Financial literacy courses for Canadian students
Teachers may incorporate two gamified financial literacy courses that are currently freely available into their lessons. Students can now access two age-appropriate courses designed to help boost students' financial knowledge and confidence at any stage of their financial journey. Course titles: Students will explore resources and tools on the FCAC website that they will be able to use well beyond high school. *Students can earn a completion certificate issued by the FCAC and ChatterHigh!
Annual report 2022
The Asset Funders Network engages philanthropy to advance equitable wealth building and economic mobility. For 18 years, AFN has provided a forum for grantmakers to connect, collaborate, and collectively invest in helping more people achieve economic security. This report reflects their work over the past year working across 7 issues areas:
Income in retirement: Expectations versus reality
In 2014, a group of non-retired Canadians aged 55 or older was asked about their financial expectations for retirement. New data from 2020 reveal how this same group of Canadians - now retired- is doing financially.
Financial Literacy for Black and African American Students
In honor of Black History Month, BestColleges in the United States interviewed financial expert Terrance Dedrick to help curate a financial literacy resource for Black and African Americans. This article includes links to these organizations in the United States that cater to Black and African Americans: "Brown Ambition": A popular podcast for Black and African American students covers important financial literacy topics and provides advice from others who have learned financial literacy and used it successfully. Urban Wallet: A selection of free guides and resources to help students learn about spending and budgeting, investing in cryptocurrencies, and using credit cards responsibly. Association of African American Financial Advisors (AAAFA): for Black and African American students looking to work with a financial advisor to learn more about money. Operation HOPE: This nonprofit works with students and other adults alike to provide financial dignity through financial literacy training, coaching, and other services to build confidence and resilience. Building Bread: Designed for Black students and young professionals, Building Bread provides a free financial planning course along with other low-cost advanced classes.
Connecting families initiative
Daily aspects of Canadians' lives are increasingly touched by digital technology, and access to high-speed Internet has become an essential service and a key driver for improving our economic and social well-being. The Government of Canada originally announced Connecting Families in Budget 2017 to help bridge the digital divide for Canadian families who struggled to afford access to home Internet. Learn more about the next phase of this initiative.
Canada’s new working class: A modern understanding of the 6.5 million Canadians in the working class
The pandemic has accelerated a polarization of jobs that has become a structural trend in the Canadian economy. Previous Cardus research has shown that this polarization of the labour market between low- and high-skilled occupations, with a declining share of jobs available for mid-skilled workers, has led to an “hourglass economy.”
Yet, even while the share of the labour force employed in professional occupations rises, the working class retains the largest share of workers in the Canadian economy, making them an important political economy constituency. But who is the working class in Canada? This paper seeks to answer this question by proposing a modern taxonomy of the workforce and a picture of the working class that draws on a rich body of demographic, economic, and labour-market data.
About the Canada Learning Bond
The Canada Learning Bond (CLB) is money that the Government adds to a Registered Education Savings Plan (RESP) for children from low-income families. This money helps to pay the costs of a child’s full- or part-time studies after high school at apprenticeship programs, CEGEPs, trade schools, colleges, or universities. Learn more about eligibility requirements and the application process using this website.
Introduction to behavioural insights for the social sector: a capacity building course
This self-paced online course will help you learn about behavioural insights and how they can help you increase impact in simple, practical ways. In this self-paced learning experience, you will learn foundational skills and tools that you can apply immediately to your work, creating a long-lasting social impact.
Social determinants and inequities in health for Black Canadians: a snapshot
The following snapshot aims to highlight how Anti-Black racism and systemic discrimination are key drivers of health inequalities faced by diverse Black Canadian communities. Evidence of institutional discrimination in key determinants of health is also presented, including education, income, and housing. Finally, national data is shared demonstrating inequalities in health outcomes and determinants of health. Readers are invited to reflect on how racism and discrimination may contribute to these inequalities.
Dimensions of poverty hub
Statistics Canada has created an "Opportunity for All"; a dashboard of 12 indicators to track progress on deep income poverty as well as the aspects of poverty other than income, including indicators of material deprivation, lack of opportunity and resilience. These indicators are broadly grouped into three categories: dignity, opportunity and inclusion and resilience and security.
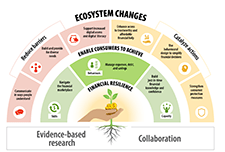
Make Change that Counts: National Financial Literacy Strategy 2021-2026
The Financial Consumer Agency of Canada’s (FCAC’s) mandate is to protect Canadian financial consumers and strengthen financial literacy. The National Strategy is a 5-year plan to create a more accessible, inclusive, and effective financial ecosystem that supports diverse Canadians in meaningful ways. The National Strategy is focused on how financial literacy stakeholders can reduce barriers, catalyze action, and work together, to collectively help Canadians build financial resilience.
Impact of the COVID-19 Crisis on Montreal “Cultural Communities”
This exploratory study aims to better understand the challenges experienced by members of cultural communities in Montreal, particularly the most disadvantaged groups, during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Spring of 2020.
Canadian Economic News, January 2021 edition
This module provides a concise summary of selected Canadian economic events, as well as international and financial market developments by calendar month. All information presented here is obtained from publicly available news and information sources, and does not reflect any protected information provided to Statistics Canada by survey respondents. This is the issue for January 2021.
The Canadian Housing Survey, 2018: Core housing need of renter households living in social and affordable housing
This article provides a high level overview of those living in social and affordable housing by painting a portrait of them based on the results of the 2018 CHS. Socio-demographic and household characteristics are examined using housing indicators such as core housing need.
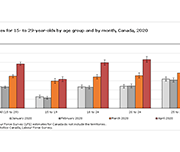
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the NEET (not in employment, education or training) indicator, March and April 2020
A fact sheet released by Statistics Canada shows that, in March and April 2020, the proportion of young Canadians who were not in employment, education or training (NEET) increased to unprecedented levels. The COVID-19 pandemic—and the public health interventions that were put in place to limit its spread—have affected young people in a number of ways, including high unemployment rates, school closures and education moving online.
Set a Goal: What to Save For
America Saves, a campaign managed by the nonprofit Consumer Federation of America, motivates, encourages, and supports low- to moderate-income households to save money, reduce debt, and build wealth. Information and tips for setting a savings goal, making a savings plan, how to save automatically, and other tools and resources are included.
Global Learning Partners: Shareable Resources
Global Learning Partners (GLP) helps individuals and organizations to learn by providing practical expertise in learning assessment, design, facilitation and evaluation. Their shareable resources cover a variety of topics in learning, taking a learning-centered approach, including: Learning Design, Needs Assessment, Facilitation, Evaluation, and others.
Webinar series on remote program delivery
A series of webinars hosted by ABC Life Literacy Canada to support literacy practitioners across the country to implement remote program delivery. Topics include:
Questions and answers to legal topics in Ontario
The Community of Legal Education Ontario (CLEO) website contains answers to common questions pertaining to a number of legal topics, including: COVID-19, debt and consumer rights, and employment and work.
Growing up in a lower-income family can have lasting effects
The infographic "Intergenerational income mobility: The lasting effects of growing up in a lower-income family" based on the article "Exploration of the role of education in intergenerational income mobility in Canada: Evidence from the Longitudinal and International Study of Adults," published in the Canadian Public Policy journal presents the effects of growing up in a lower-income family based on a longitudinal study of a cohort of Canadians born between 1963 and 1979.
The Impact of Matched Savings Programs: Building Assets & Lasting Habits
Matched Savings programs, or Individual Development Accounts, are a financial empowerment strategy that aim to build financial stability and reduce poverty. These programs build sustainable livelihoods by working with participants to earn savings while learning about money management, build regular savings habits, self-confidence, and hope for the future. Matching This brief presents key findings from Momentum's Matched Saving programs and the impact on program graduates' saving habits, establishment of emergency savings, and contribution to registered savings.
funds act as a power boost to the participants’ own savings, allowing them to purchase productive assets to move their lives forward.
Hunger Lives Here: Risks and Challenges Faced by Food Bank Clients During COVID-19
This report provides quantitative and qualitative data about the experience of hunger and poverty in Toronto during COVID-19. Based on phone surveys with over 220 food bank clients in May and June 2020 and an analysis of food bank client intake data, the report demonstrates that COVID-19 has led to increased reliance on food banks. The rate of new clients accessing food banks has tripled since the pandemic began. Among new clients, 76% report that they began accessing food banks as a result of COVID-19 and the associated economic downturn.
Youth Reconnect Program Guide: An Early Intervention Approach to Preventing Youth Homelessness
Since 2017, the Canadian Observatory on Homelessness and A Way Home Canada have been implementing and evaluating three program models that are situated across the continuum of prevention, in 10 communities and 12 sites in Ontario and Alberta. Among these is an early intervention called Youth Reconnect. This document describes the key elements of the YR program model, including program elements and objectives, case examples of YR in practice, and necessary conditions for implementation. It is intended for communities who are interested in pursuing similar early intervention strategies. The key to success, regardless of the approaches taken, lies in building and nurturing community partnerships with service providers, educators, policy professionals, and young people.
Changes in the socioeconomic situation of Canada’s Black population
This study provides disaggregated statistics on the socioeconomic outcomes of the Black population by generation status (and immigrant status), sex and country of origin, and is intended to illustrate and contribute to the relevance of disaggregation in understanding these populations and the diversity of their situation. This study sheds light on some of the issues faced by the Black population and shows differences that exist compared with the rest of the working-age population, by sex, generation and place of origin, from 2001 to 2016.
Race to Lead: Women of Color in the Nonprofit Sector
This report reveals that women of color encounter systemic obstacles to their advancement over and above the barriers faced by white women and men of color. Education and training are not the solution—women of color with high levels of education are more likely to be in administrative roles and are more likely to report frustrations about inadequate and inequitable salaries. BMP’s call to action focuses on systems change, organizational change, and individual support for women of color in the sector.
Financial well-being in America
This report provides a view into the state of financial well-being in America. It presents results from the National Financial Well-Being Survey, conducted in late 2016. The findings include the distribution of financial well-being scores for the overall adult population and for selected subgroups, which show that there is wide variation in how people feel about their financial well-being. The report provides insight into which subgroups are faring relatively well and which ones are facing greater financial challenges, and identifies opportunities to improve the financial well-being of significant portions of the U.S. adult population through practice and research.
Understanding the Pathways to Financial Well-Being
The National Financial Well-Being Survey Report is the second report in a series from the Understanding the Pathways to Financial Well-Being project. In order to measure and study the factors that support consumer financial well-being, in 2015, the Bureau of Consumer Financial Protection (the Bureau) contracted with Abt Associates to field a large, national survey to collect information on the financial well-being of U.S. adults. The present report uses data collected from that survey to answer a series of questions on the relationship among financial well-being and four key factors: objective financial situation, financial behavior, financial skill, and financial knowledge. In this study, we aim to enhance understanding of financial well-being and the factors that may support it by exploring these relationships.
English
Introduction to asset building
Asset building for your future (fillable PDF)
Asset building for your future (print version)
My long-term goal action plan (fillable PDF)
My long-term goal action plan (print version)
Introduction to savings accounts
Registered savings accounts
Investing in registered accounts
Seven tips to help you stick to your goals
Glossary – asset building
Resources – asset building
Making it easier to save
Types of investments and types of accounts
Investing basics
How to manage financial stress and avoid burnout
Education savings
RESPs and how they can help
Before you open an RESP
Individual, family and group RESPs
Federal education grants and bonds
Provincial education grants and bonds
Family income to receive RESP government incentives
RESP sample scenarios
Plan for your RESP bank visit
My RESP action plan (fillable PDF)
My RESP action plan (print version)
Glossary – education savings
Resources – education savings
Employment and Social Development Canada (ESDC) resources for the Canada Learning Bond (CLB):
Canada Learning Bond Application for Adult Beneficiaries
Q&A about the Canada Learning Bond for adult beneficiaries
Revised income brackets for Canada Learning Bond (July 2022 to June 2023)
French
L‘accumulation d’actifs
L’accumulation d’actifs pour votre avenir – fillable
L’accumulation d’actifs pour votre avenir – nonfillable
Mon plan d’action axé sur mon objectif à long terme – fillable
Mon plan d’action axé sur mon objectif à long terme – nonfillable
Introduction aux comptes d’épargne
Comptes d’épargne enregistrés (REEI, REEE, REER et CELI)
Investir dans les comptes enregistrés :les options et les questions à poser à votre banque
Sept conseils pour vous aider à respecter vos objectifs
Glossaire – Accumulation d’actifs
Epargne-études
Les REEE : comment peuvent-ils vous aider?
Comment choisir entre unREEE individuel, familial et collectif
Les subventions et les bons d’études du gouvernement fédéral
Les subventions et les bons d’études du gouvernement provincial
Le REEE : comment peut-il vous aider à faire fructifier vos épargnes pour les études?
Arrivez préparé à votre rendez-vous à la banque pour ouvrir un REEE
Mon plan d’action en matière de REEE – fillable
Mon plan d’action en matière de REEE – nonfillable
Prosperity Now Scorecard
The Prosperity Now Scorecard is a comprehensive resource featuring data on family financial health and policy recommendations to help put all U.S. households on a path to prosperity. The Scorecard equips advocates, policymakers and practitioners with national, state, and local data to jump-start a conversation about solutions and policies that put households on stronger financial footing across five issue areas: Financial Assets & Income, Businesses & Jobs, Homeownership & Housing, Health Care and Education.
Advancing Health and Wealth Integration in the Earliest Years
Despite the well-documented connection between health and wealth, investing in this intersection is still a new approach for many grantmakers. With the goal of inspiring increased philanthropic attention, exploration, and replication, this new spotlight elevates responsive philanthropic strategies that support both health and wealth. This report focuses on the in utero-toddler stage of the life cycle (0-3 years). This age segment has some health-wealth integration activity, primarily through two-generation approaches. The goal is to inspire more philanthropic investment for this cohort by highlighting research and examples and offering recommendations.
Inequality in the feasibility of working from home during and after COVID-19
The economic lockdown to stop the spread of COVID-19 has led to steep declines in employment and hours worked for many Canadians. For workers in essential services, in jobs that can be done with proper physical distancing measures or in jobs that can be done from home, the likelihood of experiencing a work interruption during the pandemic is lower than for other workers. To shed light on these issues, this article assesses how the feasibility of working from home varies across Canadian families. It also considers the implications of these differences for family earnings inequality.
Trends in the Citizenship Rate Among New Immigrants to Canada
This Economic Insights article examines trends in the citizenship rate (the percent of immigrants who become Canadian citizens) among recent immigrants who arrived in Canada five to nine years before a given census. The citizenship rate among recent immigrants aged 18 and over peaked in 1996 and declined continuously to 2016. Most of this decline occurred after 2006. The citizenship rate declined most among immigrants with low family income, poor official language skills, and lower levels of education. There was also significant variation in the decline among immigrants from different source regions, with the decline largest among Chinese immigrants.
Money and Youth
The Canadian Foundation for Economic Education (CFEE) works collaboratively with funding partners, departments of education, school boards, schools, educators, and teacher associations to develop and provide free, non-commercial programs and resources for teachers and students – developed and reviewed by educators. The online version of their curriculum Money and Youth is organized into separate modules so that users can select individual topics that align with interests. An introduction to the topic, a teachers guide containing lesson plans, and parent resources are included within each module.
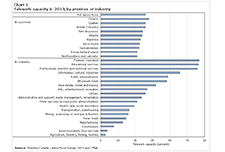
Does education pay? A comparison of earnings by level of education in Canada and its provinces and territories
This report examines the relationship between the earnings of Canadians in the labour market and their post-secondary education credentials. Findings are based upon information gathered from the 2016 Census on adults between the ages of 25 to 64 with different levels of education and working in different parts of the country.
The Effects of Education on Canadians’ Retirement Savings Behaviour
This paper assesses the extent to which education level affects how Canadians save and accumulate wealth for retirement. Data from administrative income-tax records and responses from the 1991 and 2006 censuses of Canada show that individuals with more schooling are more likely to contribute to a tax-preferred savings account and have higher saving rates, have higher home values, and are less likely to rent housing.
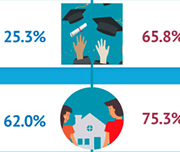
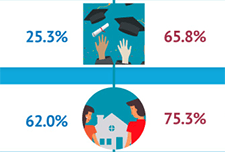
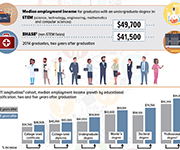
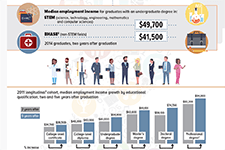
Infographic: Labour market outcomes for college and university graduates, 2010 to 2014
This infographic from Statistics Canada shows the labour market outcomes for college and university graduates between 2010 and 2014. It shows the median employment income achieved by graduates of different education levels, 2 years and 5 years post-graduation. Overall, it shows that people with higher levels of post-secondary education report higher employment income post-graduation.
Indigenous Financial Literacy – AFOA 2014 Conference panel
This is the video recording of the AFOA 2014 Conference panel on Indigenous Financial Literacy. In this session, Liz Mulholland, Dr. Paulette Tremblay, Simon Brascoupe, and Darren Googoo discuss Indigneous financial wellness, financial literacy, and community education.
Canadian Millenial Social Values Study
A major national survey conducted in 2016 reveals a bold portrait of Canada’s Millennials (those born between 1980 and 1995), that for the first time presents the social values of this generation, and the distinct segments that help make sense of the different and often contradictory stereotypes that so frequently are applied to today’s young adults. Key findings from the survey explore Millennials' relationship with money, education, work and career interests, voting turnout, and engagement with social justice.
SmartSAVER: Canada Learning Bond Infographic
An infographic highlighting how to attend post-secondary education with no student debt. It shows how a family eligible for the Canada Learning Bond, with average family savings, student earnings and available grants can cover the cost of post-secondary education (PSE) with no need to borrow.
“We’re Going to Do This Together”: Examining the Relationship between Parental Educational Expectations and a Community-Based Children’s Savings Account Program
This paper presents quantitative and qualitative evidence of the relationship between exposure to a community-based Children’s Savings Account (CSA) program and parents’ educational expectations for their children. First, we examine survey data collected as part of the rollout and implementation of The Promise Indiana CSA program. Second, we augment these findings with qualitative data gathered from interviews with parents whose children have Promise Indiana accounts. Though results differ by parental income and education, the quantitative results using the full sample suggest that parents are more likely to expect their elementary-school children to attend college if they have a 529 account or were exposed to the additional aspects of The Promise Indiana program (i.e., the marketing campaign, college and career classroom activities, information about engaging champions, trip to a University, and the opportunity to enroll into The Promise).