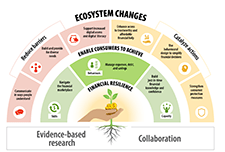
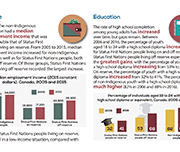
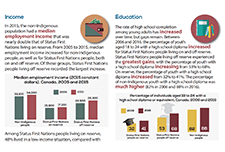
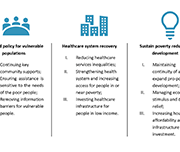
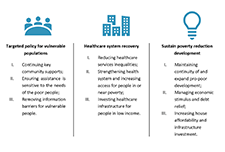
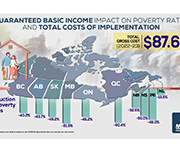
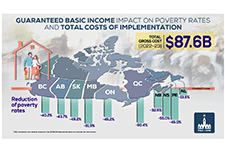
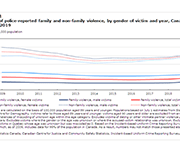
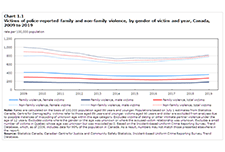
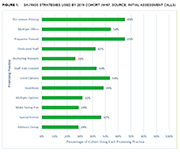
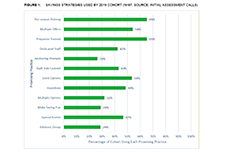
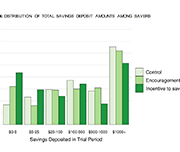
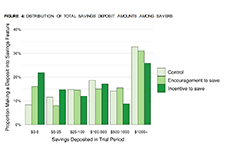
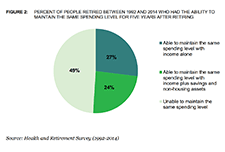
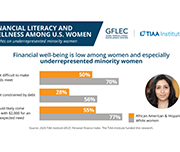
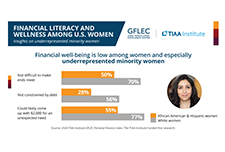
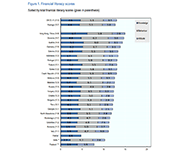
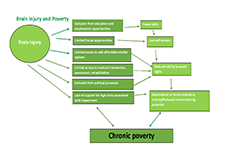
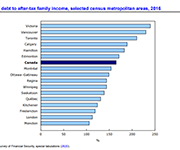
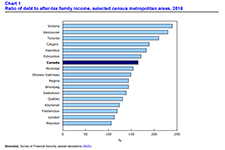
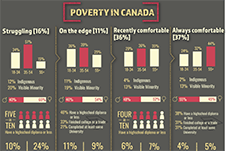
High levels of household indebtedness in Canada has been a concern for policymakers at all levels of government over the past decade. As the economic costs of COVID-19 grow, household indebtedness becomes a faster growing and increasingly more serious concern.
While responsive government policy, such as the federal government’s Canadian Emergency Response Benefit (CERB), has curbed some short-term impacts on indebtedness, the program was developed to fill a temporary gap. The most vulnerable households are low-income households with limited access to credit, who frequently turn to high cost payday lending for financial relief. While regulations on the payday lending industry have increased substantially, low-income Canadian households remain left with few, if any, practical alternatives.
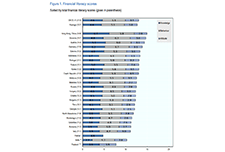
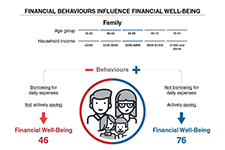
The low-income households in greatest need of alternatives are the financially excluded, specifically the underbanked and the unbanked.
At the same time, it is important to recognize that not all payday loan clients are in low-income households. A 2016 report by the Financial Consumer Agency of Canada states that close to 40% of payday loan borrowers have household income of $55,000 or greater and 20% having income of $80,000 or greater.
Thus, payday loan borrowers are not a homogeneous group.
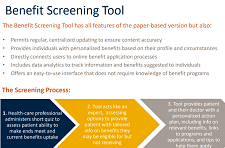
Some Canadian credit unions have developed payday loan alternatives for the financially excluded, however, these more reasonably priced loans are only accessed by a very small portion of would-be payday loan clients.
The objective of this research is to review the alternative payday loan products currently offered by Canadian credit unions, to identify the barriers to offering more payday loan alternatives, and to make recommendations to expand the offerings.