English
For frontline staff - Quick tools you can use with clients
Starting the conversation
Here are 7 questions to help you start a conversation about money with your client. Based on what you learn about your clients’ needs, the remaining links on this page to help you find answers and next steps.
Try this coaching readiness checklist to help your client ascertain if they have the time and are interested in receiving financial coaching.
Worksheets & tip sheets
Here are some “go to” worksheets and tip sheets that frontline staff have found very helpful with their clients. They focus on budgeting, saving, and debt management – common FE needs that come up. Try them out for yourself first and see which ones might work for your clients.
The Budget Spreadsheet is an excellent tool for capturing the full picture of an individual’s financial picture. The individual inputs information according to different categories and the tool calculates totals in a summary page to show how much money is left over at the end of the month. [Thunder Bay Counselling]
The Simple budget template is an alternative monthly budget tool clients can use. It includes links to an Income tracking worksheet and Expenses tracking worksheet. [Prosper Canada / Trove]
The Urgent vs Important worksheet can help clients prioritize their spending. This, in turn, can help them save or “find money” for necessary expenses. [Prosper Canada / Trove]
Knowing how to set a SMART goal is important for planning and achieving targets. In the Set a SMART financial goal, clients learn what a SMART goal is and write SMART financial goals that are important to them. [Prosper Canada / Trove]
Making a spending plan is a worksheet clients can use to create a spending plan for each week based on money coming in and out each month. [Prosper Canada / Trove]
Making a debt action plan is a worksheet to help your clients get a handle on their debt. [Prosper Canada / Trove]
Tips for Managing Debt and Bills is a reference sheet you can give clients during tough times when managing cash flow is a challenge.
Prioritizing bills helps clients prioritize what bills to pay when it’s not possible to pay for everything. Note that this tool is from the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), an American government agency and includes a link to their website. Let clients know the information on the website is geared to the US context. [Consumer Financial Protection Bureau]
Online sites and tools
Here are great online tools you can also share and use in your FE work with clients.
Benefits wayfinder [benefitswayfinder.org]
Support with access to benefits is another powerful FE intervention. The Benefits wayfinder is a simple, easy to use, plain language tool that helps people on low and modest incomes find and track benefits they could get. Clients can use it on their own or with your support.
Read the Benefits wayfinder fact sheet to learn more.
Then watch the How to use this tool video. It highlights and demonstrates how to navigate through the key features of the tool.
If you would like additional training on how to support your clients with access to benefits and use the Benefits wayfinder tool in your money conversations, you can sign up for Prosper Canada’s self-directed online course and/or live workshop.
Trove [yourtrove.org]
Trove is a free bilingual website that clients can visit on their own or with your support. Many of the tools you were introduced to above can be found on Trove, along with a wealth of other user-friendly financial tools, worksheets, and education information to help clients take charge of their spending, learn about tax filing and benefits, and manage debt.
Along with a link to the Benefits wayfinder, you can also find these online tools:
- My money in Canada is a website that can help clients build healthy money habits with simple, easy to use learning modules on a range of money topics. The site also includes videos and a financial wellness checklist for clients.
- The RDSP Calculator for Canadians can be used to assess the potential of opening and contributing to a Registered Disability Savings Plan.
For managers - Tools for getting started with financial empowerment
The resources below focus on starting steps and tools to assist in the initial planning and implementation stages for embedding FE. Future phases of the toolkit will share resources for later stage efforts, as well as non-municipal efforts, such as public libraries and health care systems.
Tool 1. Making the case for financial empowerment
For FE to be successful, it’s critical to get buy-in from staff and stakeholders.
Below are great resources to share with key players who are new to FE. They can help you get others quickly up to speed on what FE is and the value of embedding FE as you onboard them or work to build interest in FE in your municipality.
- Prosperity Gateways Primer gives a quick overview of the “what” and “why” of embedding FE into municipal services.
- FE Brochure provides a more detailed introduction to FE and embedding FE.
- Here are three case examples you can use to show the powerful impact embedding FE into municipal services can have:
- Case example: York region
- Case example: TESS
- Case example: Edmonton
Tool 2. Getting started: the internal scan
Take the time to learn about common FE interventions. Then, assess conditions, capacity and considerations in your municipality for providing these kinds of financial help to your clients.
This tool guides you through an internal scan as you envision what embedding FE might look like in your service delivery context. Consider Tool 2: Getting started: the internal scan a starting point that will continue to evolve as you move through the process.
Tool 3. Exploring partnerships: the external scan
Municipalities do not have to deliver FE supports themselves to turn their services into Prosperity Gateways. In many cases, especially at the outset, it may be more cost-effective and less resource intensive to establish referral pathways to other local service providers or to partner with non-profit organizations, foundations, or financial service providers to deliver the financial help to meet your clients’ needs.
Use Tool 3: Exploring collaborations and partnerships to perform a scan of FE services in your local community and identify potential collaborations and partnerships.
Two additional partnership resources are ‘Elements of Integration‘ and ‘Partnership Tip Sheet‘
Tool 4. Designing the initiative: the service blueprint
Having completed an internal and external scan of barriers and opportunities, you are now ready to design an FE initiative to suit your municipality’s context. Designing the initiative is an important phase where you work out the service model, clarify partnerships, and imagine the ideal client experience.
Tool 4: Designing the initiative guides you through choosing the best service delivery model for your context and designing the client and staff journey.
We hope this toolkit will grow and improve with use and feedback. Current ideas for upcoming tools include:
- Understanding your clients’ financial capability
- Building a successful team
- Supporting staff for success
- Setting up effective data collection and evaluation processes
Tool 5. Designing the initiative: a shadowing guide
Tool 5: A shadowing guide can help frontline staff understand the process from intake to service delivery.
Feedback / Suggestions
We’d love to hear your feedback and suggestions for tools that you would find useful. Please email: Helen Payne Watt at [email protected]
Learn more about FE
Canadian Publications
Prosperity Gateways: Cities for financial empowerment – Building the case outlines evidence for embedding FE.
Read the report How financial empowerment services are helping Ontarians build financial health for more supporting evidence and personal stories.
Financial Empowerment – What is it and how it helps reduce poverty [national] suggests that FE is a critical missing piece of federal government policy that can significantly boost client outcomes when it is embedded into other programs and services.
Financial Empowerment – What is it and how it helps reduce poverty [Alberta] provides an overview of provincial government action on FE in Alberta. The Alberta government adapted the national document (by the same name) to use in their internal discussions with municipal decision-makers. Create a document that you can use for your internal discussions using this as an example.
U.S. Publications
The municipal integration of FE in Canada is grounded in influential work in the US by the Cities for Financial Empowerment (CFE) Fund. Launched in 2012 in New York the CFE Fund showed that embedding FE strategies into local government infrastructure can have a “supervitamin effect” on public programs, increasing the financial stability of low to moderate income households.
- Read the pioneering article: “Municipal Financial Empowerment: A Supervitamin for Public Programs”
- Learn more about their Financial Empowerment Centers model in this 4-minute video
- Visit their website to see resources and sign up for their quarterly newsletter
- See a three-year evaluation of the model in 5 cities across the US. “An Evaluation of Financial Empowerment Centers – Building People’s Financial Stability as a Public Service”
The Urban Institute examined the cost of residents’ financial insecurity to city budgets in 10 American cities in this 2017 research. Across these cities, the costs range from the tens to hundreds of millions of dollars, suggesting that cities have an economic interest in improving their residents’ financial health.
A report by JP Morgan Chase reviews municipal efforts to integrate financial capability into public services in several US locations in “A Scan of Municipal Financial Capability Efforts.”
French
Pour le personnel de première ligne — Outils rapides que vous pouvez utiliser avec les clients
Amorcer la conversation
Voici sept questions qui vous aideront à entamer une conversation à propos de l’argent avec votre client. En fonction de ce que vous avez appris sur les besoins de vos clients, les autres liens de cette page vous aideront à trouver des réponses et à connaître les prochaines étapes.
Utilisez cette liste de vérification pour aider votre client à décider s’il a le temps et s’il souhaite recevoir un accompagnement financier.
Fiches de travail et fiches de conseils
Voici quelques feuilles de travail et des feuilles de conseils que le personnel de première ligne a trouvé très utiles pour ses clients. Elles portent principalement sur la planification budgétaire, l’épargne et la gestion des dettes — les besoins courants en matière d’AF qui se présentent. Essayez-les d’abord pour vous-même et voyez ceux qui pourraient convenir à vos clients.
La feuille de calcul du budget (anglais seulement) est un excellent outil pour saisir le portrait complet de la situation financière d’un individu. La personne saisit les données selon différentes catégories et l’outil calcule les totaux dans une page de synthèse pour montrer combien d’argent il reste à la fin du mois. [Thunder Bay Counselling]
Le modèle de budget simple est un outil alternatif de budget mensuel que les clients peuvent utiliser. Il comprend des liens vers une feuille de calcul de suivi des revenus et une feuille de calcul de suivi des dépenses. [Prospérité Canada/Trove]
La feuille de calcul Urgent versus Important peut aider les clients à établir des priorités dans leurs dépenses. Cela peut ensuite les aider à économiser ou à « trouver de l’argent » pour les dépenses nécessaires. [Prospérité Canada/Trove]
Il est important de savoir comment établir un objectif INTELLIGENT pour mettre en place et atteindre des objectifs. Avec l’outil Comment établir des objectifs financiers INTELLIGENTS, les clients apprennent ce qu’est un objectif INTELLIGENT et choisissent des objectifs financiers INTELLIGENTS qui sont importants pour eux. [Prospérité Canada/Trove]
La feuille de calcul Comment établir un plan de dépenses est un outil que les clients peuvent utiliser pour créer un plan de dépenses pour chaque semaine en fonction des entrées et sorties d’argent du mois. [Prospérité Canada/Trove]
La feuille de calcul Élaboration d’un plan d’action en matière de dettes est un outil pour aider vos clients à prendre le contrôle sur leurs dettes. [Prospérité Canada/Trove]
Conseils pour la gestion des dettes et des factures est une feuille de référence que vous pouvez donner à vos clients dans les moments difficiles où la gestion des fonds est un défi.
Le classement des factures par ordre de priorité (anglais seulement) aide les clients à déterminer les factures à payer en premier lorsqu’il n’est pas possible de tout payer. Notez que cet outil provient du Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), une agence gouvernementale américaine, et comprend un lien vers son site Web. Expliquez aux clients que les renseignements figurant sur le site Web sont adaptés au contexte américain. [Consumer Financial Protection Bureau]
Sites et outils en ligne
Voici d’excellents outils en ligne que vous pouvez également faire connaître et utiliser dans votre travail en matière d’AF avec les clients.
Orienteur en mesures d’aide [benefitswayfinder.org/fr]
L’aide à l’accès aux mesures d’aide est une autre façon puissante d’intervenir en matière d’AF. L’Orienteur en mesures d’aide est un outil simple, facile à utiliser et rédigé en langage clair qui aide les personnes à revenus faibles ou modestes à trouver et à répertorier les mesures d’aide auxquelles elles peuvent prétendre. Les clients peuvent l’utiliser seuls ou avec votre aide.
Pour en savoir plus, lisez la fiche d’information sur l’Orienteur en mesures d’aide. (anglais seulement)
Ensuite, regardez la vidéo Comment utiliser cet outil (anglais seulement). Elle explique et démontre comment naviguer à travers les principales caractéristiques de l’outil.
Si vous souhaitez obtenir une formation supplémentaire sur la façon d’aider vos clients à accéder aux mesures d’aide et d’utiliser l’Orienteur en mesures d’aide dans vos conversations au sujet de l’argent, vous pouvez vous inscrire au cours autodidacte en ligne ou à l’atelier en direct de Prospérité Canada.
Trove [yourtrove.org/fr]
Trove est un site Web bilingue gratuit que les clients peuvent visiter par eux-mêmes ou avec votre aide. La plupart des outils qui vous ont été présentés ci-dessus se trouvent sur Trove, ainsi qu’une multitude d’autres outils financiers conviviaux, des feuilles de calcul et des renseignements éducatifs pour aider les clients à prendre en charge leurs dépenses, à se renseigner sur la déclaration et les avantages fiscaux et à gérer leurs dettes.
En plus d’un lien vers l’Orienteur en mesures d’aide, vous trouverez également ces outils en ligne :
- Mon argent au Canada est un site Web qui peut aider les clients à acquérir de bonnes habitudes en matière de gestion de l’argent grâce à des modules d’apprentissage simples et faciles à utiliser sur toute une série de sujets liés à l’argent. Le site comprend également des vidéos (anglais seulement) et un questionnaire relatif au bien-être financier pour les clients.
- La calculatrice du REEI pour les Canadiens peut être utilisée pour évaluer la possibilité d’ouvrir et de cotiser à un régime enregistré d’épargne-invalidité.
Pour les gestionnaires — Outils pour démarrer avec l’autonomisation financière
The resources below focus on starting steps and tools to assist in the initial planning and implementation stages for embedding FE. Future phases of the toolkit will share resources for later stage efforts, as well as non-municipal efforts, such as public libraries and health care systems.
Outil 1. Argumenter en faveur de l’autonomisation financière.
Pour que l’AF soit un succès, il est essentiel d’obtenir l’adhésion du personnel et des intervenants.
Vous trouverez ci-dessous d’excellentes ressources à faire connaître aux acteurs clés qui ne connaissent pas encore l’AF. Elles peuvent vous aider à faire comprendre rapidement aux autres ce qu’est l’AF et la pertinence d’intégrer l’AF lorsque vous les accueillez ou lorsque vous travaillez à susciter l’intérêt pour l’AF dans votre municipalité.
● L’abécédaire des passerelles pour la prospérité (anglais seulement) donne un aperçu de « qu’est-ce que c’est » et du « pourquoi » au sujet de l’intégration de l’AF dans les services municipaux.
● La brochure de l’AF (anglais seulement) fournit une introduction plus détaillée à l’AF et à l’intégration de l’AF.
● Voici trois exemples de cas que vous pouvez utiliser pour montrer l’impact puissant que peut avoir l’intégration de l’AF dans les services municipaux :
o Exemple de cas : Région de York
o Exemple de cas : Services sociaux et d’emploi de Toronto
o Exemple de cas : Edmonton
Outil 2. Commencer : l’analyse interne
Prenez le temps de vous renseigner sur les types d’interventions courantes en matière d’AF. Ensuite, évaluez les conditions, la capacité et les considérations dans votre municipalité pour fournir ces types d’aide financière à vos clients.
Cet outil vous guide à travers une analyse interne qui vous permet d’envisager ce que pourrait être l’intégration de l’AF dans votre contexte de prestation de services.
Considérez l’outil 2 : Commencer : l’analyse interne un point de départ qui continuera à évoluer à mesure que vous avancerez dans le processus.
Outil 3. Explorer les partenariats : l’analyse externe
Les municipalités ne sont pas obligées de fournir elles-mêmes des mesures d’aides en matière d’AF pour transformer leurs services en passerelles pour la prospérité. Dans de nombreux cas, surtout au début, il peut être plus rentable et moins exigeant sur le plan des ressources d’établir des liens de référence vers d’autres prestataires de services locaux ou de s’associer à des organismes à but non lucratif, des fondations ou des prestataires de services financiers pour fournir l’aide financière répondant aux besoins de vos clients.
Utilisez l’outil 3 : Explorer les collaborations et les partenariats pour effectuer une analyse des services en matière d’AF dans votre communauté locale et identifier les collaborations et partenariats potentiels.
Deux autres ressources à propos du partenariat sont les « Éléments de l’intégration » et les « Conseils pour le partenariat » .
Outil 4. Concevoir l’initiative : le plan de service
Après avoir effectué une analyse interne et externe des obstacles et des opportunités, vous êtes maintenant prêt à concevoir une initiative d’AF adaptée au contexte de votre municipalité. La conception de l’initiative est une phase importante où vous élaborez le modèle de service, clarifiez les partenariats et imaginez l’expérience client idéale.
L’outil 4 : Conception de l’initiative vous guide dans le choix du meilleur modèle de prestation de services pour votre contexte et dans la conception du parcours du client et du personnel.
Nous espérons que cette boîte à outils se développera et s’améliorera avec l’utilisation et les commentaires. Les idées actuelles pour les outils à venir incluent :
- Comprendrela capacité financière de vos clients
- Mettresur pied une équipe performante
- Soutenirle personnel pour qu’il réussisse
- Mettreen place des processus efficaces de collecte de données et d’évaluation
Outil 5. Concevoir l’initiative : un guide d’observation
L’outil 5 : Un guide d’observation peut aider le personnel de première ligne à comprendre le processus, de l’accueil à la mise en œuvre du service.
Commentaires et suggestions
Nous serions ravis d’entendre vos commentaires et vos suggestions d’outils que vous trouveriez utiles. Veuillez nous envoyer un courriel : Helen Payne Watt à l’adresse [email protected].
En savoir plus en matière d’AF
Publications canadiennes
Passerelles de prospérité : Les villes pour l’autonomisation financière — établir le dossier (anglais seulement) décrit les preuves qui sont pour l’intégration de l’AF.
Lisez le rapport intitulé Comment les services d’autonomisation financière aident les Ontariens à renforcer leur santé financière (anglais seulement) pour obtenir plus de preuves et de récits personnels.
Le document Autonomisation financière — qu’est-ce que c’est et comment cela aide à réduire la pauvreté [national] (anglais seulement) suggère que l’autonomisation financière est une pièce manquante essentielle de la politique du gouvernement fédéral qui peut considérablement améliorer les conditions de vie des clients lorsqu’elle est intégrée à d’autres programmes et services.
Le document Autonomisation financière — qu’est-ce que c’est et comment cela aide à réduire la pauvreté [Alberta] (anglais seulement) donne un aperçu de la démarche du gouvernement provincial en matière d’AF en Alberta. Le gouvernement de l’Alberta a adapté le document national (du même nom) pour l’utiliser dans ses discussions internes avec les décideurs municipaux. Créez un document que vous pourrez utiliser pour vos discussions internes en utilisant cet exemple.
Publications américaines
L’intégration municipale de l’AF au Canada est fondée sur les travaux influents réalisés aux États-Unis par le Fonds Cities for Financial Empowerment (CFE). Lancé en 2012 à New York, le Fonds CFE Fund a montré que l’intégration de stratégies d’AF dans l’infrastructure des gouvernements locaux peut avoir un « effet super vitaminé » sur les programmes publics, en augmentant la stabilité financière des ménages à revenu faible ou modéré.
- Lisez l’article pionnier : « Municipal Financial Empowerment: A Supervitamin for Public Programs » (anglais seulement)
- Apprenez-en davantage sur leur modèle de centres d’autonomisation financière (anglais seulement) dans cette vidéo de quatre minutes.
- Visitez leur site Web (anglais seulement) pour voir les ressources et vous inscrire à leur infolettre trimestrielle.
- Découvrez une évaluation de trois ans du modèle dans cinq villes des États-Unis. « An Evaluation of Financial Empowerment Centers – Building People’s Financial Stability as a Public Service » (anglais seulement)
L’Urban Institute a examiné le coût de l’insécurité financière des résidents sur les budgets municipaux de dix villes américaines dans cette recherche de 2017 (anglais seulement). Dans ces villes, les coûts vont de dizaines à des centaines de millions de dollars, ce qui suggère que les villes ont un intérêt économique à améliorer la santé financière de leurs résidents.
Un rapport de JP Morgan Chase passe en revue les efforts déployés par les municipalités pour intégrer la capacité financière dans les services publics dans plusieurs villes américaines dans « A Scan of Municipal Financial Capability Efforts » (anglais seulement).
Household food insecurity during the COVID-19 pandemic
This study presents data on levels of household food insecurity in the 10 provinces from the September to December 2020 cycle of the Canadian Community Health Survey. In this survey, household food security status within the previous 12 months was measured using a scale that has been routinely used to monitor levels of household food insecurity in Canada. This provided the ability to draw comparisons with pre-pandemic levels. Both before and during the pandemic, certain population groups were more vulnerable to food insecurity in their household. They included people with lower levels of education, those who rent their dwelling, those in lone-parent-led households and those in households reliant on social assistance as their primary source of income. Compared with the pre-pandemic period of 2017/2018, levels of household food insecurity were either unchanged or slightly lower in fall 2020 among groups vulnerable to food insecurity.
The effects of child tax benefits on the income of single mothers
The financial resources available to families with young children are an important factor affecting child development, and they can have long-term impacts on socioeconomic outcomes in adulthood. This article summarizes the findings of a new study using Statistic Canada’s data and analyzes the effects of expanding child tax benefits on after-tax income among single mothers, in the context of the 2015 reform to the Universal Child Care Benefit (UCCB) and the 2016 introduction of the Canada Child Benefit (CCB).
Why the Time is Right for a Guaranteed Income with an Equity Lens
Over 50+ mayors in the United States have joined a national initiative Mayor’s for Guaranteed Income (MGI). Many advocates and practitioners now believe the moment has arrived for a guaranteed Income with an equity lens. In this webinar, perspectives from a diverse group of thought leaders involved in GI initiatives including practitioners, government representatives and philanthropy were heard. Panelists shared outcomes and new research results from some of the most successful GI pilots in the country (Stockton and Mississippi); goals for the newly launched Mayor’s for Guaranteed Income; how philanthropy can play a catalytic role and what this moment tells us about the future of guaranteed income initiatives.
San’yas Indigenous Cultural Safety Training
Cultural safety is about fostering a climate where the unique history of Indigenous peoples is recognized and respected in order to provide appropriate care and services in an equitable and safe way, without discrimination. This website includes information about the San’yas: Indigenous Cultural Safety Training Program delivered by the Provincial Health Services Authority of British Columbia.
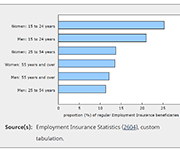
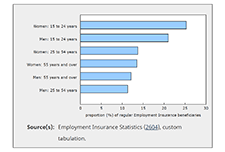
Employment Insurance, February 2021
February Employment Insurance (EI) statistics reflect labour market conditions as of the week of February 14 to 20. Ahead of the February reference week, non-essential businesses, cultural and recreation facilities, and in-person dining reopened in many provinces, subject to capacity limits and various other public health requirements. Public health measures were relaxed in Quebec, Alberta, Nova Scotia and New Brunswick on February 8, although a curfew remained in effect in Quebec. Measures were loosened in many regions of Ontario on February 10 and 15, although stay-at-home orders remained in place in the health regions of Toronto, Peel, York and North Bay Parry Sound. In Manitoba, various measures were eased on February 12. In contrast, Newfoundland and Labrador reintroduced a lockdown on February 12, requiring the widespread closure of non-essential businesses and services.
The relationship between COVID-19 pandemic and people in poverty: Exploring the impact scale and potential policy responses
This research project aims to identify the relationship between COVID-19 pandemic and poverty in Vancouver, by analyzing how the COVID-19 pandemic has pushed people into poverty and the impact of COVID-19 on people already living in poverty. Several examples of COVID-19 recovery policies and projects being implemented elsewhere that could support people experiencing poverty in Vancouver are also provided.
Budget 2021: A Recovery Plan for Jobs, Growth, and Resilience
The federal budget released on April 19, 2021 covers the Canadian government's plan for:
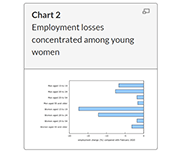
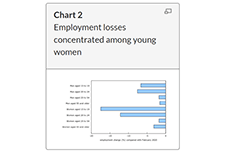
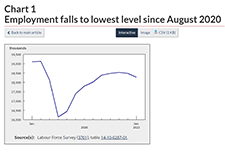
Labour Force Survey, February 2021
February Labour Force Survey (LFS) data reflect labour market conditions during the week of February 14 to 20. In early February, public health restrictions put in place in late December were eased in many provinces. This allowed for the re-opening of many non-essential businesses, cultural and recreational facilities, and some in-person dining. However, capacity limits and other public health requirements, which varied across jurisdictions, remained in place. Restrictions were eased to varying degrees in Quebec, Alberta, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia on February 8, although a curfew remained in effect in Quebec. In Ontario, previous requirements were lifted for many regions on February 10 and 15, while the Toronto, Peel, York and North Bay Parry Sound health regions remained under stay-at-home orders through the reference week. Various measures were eased in Manitoba on February 12. In contrast, Newfoundland and Labrador re-introduced a lockdown on February 12, requiring the widespread closure of non-essential businesses and services.
Labour Force Survey, January 2021
After the December Labour Force Survey (LFS) reference week—December 6 to 12—a number of provinces extended public health measures in response to increasing COVID-19 cases. January LFS data reflect the impact of these new restrictions and provide a portrait of labour market conditions as of the week of January 10 to 16. In Ontario, restrictions already in place for many regions of southern Ontario—including the closure of non-essential retail businesses—were extended to the rest of the province effective December 26. In Quebec, non-essential retail businesses were closed effective December 25 and a curfew implemented on January 14 further affected the operating hours of some businesses. As of the January reference week, existing public health measures continued in Alberta and Manitoba, including the closure of in-person dining services, recreation facilities and personal care services, as well as restrictions on retail businesses. Restrictions were eased between the December and January reference weeks in two provinces. In Prince Edward Island, closures of in-person dining and recreational and cultural facilities were lifted on December 18. In Halifax, Nova Scotia, and the surrounding area, restrictions on in-person dining were eased on January 4.
Statistics on Indigenous peoples
This data hub includes data on the following subjects:
Food insecurity and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic
Canadians living in households that experienced food insecurity (insecure or inadequate access to food because of financial constraints) during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic were significantly more likely to perceive their mental health as fair or poor and to report moderate or severe anxiety symptoms than Canadians in food-secure households. Approximately one in seven Canadians (14.6%) were estimated to live in a food-insecure household in May 2020. This study, released in Health Reports, is the first to examine the association between household food insecurity and self-perceived mental health and anxiety among Canadians during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study also estimated that 9.3% of Canadians living in food-insecure households reported having recently accessed free food or meals from a community organization.
Financial Life Stages of Older Canadians
This study, commissioned by the Ontario Securities Commission (OSC) and conducted by the Brondesbury Group, provides some insights on the knowledge that older Canadians have about the financial realities of retirement and how they would apply that knowledge earlier in life if they are able to do so. The top financial concerns and main financial risks of older Canadians are identified for each life stage and how they are being managed are discussed.
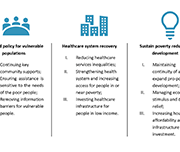
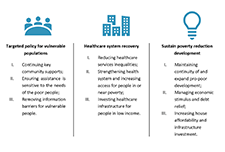
Overcoming Poverty Together 3: The New Brunswick Economic and Social Inclusion Plan 2020-2025
The new Economic and Social Inclusion plan for New Brunswick builds upon progress accomplished over the past 10 years. It includes nine priority actions divided into three pillars: The objective of the plan is to reduce income poverty by at least 50 per cent by 2030, in line with the objectives of Opportunity for All, Canada’s first poverty reduction strategy, and those of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainability of the United Nations.
State of the Child Report 2020: Protecting Child Rights in Times of Pandemic
The 2020 State of the Child Report includes six recommendations and gives a snapshot of some of the challenges New Brunswick children and youth will have to overcome as the province moves forward and juggles the new realities of public health measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19 while respecting child rights.
State of the Child Report 2019
This report's release was part of Child Rights Education Week and also in celebration of the 30th anniversary of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC). 2019 was declared the International Year of Indigenous Languages by the United Nations. The report contains an overview of some of the serious challenges facing New Brunswick children and youth, including more than 200 statistics presented in the report’s Child Rights Indicators Framework. A special emphasis was placed on education rights. Some of the concerning findings revealed in the report include:
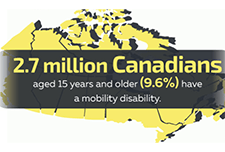
A profile of Canadians with a mobility disability and groups designated as visible minorities with a disability
Results from the 2017 Canadian Survey of Disability (CSD) have shown that over half of Canadians with a mobility disability need at least one workplace accommodation. Among population groups designated as visible minorities who have a disability, one-quarter considered themselves to be disadvantaged in employment because of their condition. In recognition of the International Day of Persons with Disabilities, Statistics Canada released three new data products based on findings from the 2017 CSD. One infographic focuses on disabilities related to mobility and another takes a look at visible minorities with disabilities. In addition, two data tables, on industry and occupation of those with and without disabilities, are now available.
COVID-19 Financial Resilience Hub
The Global Financial Literacy Excellence Center (GFLEC) focuses on financial literacy research, policy, and solutions. This toolkit contains suggestions and resources for managing personal finances and protection against the financial emergencies caused by COVID-19.
From Surviving to Thriving – Ensuring the Golden Years Remain Golden for Older Women
This brief explores the drivers of economic insecurity for older women and sets forth a number of strategies and promising practices for funders to consider which address the needs of older women. Doing so will ensure this generation and future generations of men and women in this country can age financially secure and with dignity. This publication is the fourth in a series of briefs that build on AFN’s publication, Women & Wealth, to explore how the gender wealth gap impacts women, particularly low-income women and women of color, throughout their life cycle, and provides responsive strategies and best practices that funders can employ to create greater economic security for women.
Managing Financial Health in Challenging Times
Managing financial health is difficult during ordinary times—and especially so in challenging times like the ones we're currently facing. Guest speaker RuthAnne Corley, the Senior Stakeholder Engagement Officer with the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada (FCAC), discusses how to manage your financial health despite external challenges. RuthAnne joined FCAC in 2015 where she’s been instrumental in the development of Canada’s "National Strategy for Financial Literacy - Count me in, Canada" and its implementation. Prior to joining FCAC in 2015, RuthAnne managed stakeholder engagement and outreach activities at numerous federal departments and agencies.
Beyond Hunger: the hidden impacts of food insecurity
This report illustrates the hidden impacts of food insecurity in people’s lives through a survey of 561 people in 22 communities across Canada. The people interviewed shared that food insecurity makes them ill, breaks down relationships, makes it harder to get stable work, and fully participate in society.