiences in building assets and Indigenous perspectives on generational financial wealth. Finally, the speakers gave recommendations on how foundations, corporations, non-profits, and others can partner with tribal governments and Native-led nonprofits to build financial wealth in Native communities. ONAC has produced a “List of Eighteen Suggestions to Better Support Native Practitioners Administering Asset Building Programs in their Communities”.
Aboriginal Peoples Survey: Data tables, 2017
New data tables on the labour activities of Indigenous Peoples are now available. Data are from the 2017 Aboriginal Peoples Survey and include information on labour force status, job satisfaction, skills training, skills that limit job opportunities, job permanency, part-time or full-time job status, mismatch of skills for current job, disability status and disability severity class, by Indigenous identity, age group and sex. Data are available for Canada, the provinces (Atlantic provinces combined) and the territories.
Shelters for victims of abuse with ties to Indigenous communities or organizations in Canada, 2017/2018
There were 85 shelters for victims of abuse that had ties to First Nations, Métis or Inuit communities or organizations operating across Canada in 2017/2018. These Indigenous shelters, which are primarily mandated to serve victims of abuse, play an important role for victims leaving abusive situations by providing a safe environment and basic living needs, as well as different kinds of support and outreach services. Over a one-year period, there were more than 10,500 admissions to Indigenous shelters; the vast majority of these admissions were women (63.7%) and their accompanying children (36.1%). This article uses data from the Survey of Residential Facilities for Victims of Abuse (SRFVA). Valuable insight into shelter use in Canada and the challenges that shelters and victims of abuse were facing in 2017/2018 is presented.
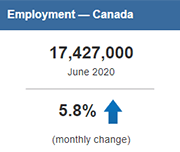
Labour Force Survey, June 2020
Labour Force Survey (LFS) results for June reflect labour market conditions as of the week of June 14 to June 20. A series of survey enhancements continued in June, including additional questions on working from home, difficulty meeting financial needs, and receipt of federal COVID-19 assistance payments. New questions were added to measure the extent to which COVID-19-related health risks are being mitigated through workplace adaptations and protective measures.
Indigenous Financial Literacy – AFOA 2014 Conference panel
This is the video recording of the AFOA 2014 Conference panel on Indigenous Financial Literacy. In this session, Liz Mulholland, Dr. Paulette Tremblay, Simon Brascoupe, and Darren Googoo discuss Indigneous financial wellness, financial literacy, and community education.
Integrating Financial Capability Services into Tribal LIHEAP
This brief is a companion resource to Building Financial Capability: A Planning Guide for Integrated Services (also known as the Guide) and provides real-world examples of financial capability integration efforts. The brief shares lessons and approaches for how tribal-serving organizations can integrate financial capability services into LIHEAP and other emergency assistance services. The brief highlights the experiences of two tribal serving organizations in Alaska that integrated financial capability services: the Kenaitze Indian Tribe and the Aleutian Pribilof Island Association (APIA). It is organized into three sections: understanding households’ financial lives, deciding which financial capability services to integrate, and assessing organizational and community capacity to plan for how to deliver services.
Financial Literacy of Indigenous Secondary Students in the Atlantic Provinces
Research conducted by agencies such as AFOA, Native Women’s Association of Canada, and various other Canadian entities, has identified the need for improved financial literacy education in Indigenous communities, particularly among youth and Elders. Such research reports are often equipped with a list of recommendations for improving and addressing the gaps in education around financial literacy. In the spirit of building upon this research into financial literacy and Indigenous peoples, the Purdy Crawford Chair in Aboriginal Business Studies (PCC) proposed a project focused on Atlantic Canada’s 14-18 year old Indigenous population and their levels of financial literacy. The results reveal that the majority of respondents would like to learn more about money. As well, they affirm that face-to-face learning from family members and in classroom settings remain the preferred way to learn about financial issues. Finally, based on the literature review, the environmental scan, survey data, and feedback from the community consultation process, a web application titled Seven Generations Financial Literacy was developed and is located at www.sevengenerationsfinancial.com.
Managing your money: Tools and tips to help you meet your goals (English)
MYM Worksheet 1: Your money goals
MYM Worksheet 1: Your money goals – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 2: Tracking your regular income
MYM Worksheet 2: Tracking your regular income – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 3: Tracking your spending
MYM Worksheet 3: Tracking your spending – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 4: Tracking your bills
MYM Worksheet 4: Tracking your bills – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 5: Monthly budgeting
MYM Worksheet 5: Monthly budgeting – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 6: Setting a savings goal
MYM Worksheet 6: Setting a savings goal – Fillable PDF
MYM Worksheet 7: Preparing for tax filing
MYM Worksheet 7: Preparing for tax filing
About the ‘Managing your money’ resource
All ‘Managing your money’ worksheets
Facilitator resources (English)
Gérer votre argent: Outils et conseils pour vous aider à atteindre vos objectifs (French)
Feuille de travail #1: Vos objectifs en lien à l’argent (MYM)
Feuille de travail #2: Suivi de votre revenu régulier (MYM)
Feuille de travail #3: Suivi de vos dépenses (MYM)
Feuille de travail #4: Suivi de vos factures (MYM)
Feuille de travail #5: Budget mensuel (MYM)
Feuille de travail #6: Fixer un objectif d’épargne (MYM)
Feuille de travail #7: Préparation pour la déclaration de revenus (MYM)
Note pour les communautés et les organismes (MYM)
Feuilles de travail complètes
Ka-paminit kisôniyâm (Plains Cree)
Managing your money #7: Preparing for tax filing
Even if you make no money, you should file a tax return each year. You may be eligible for a refund (money back). Filing your taxes triggers access to government benefits that you can’t get any other way. This worksheet will help you gather the information you will need at tax time. You will need a file folder, an envelope, or a small box to put all of your paperwork in. This is worksheet #7 from the booklet 'Managing your money'.
Managing your money #6: Setting a savings goal
Setting a savings goal means that you have decided how much money you can put away, and what you are going to save for. This activity can help you write down some money goals and when you would like to achieve them. You can build savings by putting aside small amounts on a regular basis. This is worksheet #6 from the booklet 'Managing your money'.
Managing your money #5: Monthly budgeting
When you make a budget, you give yourself a clear picture of your financial situation. A budget compares your income to your expenses, all in one place. This is worksheet #5 from the booklet 'Managing your money'.
Managing your money #4: Tracking your bills
Knowing what bills you have and when they are due can help you plan your spending. This activity will help you to be aware of two things: how much you owe each month, and at what time of the month that money is due. This will help you to pay bills on time, and avoid late fees. This is worksheet #4 from the booklet 'Managing your money.'
Managing your Money #3: Tracking your spending
Keeping track of where your money goes during the month is another helpful step towards making a budget. Then you will be able to compare your spending with your income. This is worksheet #3 from the booklet 'Managing your money.'
Managing your money #2: Tracking your regular income
Income is the money that comes into your household. This worksheet will help you see the ‘big picture’ of your income and other resources. Then you can think about how to plan your expenses. This is worksheet #2 from the booklet 'Managing your money.'